A Node.js application that receives HTML combined with raw LaTeX syntax as an input string.
It processes the string and returns the original HTML with the LaTeX elements converted into SVG and invisible MathML.
-
Make sure Node.js is installed on the system.
-
Download MathJax-Node-Accessibility-Demo and extract it's contents. You can rename the extracted folder.
-
Navigate into the extracted folder.
-
If you run MathJax-Node-Accessibility-Demo locally you can skip this step and continue with step 5. Otherwise adjust following presets to your preffered values:
4.1 Openmodules/config.jsand adjust:- the list of
apiKeys(line 2 ff.)
4.2 Open
modules/config.js:
4.3 Adjust Port3000(line 7) to the port number under which MathJax-Node-Accessibility-Demo should be accessed. - the list of
-
You are done with configuring the presets now. MathJax-Node-Accessibility-Demo requires a number of Node.js modules in order to be executed. To install these modules just follow the next two steps:
5.1 Navigate into the MathJax-Node-Accessibility-Demo folder with commandline (server.jsis located in this folder).
5.2 Exectue thenpm installcommand. This will trigger the Node Package Manager to install all required dependencies for you. -
Everything is set up now and the application is ready to start.
Runnode server.jsin commandline to start the application.
The application is now running and listening to port 3000 or to the port you specified in 4.3
(a process manager like PM2 is recommended for production use).
- /hello (GET)
- Returns "hello" as string if the service is running.
- /process (POST)
-
Requires a valid API Key in header and JSON input in body.
-
Make sure that your requests body content type is set to JSON. Input structure (body)
{ language: "en", html: { "key1": "value1", "key2": "value2", "key3": "value3", ... } }html-attribute: Contains an array of strings. Each string can be a Text/HTML combined with LaTeX notations.language-attribute: Contains a string ("en"/"de") which defines the language of thehtml-attribute's values. Thelanguage-attribute determines the language of the output speaktext.Output structure:
