Epiphanous' emr-ctl is a swiss-army knife command line utility
that can be used to manage flink clusters running jobs written with
epiphanous' flinkrunner.
emr-ctl leverages AWS' Elastic Map
Reduce (EMR) service to make deployment of
flink jobs reliable, scalable and easy to manage, in staging and
production.
Let's say you've used flinkrunner and build a system of flink jobs
called flinkydink. You can use emr-ctl to deploy the various
flink jobs in flinkydink to EMR and manage the clusters created there,
all from the comfort of your development environment.
In fact, the emr-ctl script can be run either locally in your laptop
development environment, or on the master node of a running EMR cluster. The
script has commands that work in both environments, as well as particular
commands supported only in each environment. In our examples,
we use the dev> prompt to indicate running locally on your own laptop, and
the emr> prompt to indicate running on the master node of an EMR cluster.
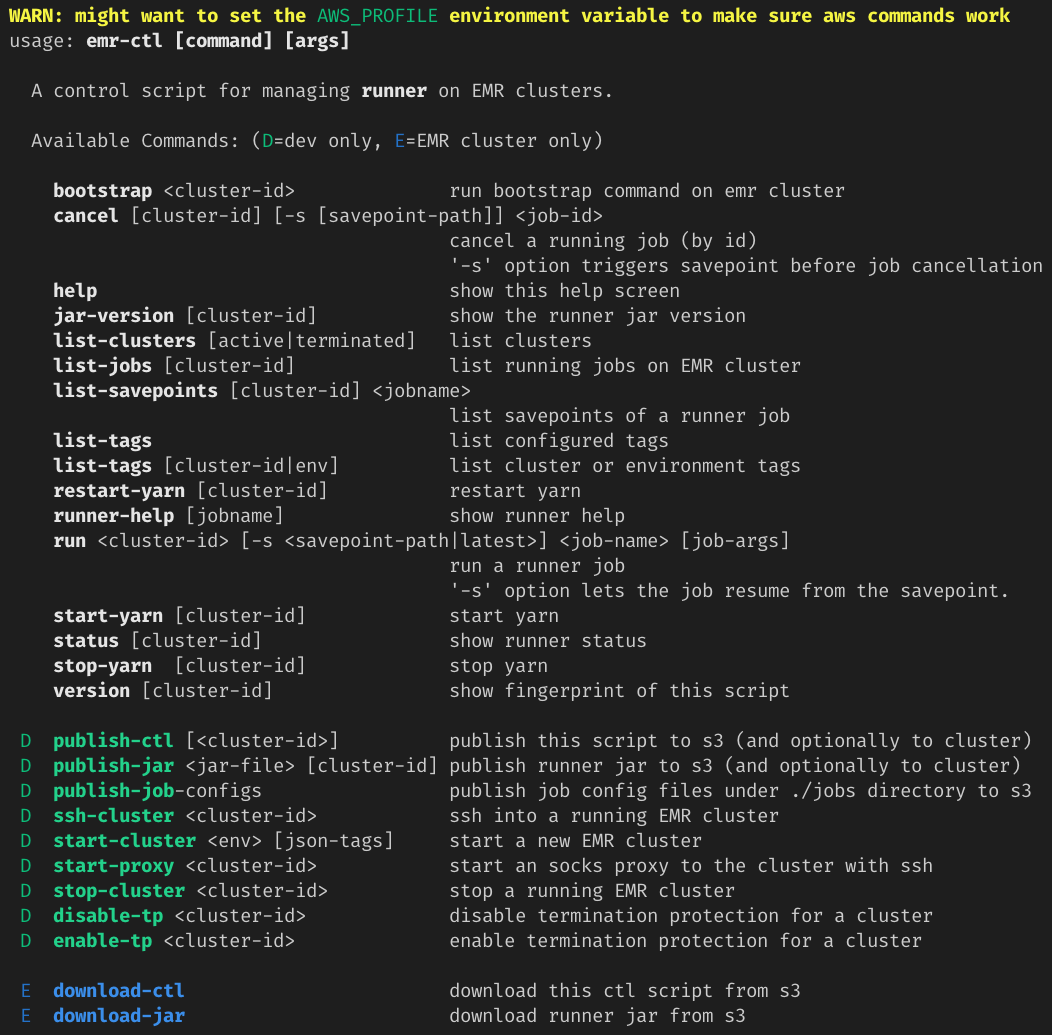
You can see a usage message by running the emr-ctl script without
arguments (or with the argument help)
dev> ./emr-ctlThe result is
Notice there is a warning emitted about a missing
AWS_PROFILEenvironment variable. This is only visible if you're indevmode.emr-ctlrelies on the AWS command line interface to interact with the your EMR clusters. When running the script from your laptop you should make sure your AWS credentials file contains proper credentials to interact with your AWS resources, and if you have multiple profiles in your credentials file, be sure to select the appropriate one using theAWS_PROFILEenvironment variable.
Most commands can be run either in local dev mode or on the EMR cluster. When
running in local dev mode, most commands require a cluster id.
emr-ctl relies on s3 to store information that needs to be shared
with running EMR clusters. This includes the script itself, your flinkrunner
application JAR file, environment defaults, job configuration files and other
files used to provision EMR clusters.
The s3 bucket emr-ctl writes to should be configured in emr-ctl's .env
config file to whatever is appropriate for your AWS setup. If you want to
keep your emr-ctl artifacts in a bucket called com.example.emr-ctl.artifacts,
then you'd set S3_BUCKET=s3://com.example.emr-ctl.artifacts in the .env file.
Obviously this needs to be a bucket you have access to. We'll discuss configuration
of other settings later.
