This Jenkins shared library provides common utility classes and functions used to support continuous integration (CI) build and test jobs for projects within the spacetelescope organization.
Note: For jobs spawned as a result of the creation of a pull request (PR), Jenkins behaves differently than the Travis CI service (https://travis-ci.org/) in that the build will use the HEAD commit of the PR branch only, while Travis typically will run the build/test job on the merge commit between the PR branch and the master branch.
Functionality provided that extends the native Groovy syntax approach
- Terminate job execution immediately (with a success status) when the string
[skip ci]or[ci skip]is found in the commit message. - Selection of either parallel (default) or sequential execution of the specified build matrix.
- Automatic creation of a conda environment with user-specified dependencies to host the build.
This library's functionality is automatically made available to every Jenkinsfile hosted in the spacetelescope Github organization.
An example job that builds three parallel combinations and runs tests on one of them, posting a summary of test results for all build configurations if any test failures or errors occur.
// Obtain files from source control system.
if (utils.scm_checkout()) return
// Allow modification of the job configuration, affects all relevant build configs.
// Pass this object in the argument list to the`run()` function below to apply
// these settings to the job's execution.
jobconfig = new JobConfig()
jobconfig.post_test_summary = true
// 'credentials' example
// To make an environment variable
// NOTE: This requires server-side configuration on the Jenkins instance hosting the builds.
// Contact a Jenkins administrator to add secrets to the credentials store.
jobconfig.credentials = [
'SECRET_VALUE_CREDENTIAL_ID', // Credential ID as stored in Jenkins, var has same name as ID.
['SECRET_VALUE_CREDENTIAL_ID, CUSTOM_ENV_VAR_NAME'] // Mapping of credental ID to custom env var.
]
// Config data to share between builds.
CFLAGS = 'CFLAGS="-m64"'
LDFLAGS = 'LDFLAGS="-m64"'
DEFAULT_FLAGS = "${CFLAGS} ${LDFLAGS}"
// Some waf flags cause a prompt for input during configuration, hence the 'yes'.
configure_cmd = "yes '' | ./waf configure --prefix=./_install ${DEFAULT_FLAGS}"
// Define each build configuration, copying and overriding values as necessary.
bc0 = new BuildConfig()
bc0.nodetype = "linux-stable"
bc0.name = "debug"
LOCAL_VARIABLE='use_me_now'
bc0.env_vars = ['MY_VAR=' + LOCAL_VARIABLE, // (Early expansion) Compose string locally, then pass to environment.
'PATH=./_install/bin:$PATH', // (Late expansion) $PATH gets expanded later by the shell hosting the build.
]
bc0.build_cmds = ["${configure_cmd} --debug",
"./waf build",
"./waf install"]
bc1 = utils.copy(bc0)
bc1.name = "release"
bc1.build_cmds[0] = "${configure_cmd} --release-with-symbols"
bc1.test_cmds = ["conda install -q -y pytest requests astropy",
"pip install -q pytest-remotedata",
"pytest tests --basetemp=tests_output --junitxml results.xml --remote-data"]
bc1.failedUnstableThresh = 1
bc1.failedFailureThresh = 6
bc2 = utils.copy(bc0)
bc2.name = "optimized"
bc2.build_cmds[0] = "${configure_cmd} --O3"
// Iterate over configurations that define the (distibuted) build matrix.
// Spawn a host of the given nodetype for each combination and run in parallel.
// Also apply the job configuration defined in `jobconfig` above.
utils.run([bc0, bc1, bc2, jobconfig])The build configuration syntax shown here is provided by the utils library which contains two main components, the utils functions and the BuildConfig class.
The utils library provides several functions:
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
if (utils.scm_checkout()) return |
[skip ci]/[ci skip] directive found in the latest commit message. This is used in certain regression testing jobs that run on a schedule, the execution of which should never be skipped due to skip directives found in the commit history. |
utils.copy() |
|
utils.run(config_list, concurrent=true) |
|
utils.convert_specifiers(s) |
|
This class contains properties that may be adjusted to control the behavior of the overall Jenkins job.
A JobConfig object must be created as shown in the example above and then passed in to the run() function in the list of BuildConfig objects for the customizations to be honored.
