Unscented Kalman Filter Project
- By: Eqbal Quran
Introduction
This Project is the seventh project (Project 2 / Term 2) of the Udacity Self-Driving Car Nanodegree program.
The main goal of the project is to apply Unscented Kalman Filter to fuse data from LIDAR and Radar sensors of a self driving car using C++. This is a more advanced and more accurate method than the one used in the previous Extended Kalman Filter project.
The code will make a prediction based on the sensor measurement and then update the expected position. See files in the 'src' folder for the primary C++ files making up this project.
This project assumes the CTRV motion model on given datasets. To deal with non-linear models, UKF works via unscented transformations.
In the Predict phase, it begins by generating Sigma points, augments them, and then predicts the mean state vector and process covariance matrices.
In the Update phase, the sigma points are transformed into measurement space, and then the updates are applied based on sensor (Radar/Lidar) measurements to get the new values for state vector and process covariance matrix.
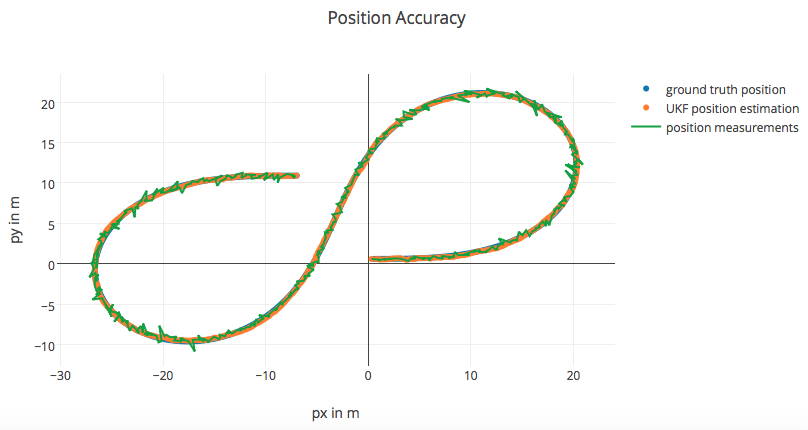
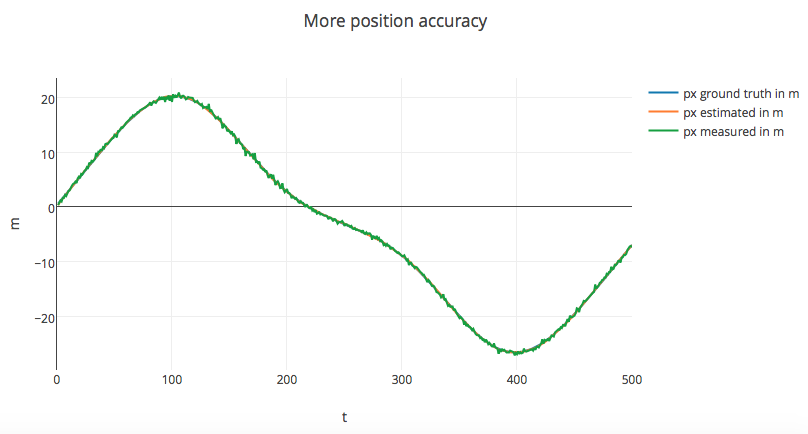
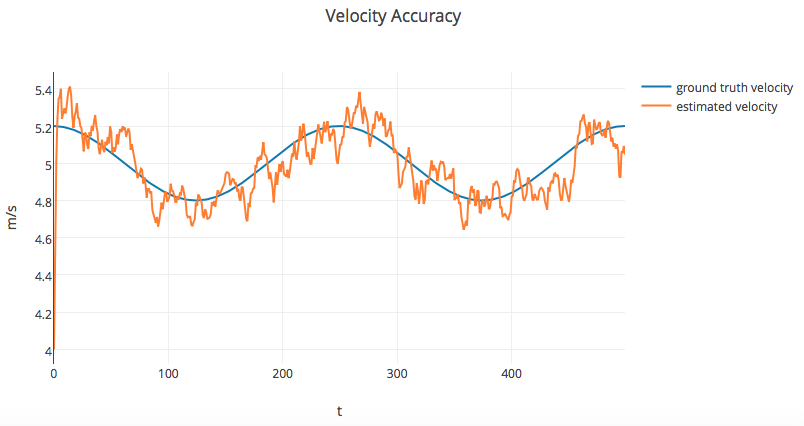
Results of the UKF project are shown below:
Dependencies
- cmake >= v3.5
- make >= v4.1
- gcc/g++ >= v5.4
Structure and Files
scr: a directory with the project code:main.cpp: reads in data, calls a function to run the Kalman filter, calls a function to calculate RMSEukf.cpp: initializes the filter, calls the predict function, calls the update functiontools.cpp: a function to calculate RMSE.data: a directory with an input file, provided by Udacityoutput: a directory which contains the output for running ukfplayground.ipynb: a python notebook for experimenting the data and output and generate some graphs.