The normal sequence of operations is to first see what clusters are running
with list-clusters.
dev> ./emr-ctl list-clustersid name state created destroyed
j-H1YWYWM3OAF2 flinkydink-sta WAITING 02/12/2019 07:07 -
j-2TTQNFV1DM0WT flinkydink-sta TERMINATED 01/24/2019 06:14 01/24/2019 07:07
j-PXGUA758BTJU flinkydink-sta TERMINATED 01/21/2019 21:22 01/22/2019 06:08
j-N24TSJ7LXEHZ flinkydink-sta TERMINATED 01/21/2019 18:46 01/20/2019 21:19
j-1JIFNZPURVXZ6 flinkydink-sta TERMINATED_WITH_ERRORS 01/20/2019 18:36 01/20/2019 18:39
j-201214UKBI0O4 My cluster TERMINATED 01/19/2019 11:18 01/20/2019 05:29
j-37VE4KY6O32LG flink Staging TERMINATED 01/18/2019 23:03 01/19/2019 05:30
j-31YSVSJBFHX9K flink Staging TERMINATED 01/18/2019 21:02 01/18/2019 22:59
This output shows one active cluster and several terminated clusters.
You can interact with clusters in a state of WAITING or RUNNING. Clusters in the state
TERMINATED are inaccessible. If you only want to see active clusters, you can grep the
output like this:
dev> ./emr-ctl list-clusters | grep -v TERMINATwhich removes TERMINATING, TERMINATED, or TERMINATED_WITH_ERRORS
clusters from the list.
If you want to create a new cluster, use the start-cluster command.
dev> ./emr-ctl start-cluster staging '{}'This command starts a new cluster in the staging environment.
The environment name is configured by you to map to a particular AWS VPC subnet, so you can isolate your EMR jobs appropriately.
The second argument to start-cluster is a list of key/value pairs in
JSON format that will be merged with the default configuration for the
requested environment and
attached to the cluster. The key value pairs are called tags because we
store them in the tags metadata of an EMR cluster to use for runtime
configuration of flink jobs. More on tags in a minute. But first, the
start-cluster command returns a cluster id:
{
"ClusterId": "j-H1YWYWM3OAF2"
}You'll use this cluster id to interact with this cluster throughout
emr-ctl.
It takes a few minutes for a new cluster to be provisioned. You can run
list-clusters to check on its status. It will begin in STARTING state when
the master node is being provisioned, then move to RUNNING state when the
master node is ready and the task nodes are being provisioned, then finally to
WAITING state when the cluster is ready to start doing work.
The default tags for an environment are also managed via emr-ctl.
To list the current default tags for an environment, run this command:
dev> ./emr-ctl list-tags stagingENV staging
SUBNET 03cb8078
CLUSTER_NAME flinkydink-${ENV}
CASSANDRA_HOST 10.23.17.204
FLINK_VERSION 1.7.2
FLINK_TARBALL ${S3_BASE}/provision/flink-${FLINK_VERSION}/flink-${FLINK_VERSION}-bin-hadoop28-scala_2.11.tgz
INSTANCE_COUNT 3
INSTANCE_TYPE m5.2xlarge
KAFKA_BROKER 10.23.17.124:9092
LOG_URI ${S3_BASE}/logs/${ENV}
CHECKPOINT_BASE ${S3_BASE}/flink-state/${ENV}
SAVEPOINT_BASE ${S3_BASE}/flink-savepoints/${ENV}
S3_BASE s3://com.example.emr-ctl-artifacts
PARALLELISM 1
RELEASE_LABEL emr-5.21.0
flinkYDINK_VERSION 2.1.17
Tags are basically environment variables that allows flexible configuration of
job runs on clusters. You can set up whatever default tags you want for jobs to configure
them. When you start a new cluster in a particular environment,
emr-ctl merges the default tags for that cluster that it finds on s3 with
the additional tags you supply to the start-cluster command. These merged
tags are then stored in the cluster's metadata to be used to configure running
jobs on the cluster. This avoids the need to run additional infrastructure
like consul to manage configuration.
Job Configuration: Cluster tags are interpolated into job-specific configuration files that
emr-ctlmanages on s3. These configuration files are stored in theemr-ctlartifacts repository under thejobsdirectory. Each supported environment has a subdirectory with JSON files, one per job. Each job file contains the arguments that should be supplied when running that job on flink. The files can reference any cluster tags like environment variables. There is a special JSON file calleddefaults.jsonfor each environment that defines its default cluster tags.
You can use the list-tags command with a cluster id to see the tags actually
configured for a running cluster:
dev> ./emr-ctl list-tags j-H1YWYWM3OAF2CLUSTER_NAME flinkydink-staging
ENV staging
JDBC_USERNAME frodomadeit
JDBC_PASSWORD ********************
LOG_URI s3://com.example.emr-ctl.artifacts/logs/flinkydink-staging
JDBC_URL postgresql://flinkyab2347878dsfs.cpodsoduzv.us-east-1.rds.amazonaws.com:5432/flinkydink
KAFKA_BROKER 10.23.17.126:9092
SUBNET 03dc803d
PARALLELISM 1
FLINK_TARBALL s3://com.example.emr-ctl.artifacts/provision/flink-1.7.2/flink-1.7.2-bin-hadoop28-scala_2.11.tgz
CASSANDRA_HOST 10.23.17.204
flinkYDINK_VERSION 2.1.17
FLINK_VERSION 1.7.2
INSTANCE_COUNT 3
INSTANCE_TYPE m5.2xlarge
RELEASE_LABEL emr-5.21.0
SAVEPOINT_BASE s3://com.example.emr-ctl.artifacts/flink-savepoints/staging
CHECKPOINT_BASE s3://com.example.emr-ctl.artifacts/flink-state/staging
You can also publish the defaults, together with other job configuration
json files to s3 with the publish-job-configs command:
dev> ./emr-ctl publish-job-configsThis command synchronizes the jobs directory in the repo with its
corresponding directory on s3.
You can shut a cluster down with the stop-cluster command.
dev> ./emr-ctl stop-cluster j-2TTQNFV1DM0WTAn error occurred (ValidationException) when calling the TerminateJobFlows operation: Could not shut down one or more job flows since they are termination protected.
