This extension provides VSCode editor support for the Lean 4 programming language. It uses the all new Language Server implemented in Lean.
-
Install the extension from the marketplace.
-
Create a new folder called
fooand add a file namedhello.leancontaining the following:import Lake #eval Lake.versionString
-
Open this folder in VS Code using
File/Open Folder. -
Open your file
hello.lean. -
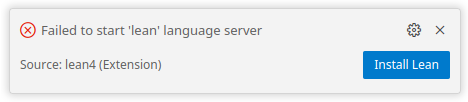
If
Leanis not yet installed on your system you will see a prompt like this: -
Click the
Install Leanoption and enter any default options that appear in the terminal window. -
After this succeeds the correct version of Lean will be installed by
elanand you should see something like this in theLean: Editoroutput panel:info: downloading component 'lean' info: installing component 'lean' Lean (version 4.0.0, commit ec941735c80d, Release)
See Complete Setup for more information on how the lean version is determined for your VS Code workspace.
This version of the VS Code extension only works on Lean 4 source files and not Lean 3. There is a separate VS Code extension for Lean 3. You can have both extensions installed at the same time, they can live side by side.
Note that once the Lean toolchain is installed you can also turn your folder into a Lake project. Lake is a build system
for Lean projects. The VS code extension will honor the Lean version specified in your lean-toolchain file.
Open a VS Code Terminal window in your foo folder and type the following:
lake init foo
lake build
This will add some package definition files to your project along with a Main.lean entry point and build an executable
program. You can run the program ./build/bin/foo and you will see the expected output:
Hello, world!
The extension supports the following features. For basic VS Code editor features, see the VS Code User Interface docs.
The extension provides:
- A set of handy
Lean4:commands available with Ctrl+Shift+P - Side-by-side compatibility with the Lean 3 VSCode extension
- Nice integration with the Lean Language Server as shown below.
- An Infoview panel showing interactive information about your Lean programs.
-
Automatic installation of Lean using elan.
-
Incremental compilation and checking via the Lean server (*)
-
Type information & documentation on hover
-
Error messages and diagnostics
-
Syntax highlighting with basic Lean 4 syntax rules
-
Semantic highlighting
-
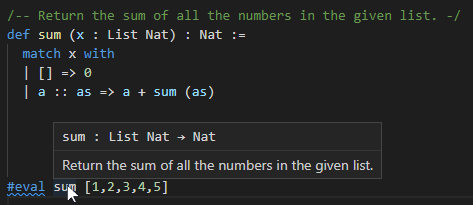
Hover shows documentation, types:
-
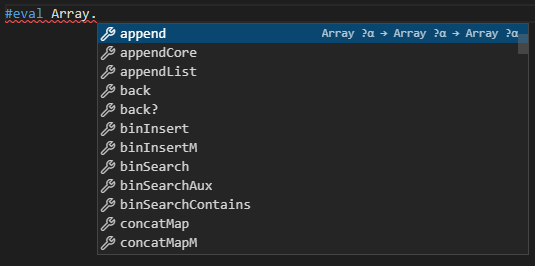
Auto-completion drop downs based on context and type via the Lean Server. For example, if you type "." after
Arrayyou will get: -
An Infoview displaying useful information about your current Lean program.
-
Goto definition (F12) will work if the Lean source code is available. A standard elan install of the Lean toolchain provides Lean source code for all the Lean standard library, so you can go to the definition of any standard library symbol which is very useful when you want to learn more about how the library works. Note also that currently goto definition does not work if the cursor is at the very end of a symbol like
Array.append|. Move the cursor one character to the leftArray.appen|dand it will work. See open issue #767.
(*) Incremental updates do not yet work automatically across files, so after changing and rebuilding the dependency of a
Lean 4 file, the language server needs to be manually informed that it should re-elaborate the full file, including the
imports. This can be done using the Lean 4: Refresh File Dependencies command, which can be activated via Ctrl+Shift+X.
- Support for completing abbreviations starting with a backslash (\).
For example you type
\alphaand the editor automatically replaces that with the nice Unicode characterα. You can disable this feature using thelean4.input.enabledsetting, see below. - When you hover the mouse over a letter that has one or more abbreviations you will see a tooltip like this:

- Auto-completing of brackets like
(),{},[],⟦ ⟧,⦃ ⦄,⟮ ⟯,⦃ ⦄and block comments/- ... -/.