Basic Build Instructions
- Clone this repo.
- Make a build directory:
mkdir build && cd build - Compile:
cmake .. && make - Run it:
./UnscentedKF path/to/input.txt path/to/output.txt. You can find some sample inputs in 'data/'.- eg.
./UnscentedKF ../data/obj_pose-laser-radar-synthetic-input.txt
- eg.
Sample Data
The format for the input data looks something like:
Sample Output
CarND-Unscented-Kalman-Filter-Project [master●●] % ./build/UnscentedKF data/obj_pose-laser-radar-synthetic-input.txt output/output.txt
RMSE
0.0690774
0.0796665
0.167352
0.200159
Done!
Paramaters Setup
To have the best results here we have to tune some params so we can improve RMSE.
Some params to be tuned include std_a, std_yawd, the initialized x_ for Radar and Lidar, and P_ for each sensor type.
| param name | description | value | why |
|---|---|---|---|
std_a_ |
process noise standard deviation longitudinal acceleration in m/s^2 | 1 | Bikes (which is what we are detecting in this project) we shouldn't expect a high acceleration. |
std_yawd_ |
process noise standard deviation yaw acceleration in rad/s^2 | .5 | A big value would have to swerve pretty heavily for a big acceleration in yaw |
-
x_andP_for Radar:-
x_: The middle value, forv, can be tuned. I set this to a value of4 m/ssince the average bike speed is15.5 km/h, which is just over4 m/s. -
P_: I used the square of the given standard deviations to calculate reasonable values forP_, for the middle value of 'v' which I used1.
-
-
x_andP_for Lidar:-
x_: The first two values are filled by the 'px' and 'py' lidar measurements. I used4 m/sforvin the same way as for radar. I chose yaw of.5as a reasonable estimate of a beginning turn, with yawd as0given no expected big swerves at the start. -
P_: We are given the from the lidar measurements, so I squared these to feed in the respective variances to the matrix. I just used1for the other variances along the diagonal as a reasonable beginning value.
-
Results
Based on the provided data set, my Unscented Kalman Filter will produce the below results.