[failure]
This error is expected because clusters are automatically created with termination protection, which prevents them from being accidentally shut down. In order to intentionally shut a cluster down, you must turn off termination protection.
dev> emr-ctl disable-tp <cluster-id>You can read more about termination protection in the AWS EMR management guide.
Once termination protection is disabled, you can run the stop-cluster command, which will immediately
return
Terminated
It actually takes a minute or two for the cluster resources to be de-provisioned. list-clusters will
show the state of the cluster as TERMINATING and then TERMINATED with a destroyed timestamp.
id name state created destroyed
j-2TTQNFV1DM0WT flinkydink-staging TERMINATED 06/20/2018 06:14 06/20/2018 07:07
NOTE: It's normal to shut down clusters. While they can remain running for long periods of time if desired, they are easy to reproduce, and committed offset consumers and flink checkpoint and savepoints make it possible to shut down clusters without losing data. They are meant to be started up and shut down as needed to accomplish company goals.
Once a cluster has been started, it needs to be bootstrapped to work with your flinkrunner application jar.
You accomplish this with the bootstrap command.
dev> ./emr-ctl start-cluster staging '{}'
{
"ClusterId": "j-394OWCGLKHED3"
}
dev> ./emr-ctl bootstrap j-394OWCGLKHED3
Warning: Permanently added 'ec2-47-87-17-126.us-east-1.compute.amazonaws.com,32.17.126.23' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts.
download: s3://<your-s3-bucket>/emr-ctl to ./emr-ctl
download: s3://<your-s3-bucket>/provision/flink-1.7.2/flink-1.7.2-bin-hadoop28-scala_2.11.tgz to ../../tmp/flink.tgz
download: s3://<your-s3-bucket>/provision/flink-1.7.2/bin-config.sh to bin/config.sh
download: s3://<your-s3-bucket>/provision/flink-1.7.2/flink-conf.yaml to conf/flink-conf.yaml
flink-1.7.2 installed
download: s3://<your-s3-bucket>/jars/flinkydink-2.1.17.jar to ./flinkydink-2.1.17.jar
Connection to ec2-47-87-17-126.us-east-1.compute.amazonaws.com closed.As can be seen from the output, the bootstrap command does three things:
- installs
emr-ctlon the cluster master node - if needed, upgrades flink on the master to the version denoted by the cluster tag
FLINK_VERSION(so you're not stuck with whatever version of flink is current in the AWS EMR package you're using) - installs your
flinkrunnerapplication jar
You are now ready to run flinkydink (or whatever less cool name you choose for you flinkrunner application)
jobs on the cluster. Before discussing running jobs, we take a look at running
emr-ctl on EMR vs. locally.
At this point, you can ssh into the master node to run emr-ctl commands, if you like. While
you can do everything remotely from your dev environment, there are times when you want to get
closer to the action, perhaps to look at a process listing, or verify something in logs you can only access
in EMR. To access the cluster master node, you run
dev> ./emr-ctl ssh j-394OWCGLKHED3
ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no -o ServerAliveInterval=10 -i ~/.ssh/staging hadoop@ec2-47-87-17-126.us-east-1.compute.amazonaws.com -t
Last login: Wed Jun 20 14:36:35 2018
__| __|_ )
_| ( / Amazon Linux AMI
___|\___|___|
https://aws.amazon.com/amazon-linux-ami/2018.03-release-notes/
9 package(s) needed for security, out of 14 available
Run "sudo yum update" to apply all updates.
EEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEE MMMMMMMM MMMMMMMM RRRRRRRRRRRRRRR
E::::::::::::::::::E M:::::::M M:::::::M R::::::::::::::R
EE:::::EEEEEEEEE:::E M::::::::M M::::::::M R:::::RRRRRR:::::R
E::::E EEEEE M:::::::::M M:::::::::M RR::::R R::::R
E::::E M::::::M:::M M:::M::::::M R:::R R::::R
E:::::EEEEEEEEEE M:::::M M:::M M:::M M:::::M R:::RRRRRR:::::R
E::::::::::::::E M:::::M M:::M:::M M:::::M R:::::::::::RR
E:::::EEEEEEEEEE M:::::M M:::::M M:::::M R:::RRRRRR::::R
E::::E M:::::M M:::M M:::::M R:::R R::::R
E::::E EEEEE M:::::M MMM M:::::M R:::R R::::R
EE:::::EEEEEEEE::::E M:::::M M:::::M R:::R R::::R
E::::::::::::::::::E M:::::M M:::::M RR::::R R::::R
EEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEE MMMMMMM MMMMMMM RRRRRRR RRRRRR
[hadoop@ip-10-26-1-56 ~]$ ls
flinkydink-2.1.17.jar emr-ctlIMPORTANT:
emr-ctlassumes you have the proper environment ssh key pairs stored in your~/.sshdirectory. That is, to access the staging environment, you need the~/.ssh/stagingprivate key.
You can run emr-ctl commands here that are intended to be run on the EMR
master. If you try to run one that isn't meant for the EMR master, you'll get
a message like this:
emr> ./emr-ctl publish-jarpublish-jar can't be run inside an emr cluster
[failure]
Most commands that you can run inside an EMR cluster can be run from a dev environment by simply passing the cluster id as an argument of the command.
EMR clusters use Hadoop YARN
to run jobs. This means to run a job you need to start a YARN application. If a YARN application isn't
running on the cluster when you start a job, emr-ctl will attempt to start a YARN application.