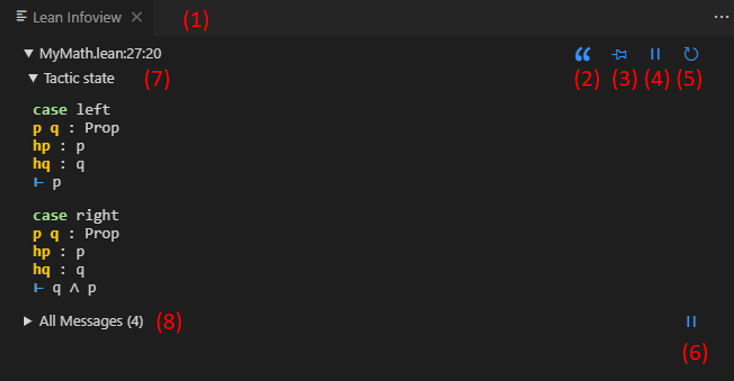
The Infoview panel is essential to working interactively with Lean. It shows:
- Tactic state widgets, with context information (hypotheses, goals) at each point in a proof / definition,
- Expected type widgets display the context for subterms.
- Types of sub-terms in the context can be inspected interactively using mouse hover.
- All Messages widget, which shows all info, warning, and error messages from the Lean server for the current file.
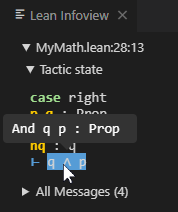
Suppose you have the following theorem:
theorem test (p q : Prop) (hp : p) (hq : q) : p ∧ q ∧ p :=
by apply And.intro
exact hp
apply And.intro
exact hq
exact hpand you place the cursor at the end of the line by apply And.intro the Infoview will display the following information:
(1). The Infoview will activate automatically when a Lean file is opened, but you can also reopen it any time using the icon in the top right of the text editor window or the Ctrl+Shift+P Lean 4: Infoview: Display Goal command or the key that is bound to the command, which is Ctrl+Shift+Enter by default.
You can also disable auto-opening behavior using the setting lean4.infoViewAutoOpen described below.
(2) through (6):
(7). Types in the context can be examined in the tactic state widget using mouse hover:
(8). The "All Messages" widget can be expanded by clicking on it (or hitting the keybind for lean4.displayList, which is Ctrl+Shift+Alt by default)
This extension contributes the following settings (for a complete list, open the VS Code Settings and type Lean4 in the search box):
-
lean4.serverArgs: specifies any additional arguments to pass on thelean --servercommand line. -
lean4.serverLogging.enabled: specifies whether to do additional logging of commands sent to the Lean 4 language server. The default isfalse. -
lean4.serverLogging.path: ifserverLogging.enabledis true this provides the name of the relative path to the store the logs. -
lean4.autofocusOutput: iftrue, automatically show the Output panel when the Lean 4 server prints a new message. -
lean4.elaborationDelay: Time (in milliseconds) which must pass since latest edit until elaboration begins. Lower values may make editing feel faster at the cost of higher CPU usage. The default is 200.
-
lean4.input.enabled: enables abbreviation input completion mode. For example, it allows you to type\alphaand have that be replaced with the greek letter (α). -
lean4.input.eagerReplacementEnabled: enables/disables eager replacement as soon as the abbreviation is unique (trueby default) -
lean4.input.leader: character to type to trigger abbreviation input completion input mode (\by default). -
lean4.input.languages: specifies which VS Code programming languages the abbreviation input completion will be used in. The default is [lean4,lean]. -
lean4.input.customTranslations: add additional input Unicode translations. Example:{"foo": "☺"}will correct\footo☺(assuming thelean.input.leaderhas its default value\). -
lean4.typesInCompletionList: controls whether the types of all items in the list of completions are displayed. By default, only the type of the highlighted item is shown. -
lean4.fallBackToStringOccurrenceHighlighting: controls whether the editor should fall back to string-based occurrence highlighting when there are no symbol occurrences found.