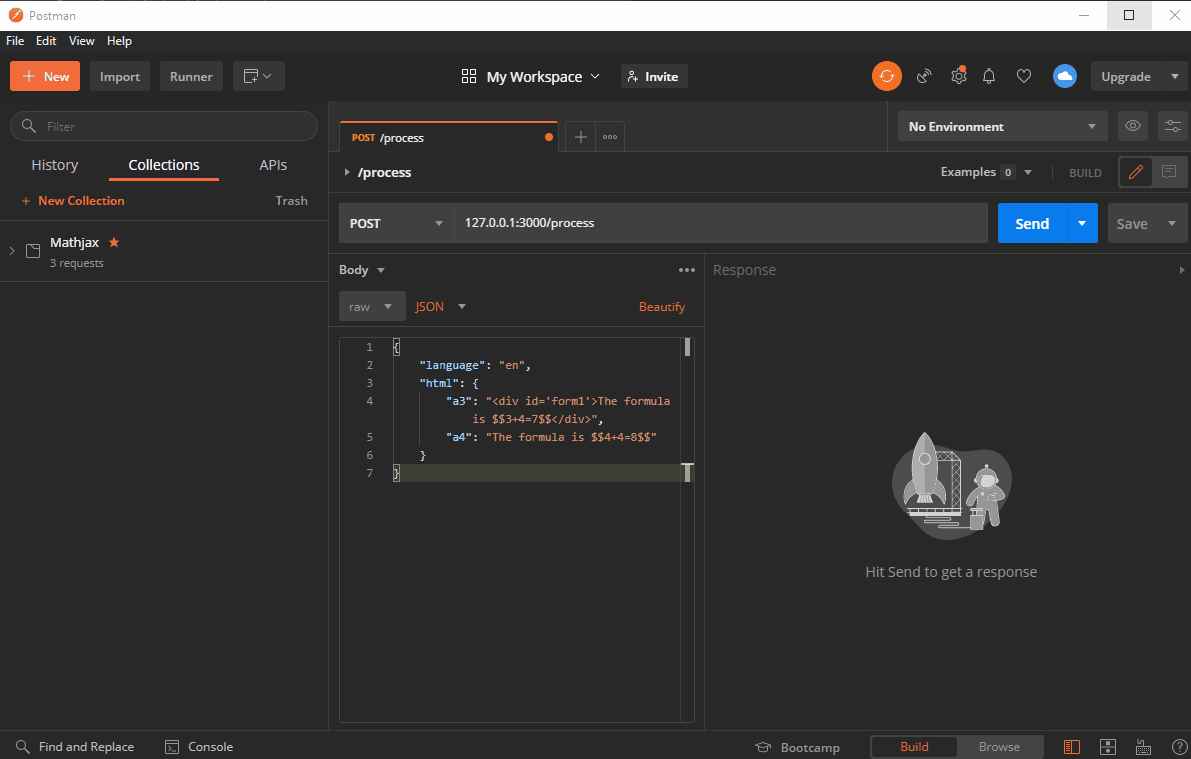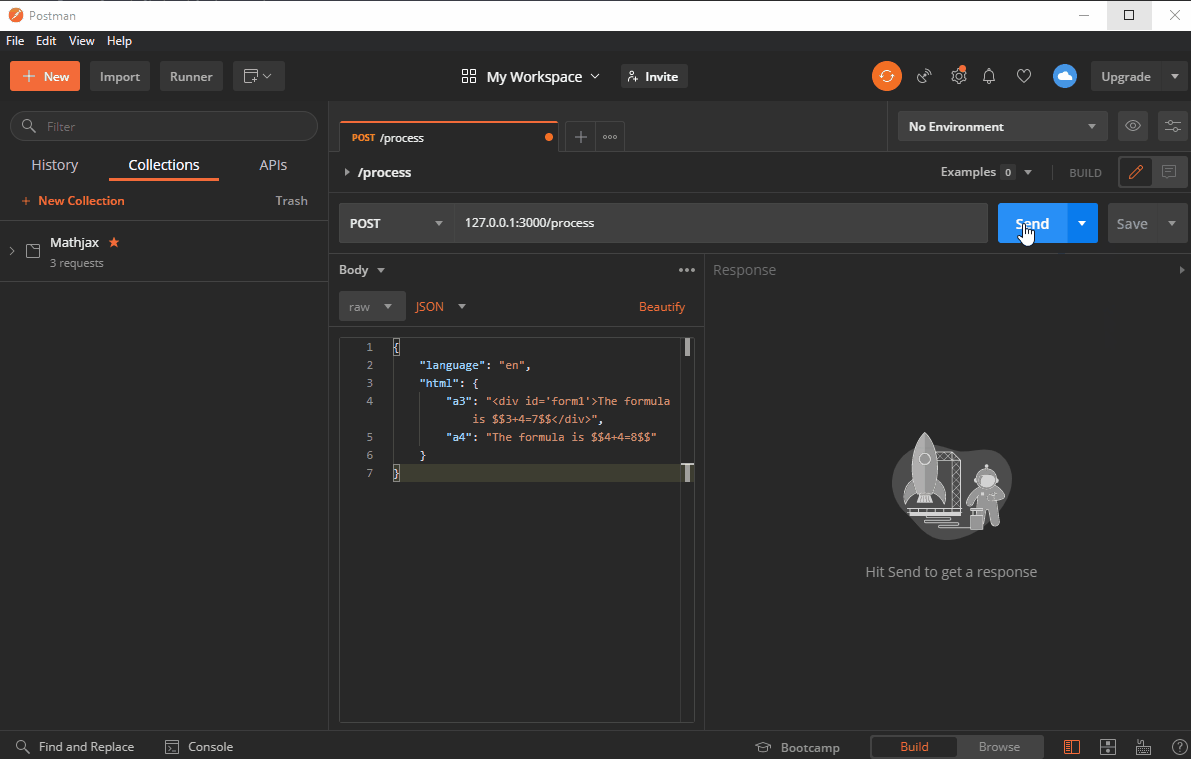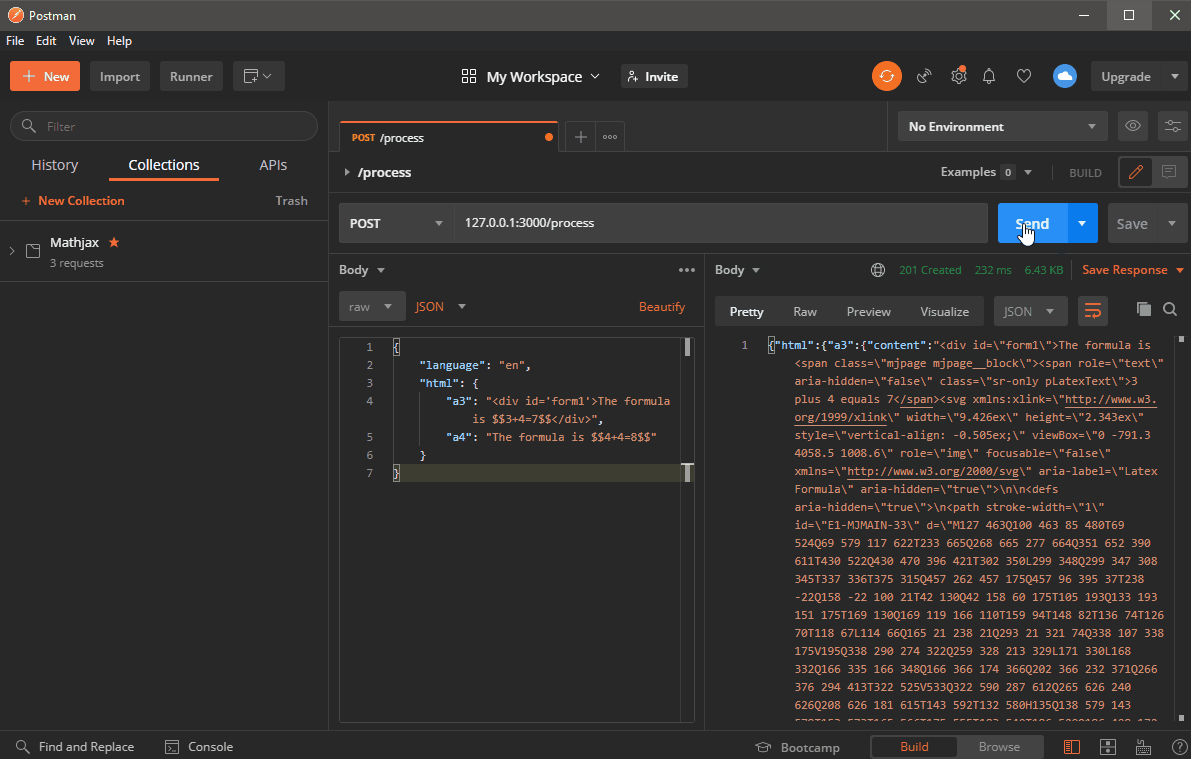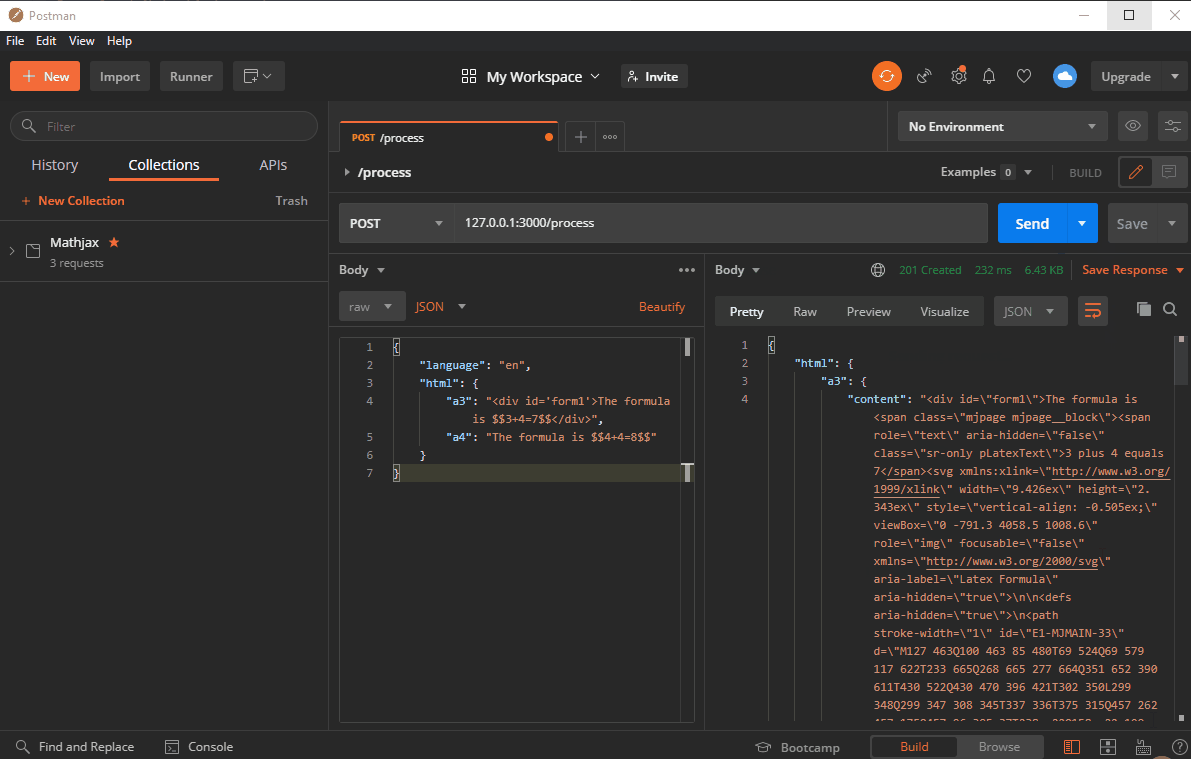
{ timeMS: value, errodCode: value, errorMsg: value, html: { "key1": { content: "...", errorMsg: null }, "key2": { content: "...", errorMsg: null }, "key3": { content: null, errorMsg: [...] }, ... } }timeMS-attribute:
the value will contain information about the serverside processing time.
errorMsg-attribute:
the attribute will contain an error message, describing an error which occured during processing the whole package.
the attribute will be null if no error occured.
errorCode-attribute:
the attribute will contain an error code, describing an error which occured during processing the whole package.
the attribute will be null if no error occured.
html-attribute (null if an error occured, while processing the whole package):
If no error occured during processing and validating the whole package this attribute will contain a list of objects.