This means you shouldn't have to mess with YARN. But if things get weird, you can stop yarn or restart it
like this:
emr> ./emr-ctl start-yarn18/06/20 14:48:43 INFO client.RMProxy: Connecting to ResourceManager at ip-10-52-1-36.us-east-1.compute.internal/10.23.1.147:8032
Using the result of 'hadoop classpath' to augment the Hadoop classpath: /etc/hadoop/conf:/usr/lib/hadoop/lib/*:/usr/lib/hadoop/.//*:/usr/lib/hadoop-hdfs/./:/usr/lib/hadoop-hdfs/lib/*:/usr/lib/hadoop-hdfs/.//*:/usr/lib/hadoop-yarn/lib/*:/usr/lib/hadoop-yarn/.//*:/usr/lib/hadoop-mapreduce/lib/*:/usr/lib/hadoop-mapreduce/.//*::/usr/lib/hadoop-lzo/lib/*:/usr/share/aws/aws-java-sdk/*:/usr/share/aws/emr/emrfs/conf:/usr/share/aws/emr/emrfs/lib/*:/usr/share/aws/emr/emrfs/auxlib/*:/usr/share/aws/emr/cloudwatch-sink/lib/*:/usr/share/aws/emr/security/conf:/usr/share/aws/emr/security/lib/*
2019-02-12 14:48:45,818 INFO org.apache.flink.configuration.GlobalConfiguration - Loading configuration property: env.yarn.conf.dir, /etc/hadoop/conf
2019-02-12 14:48:45,819 INFO org.apache.flink.configuration.GlobalConfiguration - Loading configuration property: env.hadoop.conf.dir, /etc/hadoop/conf
2019-02-12 14:48:45,819 INFO org.apache.flink.configuration.GlobalConfiguration - Loading configuration property: yarn.containers.vcores, 8
2019-02-12 14:48:46,143 WARN org.apache.hadoop.util.NativeCodeLoader - Unable to load native-hadoop library for your platform... using builtin-java classes where applicable
2019-02-12 14:48:46,215 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.security.modules.HadoopModule - Hadoop user set to hadoop (auth:SIMPLE)
2019-02-12 14:48:46,357 INFO org.apache.hadoop.yarn.client.RMProxy - Connecting to ResourceManager at ip-10-52-1-36.us-east-1.compute.internal/10.52.1.36:8032
2019-02-12 14:48:46,577 INFO org.apache.flink.yarn.AbstractYarnClusterDescriptor - Cluster specification: ClusterSpecification{masterMemoryMB=4096, taskManagerMemoryMB=4096, numberTaskManagers=2, slotsPerTaskManager=8}
2019-02-12 14:48:46,847 WARN org.apache.flink.yarn.AbstractYarnClusterDescriptor - The configuration directory ('/etc/flink/conf') contains both LOG4J and Logback configuration files. Please delete or rename one of them.
2019-02-12 14:48:52,043 INFO org.apache.flink.yarn.AbstractYarnClusterDescriptor - Submitting application master application_1529504500067_0001
2019-02-12 14:48:52,349 INFO org.apache.hadoop.yarn.client.api.impl.YarnClientImpl - Submitted application application_1529504500067_0001
2019-02-12 14:48:52,349 INFO org.apache.flink.yarn.AbstractYarnClusterDescriptor - Waiting for the cluster to be allocated
2019-02-12 14:48:52,351 INFO org.apache.flink.yarn.AbstractYarnClusterDescriptor - Deploying cluster, current state ACCEPTED
2019-02-12 14:48:57,126 INFO org.apache.flink.yarn.AbstractYarnClusterDescriptor - YARN application has been deployed successfully.
2019-02-12 14:48:57,126 INFO org.apache.flink.yarn.AbstractYarnClusterDescriptor - The flink YARN client has been started in detached mode. In order to stop flink on YARN, use the following command or a YARN web interface to stop it:
yarn application -kill application_1529504500067_0001
Please also note that the temporary files of the YARN session in the home directory will not be removed.
2019-02-12 14:48:57,469 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.rest.RestClient - Rest client endpoint started.
flink JobManager is now running on ip-10-52-1-197.us-east-1.compute.internal:40907 with leader id 00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000.
JobManager Web Interface: http://ip-10-23-1-147.us-east-1.compute.internal:40907
2019-02-12 14:48:57,482 INFO org.apache.flink.yarn.cli.flinkYarnSessionCli - The flink YARN client has been started in detached mode. In order to stop flink on YARN, use the following command or a YARN web interface to stop it:
yarn application -kill application_1529504500067_0001
NOTE: you could have achieved this by running the command
./emr-ctl start-yarn j-394OWCGLKHED3on your local dev machine.
YARN is pretty chatty. The most interesting output here is notice that the flink JobManager is running on a particular ip address and port. This is the address of the flink web ui. But if you want to view it on your local machine, this address isn't much use, since its running on an internal cluster ip address. You can access it by starting a proxy from your local machine:
dev> ./emr-ctl start-proxy j-394OWCGLKHED3Attempting to open socks proxy on port 8157...disable with Ctrl-C
ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no -o ServerAliveInterval=10 -ND 8157 -i ~/.ssh/staging hadoop@ec2-47-87-17-126.us-east-`.compute.amazonaws.com
NOTE: You can kill the proxy by typing Ctrl-C in the terminal you started it in.