-
lean4.infoview.autoOpen: controls whether the Infoview is automatically displayed when the Lean extension is activated for the first time in a given VS Code workspace(trueby default). If you manually close the Infoview it will stay closed for that workspace until. You can then open it again using the Ctrl+Shift+PLean 4: Infoview: Display Goalcommand. -
lean4.infoview.autoOpenShowsGoal: auto open shows goal and messages for the current line (instead of all messages for the whole file). In this mode the Infoview updates often every time you move the cursor to a different position so it can show context sensitive information. Default istrue. -
lean4.infoview.allErrorsOnLine: show all errors on the current line, instead of just the ones to the right of the cursor, defaulttrue. -
lean4.infoview.debounceTime: how long (in milliseconds) the infoview waits before displaying new information after the cursor has stopped moving. The optimal value depends on your machine - try experimenting. The default is50. -
lean4.infoview.showExpectedType: show the expected type by default. This display can then be toggled by clicking on the title or using the Ctrl+Alt+eLean 4: Infoview: Show Expected Typecommand. The default istrue. -
lean4.infoview.showGoalNames: show goal names (e.g.case inlin the infoview). The default istrue. -
lean4.infoview.emphasizeFirstGoal: emphasize the first goal by displaying the other goals with reduced size and opacity. The default isfalse. -
lean4.infoview.reverseTacticState: show each goal above its local context by default. This can also be toggled by clicking a button (see the Infoview panel description above). The default isfalse.
These colors are used to display proof states in the infoview:
lean4.infoView.hypothesisName: accessible hypothesis nameslean4.infoView.inaccessibleHypothesisName: inaccessible hypothesis nameslean4.infoView.goalCount: the number of goalslean4.infoView.turnstile: the turnstile (⊢) that separates the hypotheses from the goallean4.infoView.caseLabel: case labels (e.g.case zero)
They can be set in a color theme, or under workbench.colorCustomizations in the settings file.
This extension also contributes the following commands, which can be bound to keys if desired using the VS Code keyboard bindings.
The format below is: "lean4.commandName (command name): description", where lean.commandName represents the name used in settings.json and "command name" is the name found in the command palette (accessed by hitting Ctrl+Shift+P).
-
lean4.restartServer(Lean 4: Restart Server): restart the Lean 4 Language Server. Useful if you built new.oleanfiles in your workspace. -
lean4.stopServer(Lean 4: Stop Server): stop the Lean 4 Language Server. -
lean4.restartFile(Lean 4: Restart File): restarts the Lean server for a single file. Useful if the server crashes. As a side-effect this command will also recompile all dependencies. This command has a default keyboard binding of Ctrl+Shift+X. -
lean4.refreshFileDependencies(Lean 4: Refresh File Dependencies): An alias forlean4.restartFile. The Lean server does not automatically update a file when one of its dependencies is changed. So after changing a dependency, the server for the file needs to be restarted to pick up the changed dependency.
lean4.input.convert(Lean 4: Input: Convert Current Abbreviation): converts the current abbreviation (bound to tab by default)
-
lean4.displayGoal(Lean 4: Infoview: Display Goal): open the Infoview panel (bound to Ctrl+Shift+Enter by default) -
lean4.displayList(Lean 4: Infoview: Toggle "All Messages"): toggles the "All messages" widget in the Infoview (bound to ctrl+alt+shift+enter by default) -
lean4.infoView.copyToComment(Lean 4: Infoview: Copy Contents to Comment"): if there is a valid value in the Infoview marked with the icon that can be copied to a comment, this command invokes that action in the editor.
icon that can be copied to a comment, this command invokes that action in the editor. -
lean4.infoView.toggleStickyPosition(Lean 4: Infoview: Toggle Pin): enable / disable "sticky" mode. On enable, a tactic state widget will be created and pinned to this position, reporting the goal from this point even as the cursor moves and edits are made to the file. On disable the pinned widget will be removed. (same as clicking on the or
or  icon on the tactic state widget closest to the cursor.)
icon on the tactic state widget closest to the cursor.) -
lean4.infoView.toggleUpdating(Lean 4: Infoview: Toggle Updating): pause / continue live updates of the main (unpinned) tactic state widget (same as clicking on the or
or  icon on the main tactic state widget.)
icon on the main tactic state widget.) -
lean4.infoView.toggleExpectedType(Lean 4: Infoview: Toggle Expected Type): toggles the "Expected Type" widget in the Infoview (bound to ctrl+alt+e by default)
The complete flow chart for determining how elan and lean are installed is shown below:
The start state is when you have opened a folder in VS Code and opened a .lean file to activate this extension.
If the extension finds that elan is not in your path and is not installed in the default location then it will prompt
you to install lean via elan. If the folder contains a lean-toolchain version it will install that version
otherwise it will install leanprover/lean4:stable.
You can override this default version by setting an DEFAULT_LEAN_TOOLCHAIN environment variable.
Otherwise, if there is a lean-toolchain in the workspace folder or in a parent
folder then it will use the version specified in the specified version.
Then with the selected version it runs lean --version to check if that version is installed yet.
If this version is not yet installed lean --version will install it.
See Development.