Each object represents a failed or successfull rendering of the refering HTML-input string.
Each object's key equals the key of the related HTML-input string. Each object contains a content-attribute and an errorMsg-Attribute.
If no error occured during rendering the related input string, the output-object's content-attribute will contain a HTML-string while the errorMsg-Attribute will contain a null-value.
If an error occured during rendering the related input string, the output-object's content-value will be set to null while the errorMsg will contain an array of strings, describing the error(s).
If no error occured the rendered strings can be accessed with output.html.key.content.... In this case the content string must be unescaped, e.g with decodeURI().
-
curl --location --request GET '127.0.0.1:3000/hello'
- http://127.0.0.1 If run on localhost
- :3000
the application Port. Please refer Installation 4.3 - /hello
Process route. Please refer Endpoints
curl -X POST \
http://127.0.0.1:3000/process \
-H 'API-Key: apikey' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'cache-control: no-cache' \
-d '{"language":"en", "html":{"key1":"value1","key2":"value2","key3":"value3"}}'
- http://127.0.0.1 If run on localhost
- :3000
the application Port. Please refer Installation 4.3 - /process
Process route. Please refer Endpoints - apikey
Your secret API Key, as defined by an administrator inmodules/config.js(refer to Installation 4.1) Used to authenticate the client. - html
Your escaped html content strings which will be processed individually.
- LaTeX delimiters can be
\(and\)or\[and\] - Make sure that your requests body content type is set to JSON
- Remember that the following characters are reserved for JSON and must be escaped within your requests body.
- Backspace is replaced with \b
- Form feed is replaced with \f
- Newline is replaced with \n
- Carriage return is replaced with \r
- Tab is replaced with \t
- Double quote is replaced with \"
- Backslash is replaced with \\
- Apply TLS support:
Currently TLS is not used in this prototype. Add TLS support. - Validate requests:
Requests from the client must be validated. - Prevent brute-force attacks against authorization:
Add mechanics to limit the number of requests.
The point of this application is to provide a service which
- converts plain LaTeX syntax into rendered (SVG) formulas
- and also includes invisible MathML & Speaktext to the output.
The MathJax-Node-Accessibility-Demo is a Node.js application that receives and processes/answers POST-requests: This POST-requests contain
- a header which includes an api-key attribute-value pair which will be used to verify the client before further processing.
- a body (JSON) containing strings stored in induvial keys: each string consists of plain HTML combined with raw LaTeX. These strings are the main part of the whole service and are later used as individual inputs for further processing.
A client sends a request to the endpoint "/process" containing the header and body information as mentioned in "Summary".
If the header api-key has been validated successfully the body is validated for correct structure. If the seconds validation also is successful the procedure goes on with the actual processing:
Each key's value of the body's JSON is used as input and for each of these values an output consisting of a SVG, invisible MathML and Speaktext is generated. Once this step has ended successfully the application will send a response to the client containing the output data.
The service is seperated in several modules. Following modules are called in order with each request:
| Step | Fil | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1.APP.post( '/process' ... | server.js | The request is being received. The procedure starts here. |
| 2.TIMER.start | modules/timer.js | Starts a timer to check the request's processing time. The timer is later stopped before each response. |
| 3.ACCESSOR.verifyApiKey | modules/accessor.js | Checks if the api-key delivered with the request-header is correct and immediately quits/sends a response if this test fails. |
| 4.VALIDATOR.validate | modules/validator.js | Checks if the data provided with the request-body is valid and immediately quits/sends a response if this test fails. |
| 5.PROCESSOR.processRequest | modules/processor.js | Processes the actual body. The keys are seperately handled each key is being processed in an individual promise. After processing is complete a response is being sent. If a general error occurs during processing the process immediately quits and a response is being sent to the client. |
The LOGGER.logfile module which is not listed in this list, is called independently at different places of the whole code structure. It's main function is to log certain events, such as errors or general information.
After the code has been committed, Werner Schnedl werner.schnedl@id.ethz.ch will test the changes made. If the newest commit has been tested as successful the DockerSetup.zip also needs to be updated and uploaded to the repository. Michael Odermatt michael.odermatt@let.ethz.ch will update the MathJax Node Service to our systems.