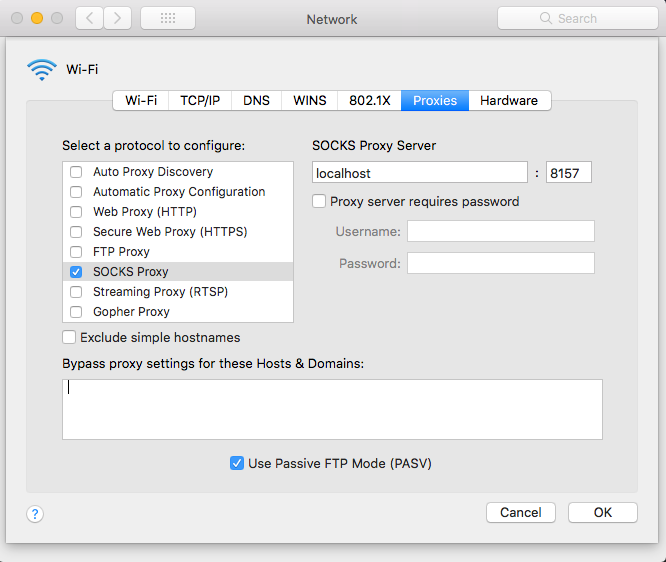
This creates a socks proxy on port 8157. You will additionally need to configure your machine's
proxy settings to use this port. On Mac, you can do this in
System Preferences > Network > Advanced... > Proxies like so:
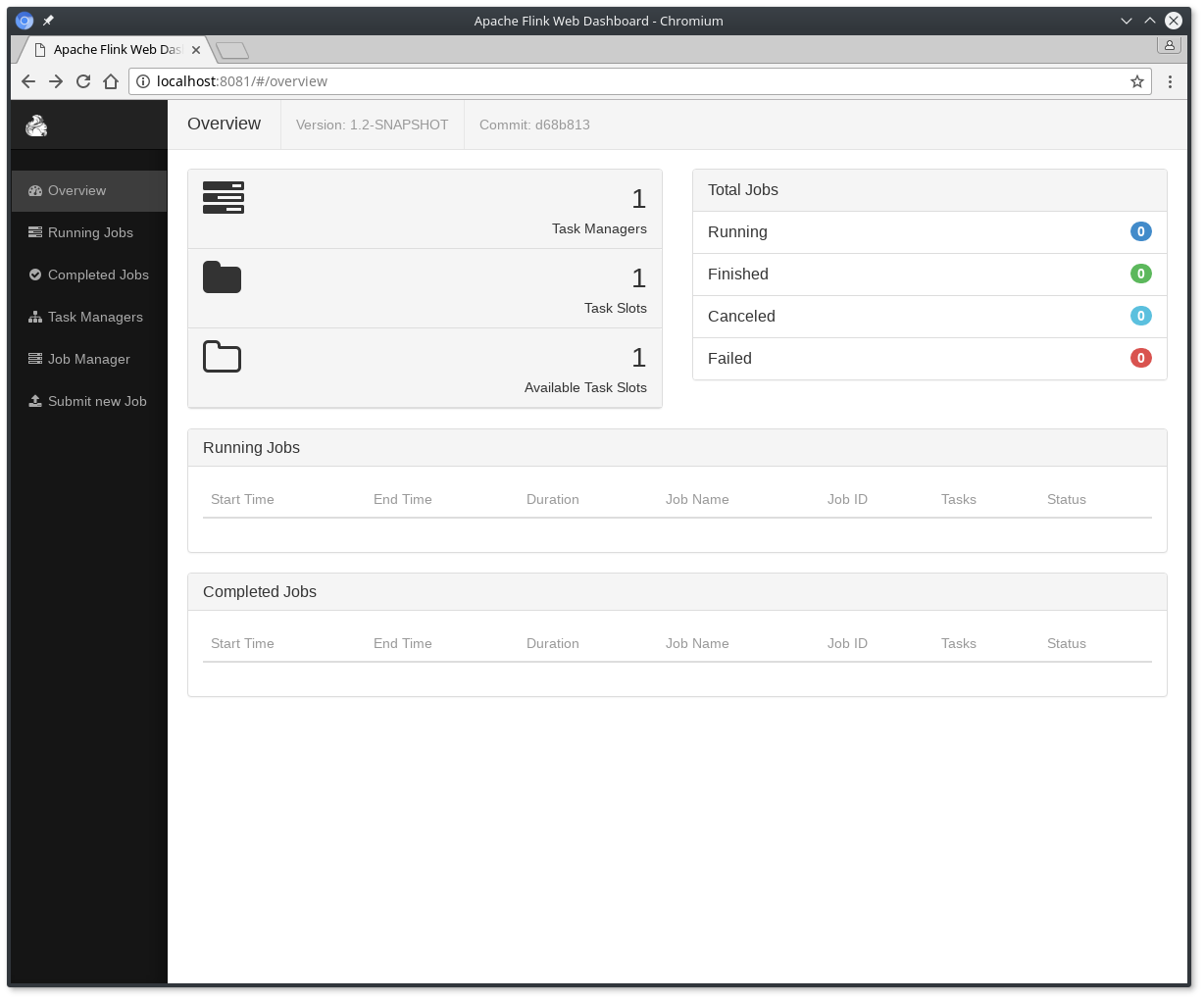
Once this is turned on, you can access the flink web ui by pointing your browser at the ip reported by YARN (in this case, http://ip-10-23-1-147.us-east-1.compute.internal:40907)
NOTE: The flink web ui sometimes reports that there are zero task managers, task slots and available task slots. This is because when running under YARN, these resources aren't allocated until a job is actually run. Once you run a job, you will see positive numbers in the web ui. If you cancel the job, these numbers go back to zero.
So, with the YARN flink client running, you can finally start a flink job!
emr> ./emr-ctl run <job-name>NOTE: You can run this command locally like
./emr-ctl run <cluster-id> <job-name> [job-args]
Using the result of 'hadoop classpath' to augment the Hadoop classpath: /etc/hadoop/conf:/usr/lib/hadoop/lib/*:/usr/lib/hadoop/.//*:/usr/lib/hadoop-hdfs/./:/usr/lib/hadoop-hdfs/lib/*:/usr/lib/hadoop-hdfs/.//*:/usr/lib/hadoop-yarn/lib/*:/usr/lib/hadoop-yarn/.//*:/usr/lib/hadoop-mapreduce/lib/*:/usr/lib/hadoop-mapreduce/.//*::/usr/lib/hadoop-lzo/lib/*:/usr/share/aws/aws-java-sdk/*:/usr/share/aws/emr/emrfs/conf:/usr/share/aws/emr/emrfs/lib/*:/usr/share/aws/emr/emrfs/auxlib/*:/usr/share/aws/emr/cloudwatch-sink/lib/*:/usr/share/aws/emr/security/conf:/usr/share/aws/emr/security/lib/*
2019-02-12 17:37:13,280 INFO org.apache.flink.yarn.cli.flinkYarnSessionCli - Found Yarn properties file under /tmp/.yarn-properties-hadoop.