It has the following properties:
| Member | Type | Required | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
post_test_summary |
boolean | no | When true, will cause the creation of a Github issue on the project's repository containing a summary of test results produced by all build configurations hosted in the the job if any tests returned a failure or error status. Default is false, meaning no summary issues will be created upon test failures or errors. When set to true, if no test failures or errors occur, a summary post will not be generated. Default value when not specified or no jobconfig object passed to run(): false |
enable_env_publication |
boolean | no | When true, and when conda is used during the job (for instance when a conda_packages list is provided in a build config), every build configuration (See BuildConfig Class below) that produces an XML test report with no test failures will also publish a list of the environment's packages to an Artifactory repository defined in either a setup.cfg [tool:pytest] section OR in a pytest.ini file (but not both) using the results_root configuration value. i.e. results_root = <artifactory destination repo> The environment list file produced is the result of the command conda list --explicit from within the active environment and will be named conda_env_dump_<value of buildconfig.name>.txt. Note: the Artifactory repository specified must be configured to allow files to be published there. Default value when not specified or no jobconfig object passed to run(): false |
publish_env_filter |
string | yes | Only publish the environment when the current git origin and branch matches within the pipeline job. The expected format is user/branch (e.g. spacetelescope/master). Wildcard operators are not supported. To override this behavior set the environment variable JSCIU_ENV_PUBLISH_FORCE=1. |
publish_env_on_success_only |
boolean | no | When enable_env_publication is set to true, a false value for this option will publish a package list of any conda environments that are used in each build configuration, even if the test results contain failures. Default value when not specified or no jobconfig object passed to run(): true |
credentials |
list of strings or lists | no | If string-type credentials have been added to Jenkins's internal credentials store in a scope available to the job in question, adding the credential ID value(s) here in a comma separated list of strings will cause the value of each credential item to be injected into the runtime environment of each build configuration hosted by the job as an environment variable with the same name as the credential ID. If instead a custom environment variable name is desired onto which the value of a stored credential secret is to be mapped, it may be supplied as the second element of a list. I.e. ['SECRET_VALUE_CREDENTIAL_ID, CUSTOM_ENV_VAR_NAME'] as shown in the example Jenkinsfile above. |
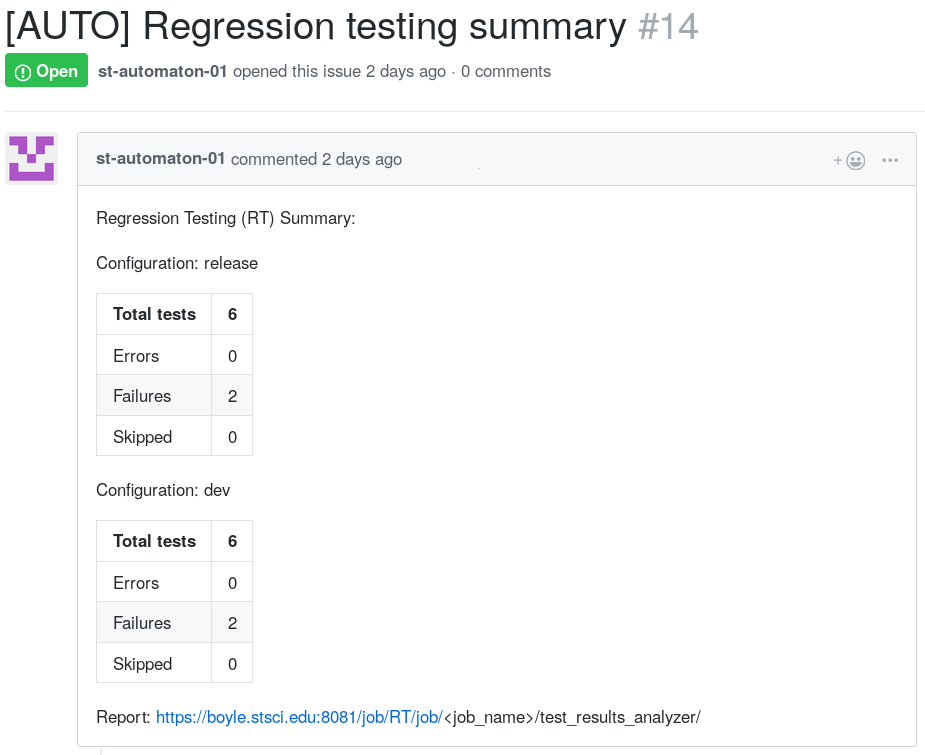
If test summaries are requested using the post_test_summary property of the JobConfig class as described above, each Jenkins job that produces one or more test errors or failures will result in a single new Github issue being posted to the project's repository.
If the label testing has been defined in the Github repository and a test summary issue ends up being generated for a job run, the issue that results will have the testing label applied. If a label with the name testing has not been defined on the repository, then the issue will be created without a label.
If tests continue to fail or error in the periodically scheduled job, a (possibly redundant) issue will be posted each time the job runs.
The utils library also provides the definition of a class called BuildConfig that may be used to create build configuration objects used to define build tasks to be run on various hosts.
