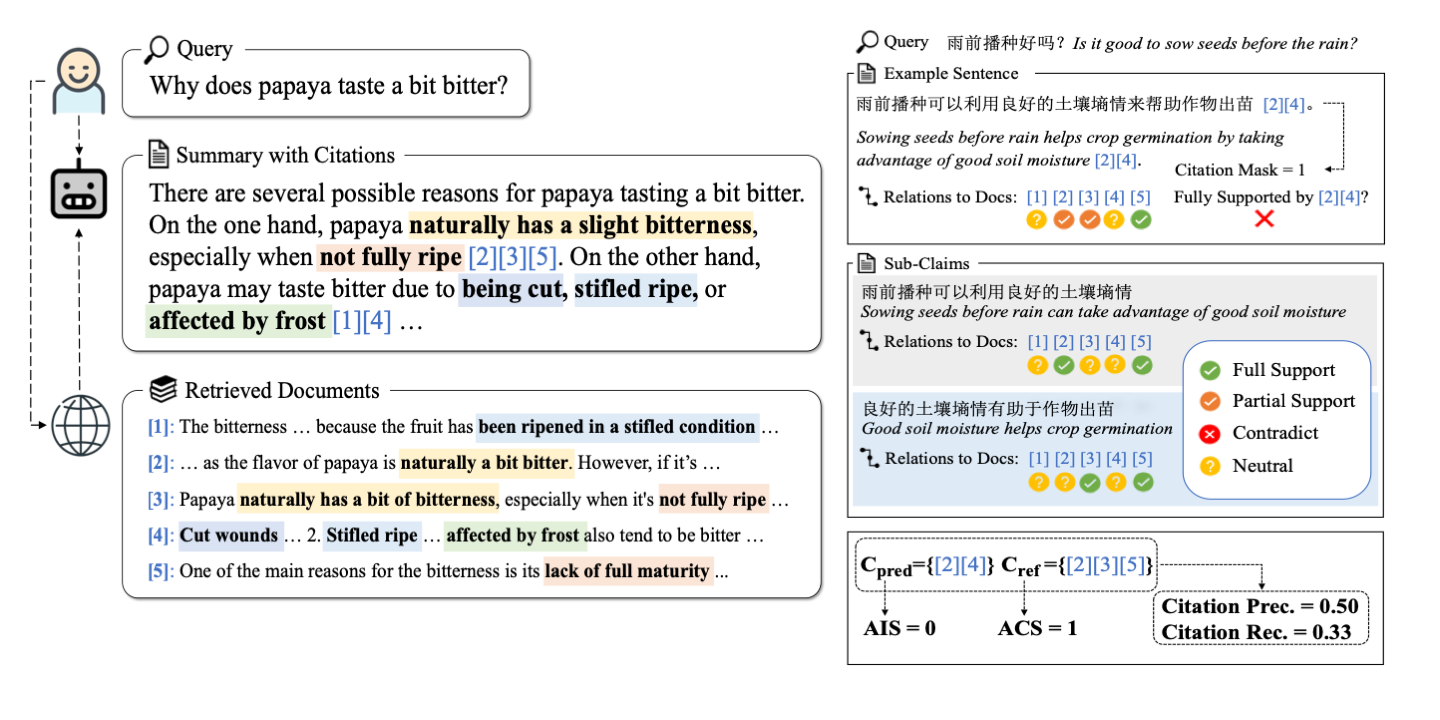
This repository contains the code associated with the paper WebCiteS: Attributed Query-Focused Summarization on Chinese Web Search Results with Citations. In this work, we formulate the task of attributed query-focused summarization (AQFS) and present WebCiteS, a Chinese dataset featuring 7k human-annotated summaries with citations. WebCiteS derives from real-world user queries and web search results, offering a valuable resource for model training and evaluation. We adopt comprehensive evaluation metrics on summarization utility and attribution and develop an cost-effective automatic evaluator based on open-source models for scalable and robust evaluation. Please refer to the paper for more details.
- (2024.9) The fine-tuned claim-split model is uploaded to huggingface.
- (2024.5) WebCiteS is accepted to ACL 2024 main conference. 🎉
Clone the repository and navigate to the root directory.
git clone https://github.com/HarlynDN/WebCiteS.git
cd WebCiteSpip install -r requirements.txtRun the following command to download and preprocess the dataset.
wget https://huggingface.co/datasets/HarlynDN/WebCiteS/resolve/main/data.tar
tar -xvf data.tar
echo "deleting tar file"
rm data.tar
cd data
echo "preprocessing the data"
python prepare_data.py --raw_data webcites.json
cd ..The claim-split model receives a sentence and generates a list of its sub-claims. Here we fine-tune the google/mt5-large model on this task.
cd src
NUM_GPUs=8
torchrun --standalone --nnodes=1 --nproc-per-node=$NUM_GPUs claimsplit/main.py \
--do_train \
--do_eval \
--do_predict \
--data_dir ../data/claimsplit \
--source_column sentence \
--target_column claims \
--overwrite_cache \
--model_name_or_path google/mt5-large \
--output_dir {path/to/output/directory} \
--overwrite_output_dir \
--max_source_length 64 \
--max_target_length 128 \
--per_device_train_batch_size 8 \
--num_train_epochs 5 \
--learning_rate 1e-4 \
--logging_steps 10 \
--evaluation_strategy epoch \
--save_strategy epoch \
--predict_with_generate We use an NLI model to evaluate the redundancy, correctness, and completeness of the generated sub-claims against their source sentences. Here we use the alan-turing-institute/mt5-large-finetuned-mnli-xtreme-xnli model as the NLI model.
cd src
python claimsplit/eval.py \
--f {path/to/claimsplit/generation/file} \
--nli_model alan-turing-institute/mt5-large-finetuned-mnli-xtreme-xnli \
--batch_size 256If you are hitting OOM, try to reduce batch_size.