2019-02-12 17:37:13,280 INFO org.apache.flink.yarn.cli.flinkYarnSessionCli - Found Yarn properties file under /tmp/.yarn-properties-hadoop.
2019-02-12 17:37:13,528 INFO org.apache.flink.yarn.cli.flinkYarnSessionCli - YARN properties set default parallelism to 16
2019-02-12 17:37:13,528 INFO org.apache.flink.yarn.cli.flinkYarnSessionCli - YARN properties set default parallelism to 16
YARN properties set default parallelism to 16
2019-02-12 17:37:13,640 INFO org.apache.hadoop.yarn.client.RMProxy - Connecting to ResourceManager at ip-10-52-1-36.us-east-1.compute.internal/10.52.1.36:8032
2019-02-12 17:37:13,727 INFO org.apache.flink.yarn.cli.flinkYarnSessionCli - No path for the flink jar passed. Using the location of class org.apache.flink.yarn.YarnClusterDescriptor to locate the jar
2019-02-12 17:37:13,727 INFO org.apache.flink.yarn.cli.flinkYarnSessionCli - No path for the flink jar passed. Using the location of class org.apache.flink.yarn.YarnClusterDescriptor to locate the jar
2019-02-12 17:37:13,818 INFO org.apache.flink.yarn.AbstractYarnClusterDescriptor - Found application JobManager host name 'ip-10-23-1-147.us-east-1.compute.internal' and port '40907' from supplied application id 'application_1529504500067_0001'
Starting execution of program
Job has been submitted with JobID 5d040f73602296d5cd0f72706c8b71c5
The job starts up, attaches to the running flink session and provides you with a job id. You can see the job immediately in the flink web ui (if you've got a proxy running).
You can also see the job by running the list-jobs command:
dev> ./emr-ctl list-jobs j-394OWCGLKHED3NOTE: This time we ran this from a dev environment instead of on the cluster
id name state start end
5d040f73602296d5cd0f72706c8b71c5 MyJob1 RUNNING 02/23/2019 04:43:29 -
e810f8631f1cc2402cb2b329c7b19a9d MyJob1 CANCELED 02/22/2019 21:23:55 02/22/2019 23:12:17
Connection to ec2-47-87-17-126.us-east-1.compute.amazonaws.com closed.
This shows our current job, as well as a previous canceled job, the same as in the web ui.
You can cancel a running job with the cancel command:
dev> ./emr-ctl cancel j-394OWCGLKHED3 5d040f73602296d5cd0f72706c8b71c5Using the result of 'hadoop classpath' to augment the Hadoop classpath: /etc/hadoop/conf:/usr/lib/hadoop/lib/*:/usr/lib/hadoop/.//*:/usr/lib/hadoop-hdfs/./:/usr/lib/hadoop-hdfs/lib/*:/usr/lib/hadoop-hdfs/.//*:/usr/lib/hadoop-yarn/lib/*:/usr/lib/hadoop-yarn/.//*:/usr/lib/hadoop-mapreduce/lib/*:/usr/lib/hadoop-mapreduce/.//*::/usr/lib/hadoop-lzo/lib/*:/usr/share/aws/aws-java-sdk/*:/usr/share/aws/emr/emrfs/conf:/usr/share/aws/emr/emrfs/lib/*:/usr/share/aws/emr/emrfs/auxlib/*:/usr/share/aws/emr/cloudwatch-sink/lib/*:/usr/share/aws/emr/security/conf:/usr/share/aws/emr/security/lib/*
2019-02-12 17:53:10,043 INFO org.apache.flink.yarn.cli.flinkYarnSessionCli - Found Yarn properties file under /tmp/.yarn-properties-hadoop.
2019-02-12 17:53:10,043 INFO org.apache.flink.yarn.cli.flinkYarnSessionCli - Found Yarn properties file under /tmp/.yarn-properties-hadoop.
Cancelling job 5d040f73602296d5cd0f72706c8b71c5.
2019-02-12 17:53:10,281 INFO org.apache.flink.yarn.cli.flinkYarnSessionCli - YARN properties set default parallelism to 16
2019-02-12 17:53:10,281 INFO org.apache.flink.yarn.cli.flinkYarnSessionCli - YARN properties set default parallelism to 16
YARN properties set default parallelism to 16
2019-02-12 17:53:10,434 INFO org.apache.hadoop.yarn.client.RMProxy - Connecting to ResourceManager at ip-10-52-1-36.us-east-1.compute.internal/10.52.1.36:8032
2019-02-12 17:53:10,523 INFO org.apache.flink.yarn.cli.flinkYarnSessionCli - No path for the flink jar passed. Using the location of class org.apache.flink.yarn.YarnClusterDescriptor to locate the jar
2019-02-12 17:53:10,523 INFO org.apache.flink.yarn.cli.flinkYarnSessionCli - No path for the flink jar passed. Using the location of class org.apache.flink.yarn.YarnClusterDescriptor to locate the jar
2019-02-12 17:53:10,612 INFO org.apache.flink.yarn.AbstractYarnClusterDescriptor - Found application JobManager host name 'ip-10-23-1-147.us-east-1.compute.internal' and port '40907' from supplied application id 'application_1529504500067_0001'
Cancelled job 5d040f73602296d5cd0f72706c8b71c5.
Connection to ec2-47-87-17-126.us-east-1.compute.amazonaws.com closed.
Now we can see the job has been cancelled:
dev> ./emr-ctl list-jobs j-394OWCGLKHED3id name state start end
5d040f73602296d5cd0f72706c8b71c5 MyJob1 CANCELED 02/23/2019 04:43:29 02/23/2019 04:48:12
e810f8631f1cc2402cb2b329c7b19a9d MyJob1 CANCELED 02/22/2019 21:23:55 02/22/2019 23:12:17
Connection to ec2-47-87-17-126.us-east-1.compute.amazonaws.com closed.
