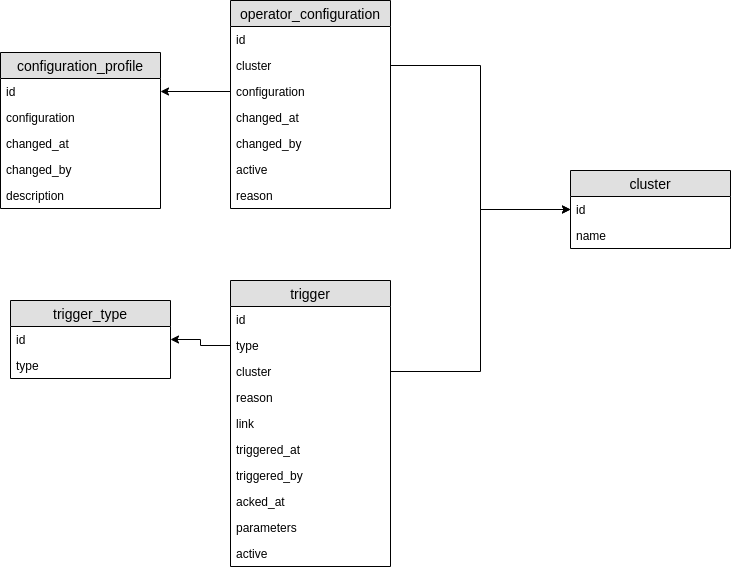
A service to be used to store Insights operator configuration and to offer the configuration to selected operator.
Use the standard Go command:
go build
This command should create an executable file named insights-operator-controller.
Alternatively you can use GNU make to perform the same operation:
make build
Just run the executable file created by go build:
./insights-operator-controller
If you need to start the cleanly built controller, use the following command:
make run
Change the following lines in config.toml:
use_https=true
address=":4443"
tls_cert="certs/cert.pem"
tls_key="certs/key.pem"
Please note that the service (when run locally) use the self-signed certificate.
You'd need to use certs.pem file on client side (curl, web browser etc.)
use_httpsis boolean flag that defines if connection should be securedaddressis address of controller servertls_certis path to certificate, can be used only ifuse_https == truetls_keyis path to key of certificate, can be used only ifuse_https == true
Default configuration file is config.toml. It is possible to specify config file via environment variable
named INSIGHTS_CONTROLLER_CONFIG_FILE. For example:
export INSIGHTS_CONTROLLER_CONFIG_FILE=~/config.toml
./insights-operator-controller
INSIGHTS_CONTROLLER_CONFIG_FILE- custom path to config file (default:./config.toml)CONTROLLER_ENV- specify environment (development,test,production. Default:development)CONTROLLER_PREFIX- specify URL path prefix (Default:/api/v1/)
For authentication we using Insights operator LDAP Auth that are working as proxy between client and controller. For turning on authentication need set export CONTROLLER_ENV=production, by default for development and test purposes it turned off.
Data storage used by the service is configurable via the command line parameters. Currently it is possible to configure the following data storages:
- SQLite local database:
controller.dbfor the local deployment andtest.dbfor functional tests - PostgreSQL database: for local deployment and to be able to deploy the application to developer development
Use the following scripts from the local_storage subdirectory to work with SQLite database:
create_database_sqlite.shto create new database stored in filecontroller.dbcreate_test_database_sqlite.shto create new database stored in filetest.db, this database will be used by tests
PostgreSQL needs to be setup correctly:
- User
postgresshould have password set topostgres - In the configuration file
/var/lib/pgsql/data/pg_hba.conf, the methodmd5needs to be selected for userpostgresandall - The PostgreSQL daemon (service) has to be started, of course:
sudo systemctl start postgresql
For more information how to install PostgreSQL on Fedora (or RHEL) machine, please follow this guide: https://computingforgeeks.com/how-to-install-postgresql-on-fedora/
Use the following scripts from the local_storage subdirectory to work with PostgreSQL database:
create_database_postgres.shto create new database namedcontrollercreate_test_database_postgres.shto create new database namedtest_db
The following two scripts can be used to drop existing database(s):
drop_database_postgres.shto drop database namedcontrollerdrop_test_database_postgres.shto drop database namedtest_db
You can also run PostgreSQL containerized with the prepared Dockerfile local_storage/Dockerfile.postgres
- there is a simple shortcut script
local_storage/dockerize_postgres.shwhich stops the container if it exists, then builds and runs a detached image. - to automatically fill the database with test data, set an environment variable
MOCK_DATA=trueand pass it to docker run - the environment variables from the original postgres image, such as
PGDATAalso work
To set up a database on RDS AWS, an AWS account is needed. To set up the AWS account follow instructions: https://aws.amazon.com/premiumsupport/knowledge-center/create-and-activate-aws-account/
After AWS account is set up, follow instructions to set up a PostreSQL database instance here : https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonRDS/latest/UserGuide/USER_CreatePostgreSQLInstance.html
Set up the database instance as needed.
Set the name of the database as postgres. (Not the DB instance identifier.)
When database instance status becomes available, set environment variables $RDS_MASTERUSER, $RDS_MASTERPASSWORD and $RDS_ENDPOINT with values
master username, master password, and endpoint including port, of your database instance.
Run create_RDS_database_postgres.sh to create database.
To drop previously created database, run drop_RDS_database_postgres.sh.
The following command runs all unit tests against newly built controller:
make test
In case you just need to start unit tests without the clean+build step, use following command:
go test ./...
It is also possible to increase verbosity level:
go test -v ./...
REST API tests need the running service and the test database to be prepared. In order to perform REST API tests, start the following script:
./test.sh
Please note that the service should not be running at the same moment (as it used the same port).
All code style checks, cyclomatic complexity measurement etc. can be started from command line by using:
make style
Travis CI is configured for this repository. Several tests and checks are started for all pull requests:
- Unit tests that use the standard tool
go test go fmttool to check code formatting. That tool is run with-sflag to perform following transformationsgo vetto report likely mistakes in source code, for example suspicious constructs, such as Printf calls whose arguments do not align with the format string.golintas a linter for all Go sources stored in this repositorygocycloto report all functions and methods with too high cyclomatic complexity. The cyclomatic complexity of a function is calculated according to the following rules: 1 is the base complexity of a function +1 for each 'if', 'for', 'case', '&&' or '||' Go Report Card warns on functions with cyclomatic complexity > 9gosecto inspect source code for security problems by scanning the Go ASTineffassignto detect and print all ineffectual assignments in Go codeerrcheckfor checking for all unchecked errors in go programsshellcheckto perform static analysis for all shell scripts used in this repositoryabcgoto measure ABC metrics for Go source code and check if the metrics does not exceed specified threshold
History of checks done by CI is available at RedHatInsights / insights-operator-controller.
Please look into document CONTRIBUTING.md that contains all information about how to contribute to this project.
Please look also at Definition of Done document with further informations.