This repository is The Carpentries' template for creating websites for Instructor Training workshops.
-
Please do not fork this repository directly on GitHub. Instead, please use the instructions below to copy this
training-templaterepository and customize it for your workshop. -
Please do your work in your repository's
gh-pagesbranch, since that is what is automatically published as a website by GitHub. -
Once you are done, please send your repository's URL to The Carpentries' administrator. We build the list of workshops on our websites from the data included in your
index.mdpage. We can only do that if you [customize][customization] that page correctly and send us a link to your workshop website.
If you run into problems, or have ideas about how to make this process simpler, please get in touch. The pages on [customizing your website][customization], the FAQ, and the [design notes][design] have more detail on what we do and why.
-
Log in to GitHub. (If you do not have an account, you can quickly create one for free.) You must be logged in for the remaining steps to work.
-
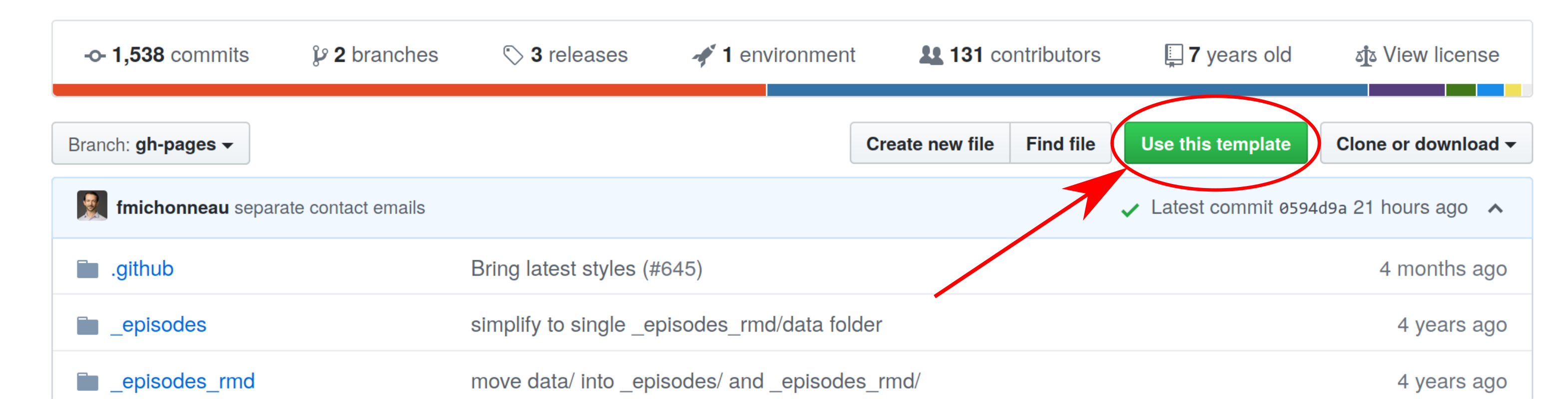
On this page (https://github.com/carpentries/training-template), click on the green "Use this template" button (top right)
-
Select the owner for your new repository. (This will probably be you, but may instead be an organization you belong to.)
-
Choose a name for your workshop website repository. This name should have the form
YYYY-MM-DD-ttt-site, e.g.,2016-12-01-ttt-oomza, whereYYYY-MM-DDis the start date of the workshop. For online workshops, chooseonlineassite. In most cases, the Instructor Training Team will tell you the name of the repository you should use. -
Make sure the repository is public, leave "Include all branches" unchecked, and click on "Create repository from template". You will be redirected to your new copy of the workshop template respository.
-
Your new website will be rendered at
https://your_username.github.io/YYYY-MM-DD-ttt-site.
-
Go into your newly-created repository, which will be at
https://github.com/your_username/YYYY-MM-DD-ttt-site. For example, if your username isgvwilson, the repository's URL will behttps://github.com/gvwilson/2016-12-01-ttt-oomza. -
Ensure you are on the gh-pages branch by clicking on the branch under the drop down in the menu bar (see the note below):
-
Edit the header of
index.mdto customize the list of instructors, workshop venue, etc. You can do this in the browser by clicking on it in the file view on GitHub and then selecting the pencil icon in the menu bar:Editing hints are embedded in
index.md, and full instructions are in [the customization instructions][customization]. -
Alternatively, if you are already familiar with Git, you can clone the repository to your desktop, and edit
index.mdthere, and push your changes back to the repository.git clone -b gh-pages https://github.com/your_username/YYYY-MM-DD-ttt-siteYou should specify
-b gh-pagesto checkout the gh-pages branch because the imported repository doesn't have amasterbranch.In order to view your changes once you are done editing, you must push to your GitHub repository:
git push origin gh-pages -
When you are done editing, go to the GitHub Pages URL for your workshop and preview your changes. In the example above, this is
https://gvwilson.github.io/2016-12-01-ttt-oomza. The finished page should look something like this. -
Optional: you can now change the
README.mdfile in your website's repository, which contains these instructions, so that it contains a short description of your workshop and a link to the training website. -
Optional: Add a link to your workshop website on the repository main page in the description/website section (look for the
Editbutton on the right to add).
Note:
please do all of your work in your repository's gh-pages branch,
since GitHub automatically publishes that as a website.
If you want to preview your changes on your own machine before publishing them on GitHub, you can do so as described below.
-
Install the software described below. This may require some work, so feel free to preview by pushing to the website.
-
Run the command
make serveand go to http://0.0.0.0:4000 to preview your site. You can also run this command by typing
make serve(if you have Make installed). -
Run the command
make workshop-checkto check for a few common errors in your workshop's home page. (You must have Python 3 installed to do this.)
At the top of your repository on GitHub you'll see
No description, website, or topics provided. — Edit
Click 'Edit' and add:
-
A very brief description of your workshop in the "Description" box (e.g., "Oomza University workshop, Dec. 2016")
-
The URL for your workshop in the "Website" box (e.g.,
https://gvwilson.github.io/2016-12-01-ttt-oomza)
This will help people find your website if they come to your repository's home page.
In rare cases,
you may want to add extra pages to your workshop website.
You can do this by putting either Markdown or HTML pages in the website's root directory
and styling them according to the instructions give in
the lesson template.
If you do this,
you must also edit _config.yml to set these three values:
-
carpentryis "cp" (for The Carpentries). This determines which logo is loaded. -
titleis the title of your workshop (typically the venue and date).
Note: carpentry and emailduplicate information that's inindex.md`,
but there is no way to avoid this
without requiring people to edit both files in the usual case
where no extra pages are created.
If you want to set up Jekyll so that you can preview changes on your own machine before pushing them to GitHub, you must install the software described below. (Note: Julian Thilo has written instructions for installing Jekyll on Windows.)
-
Ruby. This is included with Linux and macOS; the simplest option on Windows is to use RubyInstaller. You can test your installation by running
ruby --version. For more information, see the Ruby installation guidelines. -
RubyGems (the package manager for Ruby). You can test your installation by running
gem --version. -
Jekyll. You can install this by running
gem install jekyll.
You can check the formatting of your header by running bin/workshop_check.py
(which is invoked by make workshop-check).
You must have Python 3 installed in order to do this,
and you will also need the PyYAML module.
We are committed to offering a pleasant setup experience for our learners, Trainers, Instructors and workshop hosts. If you find bugs in our instructions, or would like to suggest improvements, please file an issue or [mail us][email].