by Niklas Köhn, Esri Deutschland
Some Widgets and a theme.
- Clone the sample repo into your Experience Builder Client root folder and restart your watcher.
- Some widgets depend on 3rd party NPM packages, which need to be installed before compiling. These widgets have their own
package.jsonin their root folder. Either navigate to the particular folders and executenpm iin there or run the scriptnpm run install-subfoldersright in the repository root. This will scan through the widget folders and install all dependencies.
It's a good practice to npm init within the widget folder and install dependencies there. During development, it will work also with a central package.json file containing the dependencies for all your widgets (resulting in one single node_modules folder outside widgets), but fails to resolve dependencies for production use. We'll end up with one package.json per widget using packages, but that's what npm run install-subfolders (see above) is for.
For example, when following this guide, the npm run build:prod will not find the installed packages after copying only the subfolder with your widget into your-extensions/widgets.
- Link the config of the app in the server folder:
- Open command prompt (does not work with Git Bash or similar)
- If the subfolders
public\appsdo not yet exist on the server side, create them manually mklink /j "<ExB path>\server\public\apps\fah_basis" "<ExB path>\client\WebClient_LastGen\apps\fah_basis"- The success message:
Junction created for <ExB path>\server\public\apps\fah_basis <<===>> <ExB path>\client\WebClient_LastGen\apps\fah_basis
- In the file
client/tsconfig.json, include the folder name of the repository in the include array. Or remove / comment out the include array completely from the file. - Restart Watcher (call
npm startin the client folder)
This one was moved to its own repo: w3w-arcgis-exb-widget
As an example, widgets/maplyr-ext adds custom actions to the standard map-layers widget.
Steps:
- copy the original class-based widget from
dist/widgets/arcgisinto<your repo folder>/widgetsoryour-extensions/widgets - rename
widget.tsxto<widget-name>.tsx, e.g.map-layers.tsx, in there:- create a new empty
widget.tsxin theruntimefolder, next to the renamed original file - import original widget with alias name:
import { Widget as <Widget-Name> } from '<widget-name>.tsx - create your own derived widget class:
export default class Widget extends <Widget-Name> - overwrite methods as needed, but call
super.<method>()to keep the functionality of the base class
- create a new empty
For Jest to be able to import anything, add "esModuleInterop": true to your tsconfig.json.
By default, the paths.widgets array in your tsconfig.json only contains a reference to "./your-extensions/widgets/*". To enable the TS compiler to find your shared code when importing it in your widget and business code, enhance the array with the folder names of the repositories with /widgets/ postfix:
"paths": {
[...]
"widgets/*": [
"./your-extensions/widgets/*",
"./<your_repository>/widgets/*"
]
}
To ensure that no entries are overwritten, the central ts file with the collected exports should be named individually. For example, instead of entry1.ts, you would be using entry_<project_name>.ts in your repository.
Webpack 5 no longer includes polyfills for node core modules. This manifests in the error message BREAKING CHANGE: webpack < 5 used to include polyfills for node.js core modules by default, meaning: Packages that use node.js core modules no longer work natively with webpack 5.
For more information on this topic, here is a good explanation: "Webpack 4 automatically polyfilled many node APIs in the browser. This was not a great system, because it could lead to surprisingly giant libraries getting pulled into your app by accident, and it gave you no control over the exact versions of the polyfills you were using. So Webpack 5 removed this functionality."
There are many descriptions for the workaround, directly in the error messages in the console and also under the above mentioned source: The required sources have to be entered in webpack.config under resolve.fallback and installed via npm i.