Savepoints are externally stored self-contained checkpoints that you can use to stop-and-resume or update your flink programs. They use flink’s checkpointing mechanism to create a (non-incremental) snapshot of the state of your streaming program and write the checkpoint data and meta data out to an external file system.
When you want to cancel a job, you can provide -s option, which will persist your job's
state before cancellation so that you can safely resume your job without losing its state.
To cancel a job with a savepoint, pass -s option, and optionally a savepoint path.
dev> ./emr-ctl list-jobs j-394OWCGLKHED3id name state start end
0711de4ca14ebc7ba7f6ee59f0b52af2 MyJob1 RUNNING 02/12/2019 17:33:03 -:S
bb92b21b0e49cdfbfda8a23827dabe73 MyJob2 RUNNING 02/12/2019 17:35:44 -:S
43050ebf8c1148769ec26512a017667f MyJob3 RUNNING 02/12/2019 17:33:35 -:S
23898dfe5219e74936faf6a8f09fdf5d MyJob4 RUNNING 02/12/2019 17:35:34 -:S
26d1338063c323ad657e55c2f07d2906 MyJob5 RUNNING 02/12/2019 17:32:02 -:S
b5a15378195f7096ed1347e7ae45f07a MyJob6 RUNNING 02/12/2019 17:33:22 -:S
Connection to ec2-47-87-17-126.us-east-1.compute.amazonaws.com closed.
dev> ./emr-ctl cancel j-394OWCGLKHED3 -s 0711de4ca14ebc7ba7f6ee59f0b52af2flink cancel -s s3://<s3-bucket>/v2/flink-savepoints/staging/MyJob1/20180822-202536 5449dc71489626ef497886dbec513010
Using the result of 'hadoop classpath' to augment the Hadoop classpath: /etc/hadoop/conf:/usr/lib/hadoop/lib/*:/usr/lib/hadoop/.//*:/usr/lib/hadoop-hdfs/./:/usr/lib/hadoop-hdfs/lib/*:/usr/lib/hadoop-hdfs/.//*:/usr/lib/hadoop-yarn/lib/*:/usr/lib/hadoop-yarn/.//*:/usr/lib/hadoop-mapreduce/lib/*:/usr/lib/hadoop-mapreduce/.//*::/usr/lib/hadoop-lzo/lib/*:/usr/share/aws/aws-java-sdk/*:/usr/share/aws/emr/emrfs/conf:/usr/share/aws/emr/emrfs/lib/*:/usr/share/aws/emr/emrfs/auxlib/*:/usr/share/aws/emr/cloudwatch-sink/lib/*:/usr/share/aws/emr/security/conf:/usr/share/aws/emr/security/lib/*
SLF4J: Class path contains multiple SLF4J bindings.
SLF4J: Found binding in [jar:file:/usr/lib/flink-1.6.0/lib/slf4j-log4j12-1.7.7.jar!/org/slf4j/impl/StaticLoggerBinder.class]
SLF4J: Found binding in [jar:file:/usr/lib/hadoop/lib/slf4j-log4j12-1.7.10.jar!/org/slf4j/impl/StaticLoggerBinder.class]
SLF4J: See http://www.slf4j.org/codes.html#multiple_bindings for an explanation.
SLF4J: Actual binding is of type [org.slf4j.impl.Log4jLoggerFactory]
2019-02-12 20:25:37,469 INFO org.apache.flink.yarn.cli.flinkYarnSessionCli - Found Yarn properties file under /tmp/.yarn-properties-hadoop.
2019-02-12 20:25:37,469 INFO org.apache.flink.yarn.cli.flinkYarnSessionCli - Found Yarn properties file under /tmp/.yarn-properties-hadoop.
Cancelling job 5449dc71489626ef497886dbec513010 with savepoint to s3://<s3-bucket>/flink-savepoints/staging/MyJob1/20190212-202536.
2019-02-12 20:25:37,711 INFO org.apache.flink.yarn.cli.flinkYarnSessionCli - YARN properties set default parallelism to 16
2019-02-12 20:25:37,711 INFO org.apache.flink.yarn.cli.flinkYarnSessionCli - YARN properties set default parallelism to 16
YARN properties set default parallelism to 16
2019-02-12 20:25:37,835 INFO org.apache.hadoop.yarn.client.RMProxy - Connecting to ResourceManager at ip-10-32-1-134.us-east-1.compute.internal/10.32.1.134:8032
2019-02-12 20:25:37,934 INFO org.apache.flink.yarn.cli.flinkYarnSessionCli - No path for the flink jar passed. Using the location of class org.apache.flink.yarn.YarnClusterDescriptor to locate the jar
2019-02-12 20:25:37,934 INFO org.apache.flink.yarn.cli.flinkYarnSessionCli - No path for the flink jar passed. Using the location of class org.apache.flink.yarn.YarnClusterDescriptor to locate the jar
2019-02-12 20:25:38,026 INFO org.apache.flink.yarn.AbstractYarnClusterDescriptor - Found application JobManager host name 'ip-10-32-1-134.us-east-1.compute.internal' and port '46875' from supplied application id 'application_1533935339979_0029'
Cancelled job 5449dc71489626ef497886dbec513010. Savepoint stored in s3://<s3-bucket>/flink-savepoints/staging/MyJob1/20190212-202536/savepoint-5449dc-d29da9fdfad8.
Or, with specific path:
dev> ./emr-ctl cancel j-394OWCGLKHED3 \
-s s3://<s3-bucket>/flink-savepoints/temporary/job1 \
0711de4ca14ebc7ba7f6ee59f0b52af2To resume a job with a savepoint, pass the savepoint's path with the -s option.
The path can be full s3 url or just the date part and savepoint-id, which can be found using the
list-savepoints command. If you want to restore a job from the latest savepoint, you can simply pass
latest as a savepoint path.