It has the following properties:
| Member | Type | Required | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
nodetype |
string | yes | The Jenkins node label to which the build is assigned |
name |
string | yes | A (short) arbitrary name/description of the build configuration. Builds are named <nodetype>/<name> in the build status GUI. I.e. "linux/stable" or "linux/debug" |
run_on_days |
list of strings | no | (When absent, default behavior is to always run the BuildConfig.) Primarily for periodic regression test (RT) job use. A list of day-of-week names on which to execute the associated BuildConfig. Example: bc0.run_on_days = ['sat', 'sun'] to only run the BuildConfig on those two days. Valid day names are sun, mon, tue, wed, thu, fri, sat. |
conda_packages |
list of strings | no | If this list is defined, the associated build job will create a temporary conda environment to host the job which contains the packages specified. Package specifications are of the form
bc0.conda_packages = ["pytest", "requests", "numpy=1.14.3"] |
conda_override_channels |
boolean | no | Instructs the conda environment creation process to not implicitly prepend the anaconda defaults channel to the list of channels used. This allows the priority of channels to be used for environment creation to be specified exactly in the order of channels provided in the conda_channels list, described below. If conda_packages is not defined in the Jenkinsfile this property is ignored. |
conda_channels |
list of strings | no | The list of channels, in order of search priority, to use when retrieving packages for installation. If conda_override_channels is not defined, this list will have the conda defaults channel implicitly prepended to it at installation time. If conda_packages is not defined in the Jenkinsfile this property is ignored. Example: bc0.conda_channels = ["http://ssb.stsci.edu/astroconda"] |
conda_ver |
string | no | The version of conda to use when creating environments to host the build. If not supplied, a recent version of conda will be obtained. |
pip_reqs_files |
list of strings | no | Name(s) of pip requirements files to use to install python packages into the build environment. Each file will be processed with a pip install -r [file] in the order in which they appear in the list. |
env_vars |
list of strings | no | Allow configuration of the shell environment in which build and test commands are run. Of note:
|
build_cmds |
list of strings | yes | These commands are run in their order of appearance in this list with the default shell environment and any modifications to that environment provided by the env_vars list described above.
|
test_cmds |
list of strings | no | These commands are run in their order of appearance in this list with the default shell environment plus any modifications to that environment provided by the env_vars list described above.
|
failedFailureNewThresh |
integer | no | (Default is no threshold set.) The threshold for the number of newly appearing test failures that will cause the build to be flagged as "FAILED". |
failedFailureThresh |
integer | no | (Default is no threshold set.) The threshold for the number of test failures that will cause the build to be flagged as "FAILED". |
failedUnstableNewThresh |
integer | no | (Default is no threshold set.) The threshold for the number of newly appearing test failures that will cause the build to be flagged as "UNSTABLE". |
failedUnstableThresh |
integer | no | (Default is no threshold set.) The threshold for the number of test failures that will cause the build to be flagged as "UNSTABLE". |
skippedFailureNewThresh |
integer | no | (Default is no threshold set.) The threshold for the number of newly appearing skipped tests that will cause the build to be flagged as "FAILED". |
skippedFailureThresh |
integer | no | (Default is no threshold set.) The threshold for the number of skipped tests that will cause the build to be flagged as "FAILED". |
skippedUnstableNewThresh |
integer | no | (Default is no threshold set.) The threshold for the number of newly appearing skipped tests that will cause the build to be flagged as "UNSTABLE". |
skippedUnstableThresh |
integer | no | (Default is no threshold set.) The threshold for the number of skipped tests that will cause the build to be flagged as "UNSTABLE". |
The following documentation for the xUnit plugin which is used to provide the test report functionality in the CI system may be useful when customizing test thresholds. The heading "Accept a Baseline". https://jenkins.io/blog/2016/10/31/xunit-reporting/ describes the scenario and how to set the appropriate thresholds.
The return code of all commands specified in the test_cmds list are explicitly ignored and do not affect the overall job status (Success/Unstable/Failure) in Jenkins.
This is a brief description of the job execution sequence to aid in understanding CI system behavior when constructing build configuration scripts.
- A repository in https://github.com/spacetelescope has a Jenkinsfile added to one or more branches or PRs. The Jenkinsfile describes the build and test activities to take place upon a git push event.
- A git push event takes place on a branch containing a Jenkinsfile.
- Jenkins initiates a clone of the repository where the push event occurred INTO A SUBDIRECTORY of the job workspace called 'clone'. If you wish to modify the PATH variable, for instance to refer to some path in the source tree or a directory generated from the configuration or build process, bear this in mind. The CI job tree looks like:
<WORKSPACE_ROOT>
+- clone (project source tree)
+- <project_source_root>
+- miniconda (if conda was requested)
- Source check out
a. When the
if (utils.scm_checkout()) returnconstruct is used, the commit message is examined and the build is immediately terminated with a SUCCESS status if the string[skip ci]or[ci skip]appears in the latest commit message. If no such string is found, job execution continues. b. Jenkins creates a "stash" of all the files that were retrieved by the git clone and distributes them internally ("unstashes" them) to each build host that is spawned later in this sequence. This is done to minimize network calls to external resources. - The Jenkinsfile is executed as a Jenkins "pipeline script"
- For every build configuration passed in to the utils.run() function a docker container will be created to host the build and test activities for that configuration.
- Environment variables specified in env_vars list are added to the environment before executing each command in build_cmds and then test_cmds in their order of appearance in those lists.
- After the last test_cmds command is executed, Jenkins examines the build environment for a filename with an .xml extension. If one is found, it is assumed to be a JUnit-compliant test report and is read.
- Any test reporting thresholds supplied in the build configuration are applied and the results presented accordingly via the Jenkins user interface.