| Input | MSE |
|---|---|
| px | 0.06908 |
| py | 0.07967 |
| vx | 0.16735 |
| vy | 0.20016 |
Comparisons
| Input | UKF-Lidar | UKF-Radar | EKF-Fused | UKF-Fused |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| px | 0.09346 | 0.15123 | 0.13997 | 0.06908 |
| py | 0.09683 | 0.19708 | 0.66551 | 0.07967 |
| vx | 0.24238 | 0.20591 | 0.60388 | 0.16735 |
| vy | 0.31516 | 0.24436 | 1.62373 | 0.20016 |
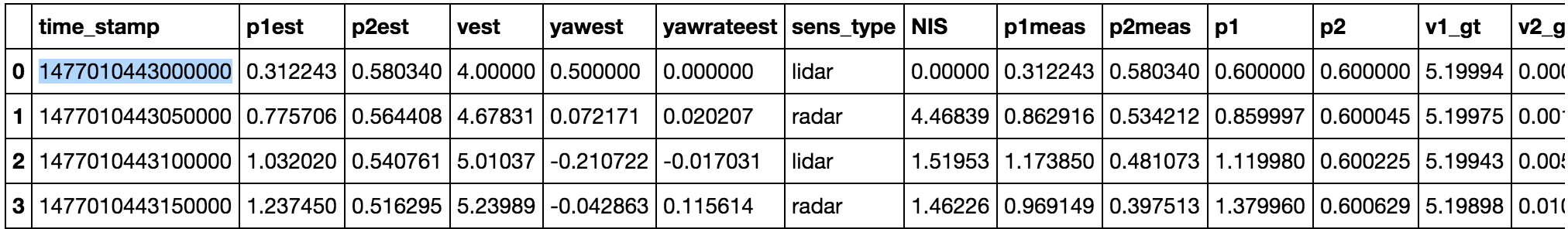
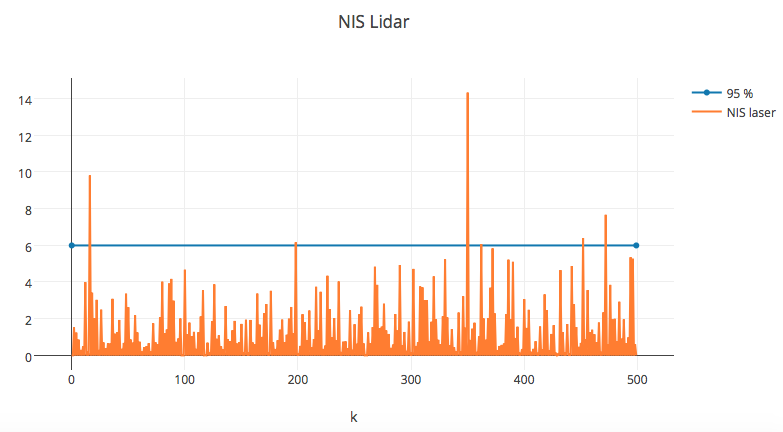
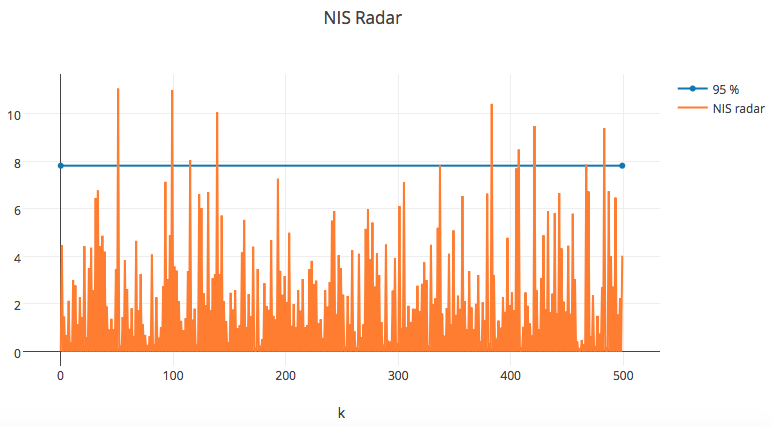
NIS Visualization
Conclusion
As expected, the Unscented Kalman Filter that uses sensor fusion to combine lidar and radar measurements is the most accurate (lowest MSE) of the results.
Editor Settings
We've purposefully kept editor configuration files out of this repo in order to keep it as simple and environment agnostic as possible. However, we recommend using the following settings:
- indent using spaces
- set tab width to 2 spaces (keeps the matrices in source code aligned)
Code Style
Please stick to Google's C++ style guide as much as possible.
Generating Additional Data
This is optional!
If you'd like to generate your own radar and lidar data, see the utilities repo for Matlab scripts that can generate additional data.
Project Instructions and Rubric
This information is only accessible by people who are already enrolled in Term 2 of CarND. If you are enrolled, see the project page for instructions and the project rubric.