We evaluate the performance of the evaluator consisting of a claim-split model and an NLI model on the test set of WebCiteS.
cd src
python aqfs/eval_evaluator.py \
--f ../data/aqfs_snippet/test.json \
--nli_model alan-turing-institute/mt5-large-finetuned-mnli-xtreme-xnli \
--claimsplit_model {path/to/the/fine-tuned/claimsplit/model/checkpoint} \
--nli_batch_size 256 \
--claimsplit_batch_size 512 If you are hitting OOM, try to reduce nli_batch_size and claimsplit_batch_size.
We use the deepspeed library for LLM fine-tuning. The configuration file is src/deepspeed.json.
Here is an example of fine-tuning the THUDM/chatglm3 model on this task.
cd src
deepspeed --num_gpus=8 aqfs/main.py \
--deepspeed deepspeed.json \
--do_train \
--data_dir ../data/aqfs_snippet \
--source_column prompt \
--target_column summary \
--overwrite_cache \
--model_name_or_path THUDM/chatglm3-6b \
--output_dir {path/to/output/directory} \
--overwrite_output_dir \
--max_source_length 1280 \
--max_target_length 400 \
--per_device_train_batch_size 1 \
--gradient_accumulation_steps 8 \
--gradient_checkpointing \
--num_train_epochs 1 \
--save_strategy epoch \
--logging_steps 2 \
--learning_rate 2e-5 \
--fp16We tested the above command on 8 A100-40GB GPUs. However, you might be able to run the code with less computational resources by enabling CPU offloading. See this tutorial for more details.
Here is an example of inference using the fine-tuned model.
cd src
NUM_GPUs=8
torchrun --standalone --nnodes=1 --nproc-per-node=$NUM_GPUs aqfs/main.py \
--do_predict \
--data_dir ../data/aqfs_snippet \
--source_column prompt \
--target_column summary \
--overwrite_cache \
--model_name_or_path {path/to/the/model/checkpoint} \
--output_dir {path/to/output/directory} \
--overwrite_output_dir \
--max_source_length 1280 \
--max_target_length 400 \
--per_device_eval_batch_size 1 \
--predict_with_generate The above command executes the data-paralleled inference, where each GPU loads the entire weights of the model and processes a mini-batch of data. We aslo provide the script for model-parallel inference, where the weights of model are sharded across multiple GPUs. If you are hitting OOM when running the above command, try the following command.
python aqfs/inference.py --{same arguments as above}Here is an example of few-shot prompting.
cd src
NUM_GPUs=8
torchrun --standalone --nnodes=1 --nproc-per-node=$NUM_GPUs aqfs/main.py \
--do_predict \
--use_chat_format \
--data_dir ../data/aqfs_snippet \
--source_column prompt \
--target_column summary \
--exemplar_id a18f3958-3d98-4e1a-bca6-d8c83712ec64 \
--overwrite_cache \
--model_name_or_path THUDM/chatglm3-6b \
--output_dir {path/to/output/directory} \
--overwrite_output_dir \
--max_source_length 3680 \
--max_target_length 400 \
--per_device_eval_batch_size 1 \
--predict_with_generate There are two additional arguments --use_chat_format and --exemplar_id in the above command. Similarly, use aqfs/inference.py for model-parallel inference.
In the long-context setting, models are provided with full content of web pages to summarize. To adopt this setting, set --data_dir to ../data/aqfs_full_chunk256 or ../data/aqfs_full_chunk512, and set --max_source_length to 7680.
We use the evaluator for automatic evaluation. Here is an example of evaluating the AQFS outputs.
cd src
python aqfs/eval.py \
--f {path/to/model/outputs} \
--nli_model alan-turing-institute/mt5-large-finetuned-mnli-xtreme-xnli \
--claimsplit_model {path/to/the/fine-tuned/claimsplit/model/checkpoint} \
--nli_batch_size 256 \
--claimsplit_batch_size 512 If you are hitting OOM, try to reduce nli_batch_size and claimsplit_batch_size.
Run the folowing command to download outputs from GPT-3.5 and GPT-4.
wget https://huggingface.co/datasets/HarlynDN/WebCiteS/resolve/main/gpt_outputs.tar
tar -xvf gpt_outputs.tar
echo "deleting tar file"
rm gpt_outputs.tarIf you find this work helpful, please consider citing our paper.
@inproceedings{deng-etal-2024-webcites,
title = "{W}eb{C}ite{S}: Attributed Query-Focused Summarization on {C}hinese Web Search Results with Citations",
author = "Deng, Haolin and
Wang, Chang and
Xin, Li and
Yuan, Dezhang and
Zhan, Junlang and
Zhou, Tian and
Ma, Jin and
Gao, Jun and
Xu, Ruifeng",
editor = "Ku, Lun-Wei and
Martins, Andre and
Srikumar, Vivek",
booktitle = "Proceedings of the 62nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers)",
month = aug,
year = "2024",
address = "Bangkok, Thailand",
publisher = "Association for Computational Linguistics",
url = "https://aclanthology.org/2024.acl-long.806",
pages = "15095--15114"
}