- Resume with a full
s3path:dev> ./emr-ctl run j-394OWCGLKHED3 -s \ s3://<s3-bucket>/flink-savepoints/staging/MyJob1/2019/02/12/214349/savepoint-20e97c-ba2c02e9e25e \ MyJob1
- Resume with a partial
s3path:dev> ./emr-ctl run j-394OWCGLKHED3 -s 2019/02/12/214349/savepoint-20e97c-ba2c02e9e25e \ MyJob1 - Resume with
latest:dev> ./emr-ctl run j-394OWCGLKHED3 -s latest MyJob1
You can list savepoints saved for a job. This command is useful when you want to resume the job from a specific savepoint.
dev> ./emr-ctl list-savepoints j-394OWCGLKHED3 MyOtherJob2019/02/12/214349/savepoint-20e97c-ba2c02e9e25e
2019/02/12/215045/savepoint-c2e175-293b5ea1954a
2019/02/12/222713/savepoint-e958b6-03604403e50b
You can use the version command to verify that the version of the
emr-ctl script is the same in your dev environment and on a cluster.
This shouldn't be an issue under normal circumstances, but if you're fixing a
bug in, or adding a feature to, emr-ctl, there might be a deviation
between the two. You can check this by typing
dev> ./emr-ctl versionMD5 (./emr-ctl) = ed76c1b83e0aed4a48a2bd25f601ab8c
dev> ./emr-ctl version j-394OWCGLKHED396f1b01b53b94d0ab1aa985e9c81542b ./emr-ctl
NOTE: the md5 programs have slightly different output formats on Mac and Linux, but what matters is checking that the digests of the scripts are the same.
In this case, we can see the scripts differ. You can publish your local script to s3 and the cluster like this:
dev> ./emr-ctl publish-ctl j-394OWCGLKHED3upload: ./emr-ctl to s3://<s3-bucket>/emr-ctl
download: s3://<s3-bucket>/emr-ctl to ./emr-ctl
Connection to ec2-47-87-17-126.us-east-1.compute.amazonaws.com closed.
Now you can verify the cluster script is the right version:
/emr-ctl version j-394OWCGLKHED3ed76c1b83e0aed4a48a2bd25f601ab8c ./emr-ctl
Connection to ec2-47-87-17-126.us-east-1.compute.amazonaws.com closed.
Similarly to emr-ctl versions and publishing,
you can also track md5 fingerprints and publish changes for the flinkydink jar.
To check the local jar version, provide its path to the jar-version command:
dev> ./emr-ctl jar-version target/2.11/flinkydink-2.1.17.jarMD5 (target/scala-2.11/flinkydink-2.1.17.jar) = 9ec35a2f59ea5b7661ef04c58ed1efd9
To check the remote jar version, provide the cluster id:
dev> ./emr-ctl jar-version j-394OWCGLKHED39ec35a2f59ea5b7661ef04c58ed1efd9 flinkydink-2.1.17.jar
Connection to ec2-47-87-17-126.us-east-1.compute.amazonaws.com closed.
After building a new version of the jar, you can publish it to s3 (and to a running cluster if you provide the cluster id):
dev> ./emr-ctl publish-jar target/scala-2.11/flinkydink-2.1.17.jar j-394OWCGLKHED3upload: target/scala-2.11/flinkydink-2.1.17.jar to s3://<s3-bucket>/v2/jars/flinkydink-2.1.17.jar
download: s3://<s3-bucket>/v2/jars/flinkydink-2.1.17.jar to ./flinkydink-2.1.17.jar
Connection to ec2-47-87-17-126.us-east-1.compute.amazonaws.com closed.
The flinkydink-help command gets help for running flinkydink jobs themselves,
in particular it shows the list of available jobs and the arguments available
for each job.
To get a list of jobs:
dev> ./emr-ctl flinkydink-help[info] Loading settings from idea.sbt ...
[info] Loading global plugins from /Users/nextdude/.sbt/1.0/plugins
[info] Loading settings from assembly.sbt ...
[info] Loading project definition from //flinky/git/flinkydink-2/project
[info] Loading settings from build.sbt ...
[info] Set current project to flinkydink
[info] Running (fork) com.example.flinkydink help
[info] Usage: flinkydink <jobName> [job parameters]
[info] Jobs (try "flinkydink <jobName> help" for details)
[info] -------------------------------------------------
[info] - MyJob1
[info] - MyOtherJob
[info] - AnotherCoolflinkDinkJob
[info]
[success] Total time: 2 s, completed Feb 12, 2019 12:50:35 PM
NOTE: The formatting of the help is decorated by
sbtwhich is used to run the command locally. When you run theflinkydink-helpcommand on a cluster, the result is cleaner.
You can also run this with a particular job name to find out what arguments are available for customizing that job.
The following variables should be configured in a .env file in the root of the repo.
RUNNER- the name of your flinkrunner applicationRUNNER_VERSION- the version of your flinkrunner applicationS3_BUCKET- your s3 bucket for emr-ctl artifacts
These variables should be configured per environment under the jobs directory.
Default values should go in jobs/<env>/defaults.json with job specific configs
in jobs/<env>/<jobname>.json. You may include any other values your jobs need,
either in defaults.json or in the job specific files.
-
CLUSTER_NAME- the name of your cluster (defaults to ${RUNNER}-${ENV}) -
ENV- the name of the environment (required) -
FLINK_TARBALL- the path on s3 to a flink tarball for the version of flink you're deploying to EMR -
FLINK_VERSION- the version of flink you want to deploy to EMR -
INSTANCE_COUNT- the number of instances to create in a cluster -
INSTANCE_TYPE- the AWS instance type to use in creating instances in your EMR cluster -
LOG_URI- path on s3 to log events to -
RELEASE_LABEL- the EMR release label you want to use -
SAVEPOINT_BASE- the path on s3 to store savepoints in -
SUBNET- the AWS VPC subnet id (minus the "subnet-" prefix) for this environment