So far so good. Except that this configuration has been chopped up in ArcGIS Experience Builder and spread over several files:
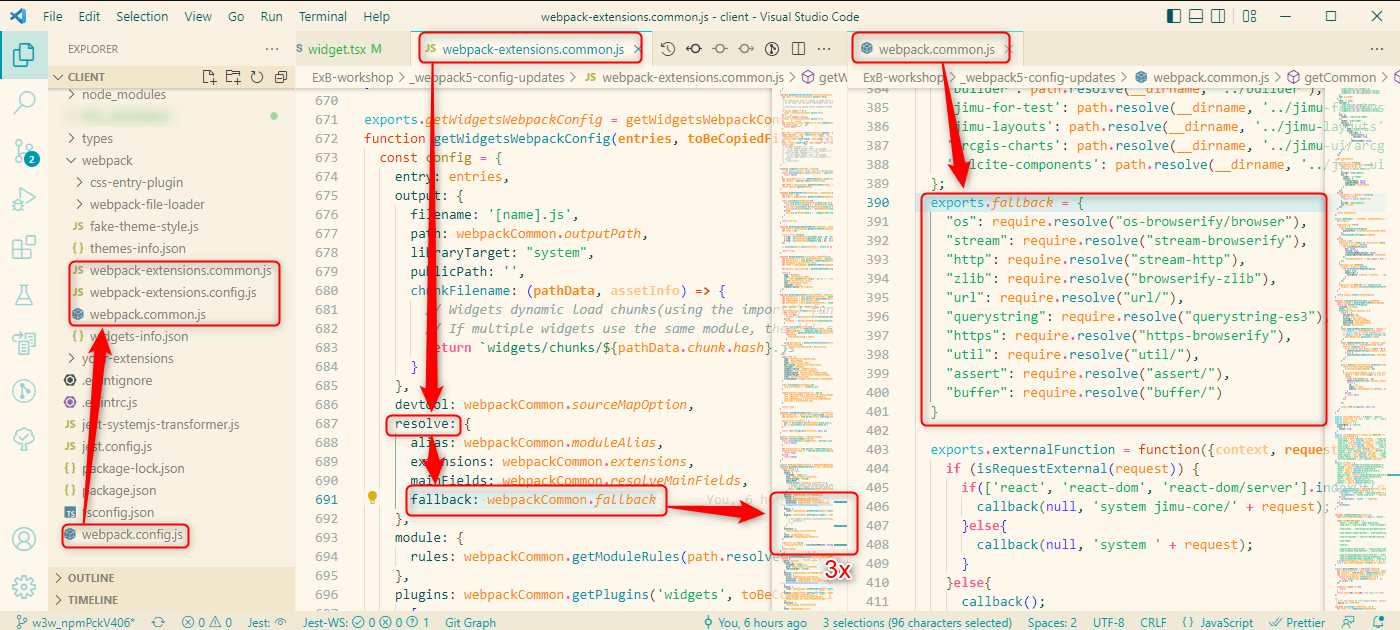
webpack.config.jsin theclientroot folder referencingwebpack-extensions.config.jsin thewebpacksubfolder.webpack-extensions.config.jsbuilds the config from references towebpack-extensions.common.jswebpack-extensions.common.jsreferences the actual polyfills inwebpack.common.js.
- In
webpack-extensions.common.js, add afallbackproperty to theresolveobject in 3 places:getTemplatesWebpackConfig(),getWidgetsWebpackConfig()andgetThemesWebpackConfig():resolve: { alias: webpackCommon.moduleAlias, extensions: webpackCommon.extensions, mainFields: webpackCommon.resolveMainFields, fallback: webpackCommon.fallback }, - In
webpack.common.js, add the references to the polyfilled packages underexports.fallback, e.g.:exports.fallback = { "os": require.resolve("os-browserify/browser"), "util": require.resolve("util/"), "http": require.resolve("stream-http"), "url": require.resolve("url/"), "stream": require.resolve("stream-browserify"), "https": require.resolve("https-browserify"), "zlib": require.resolve("browserify-zlib"), "assert": require.resolve("assert/"), "buffer": require.resolve("buffer/"), } - ToDo: Install all referenced NPM packages on
clientlevel, e.g.:npm i os-browserify npm i util npm i stream-http npm i stream-browserify npm i https-browserify npm i browserify-zlib npm i buffer npm i assert npm i url npm i querystring-es3
That works.
The trouble is, that the webpack files on root level of the "client" folder are not part of the "exb-web-extension-repo", but are delivered with ExB. Now if you use NPM packages in your custom widgets that require polyfills, you have to update the webpack configs on Node JS root level. Please refer to the _webpack5-config-updates subfolder in this repository for sample files.
Originally published in the ArcGIS community.
This package is based on the Excel tool library "SheetJS" and is no longer maintained. The GitHub advisory db says: "All versions of SheetJS CE through 0.19.2 are vulnerable to "Prototype Pollution" when reading specially crafted files. Workflows that do not read arbitrary files (for example, exporting data to spreadsheet files) are unaffected." As we're not reading anything, I guess it's not that urgent.. .. but maybe try out Mr.Excel some day?
The patch as suggested here does not work for me. I need to remove the include array from tsconfig.json (no whitelist means including everyting).
Additionally, in ExB 1.12, the TypeScript definition file is missing. Download from here, place in client/types and rename to arcgis-js-api.d.ts.