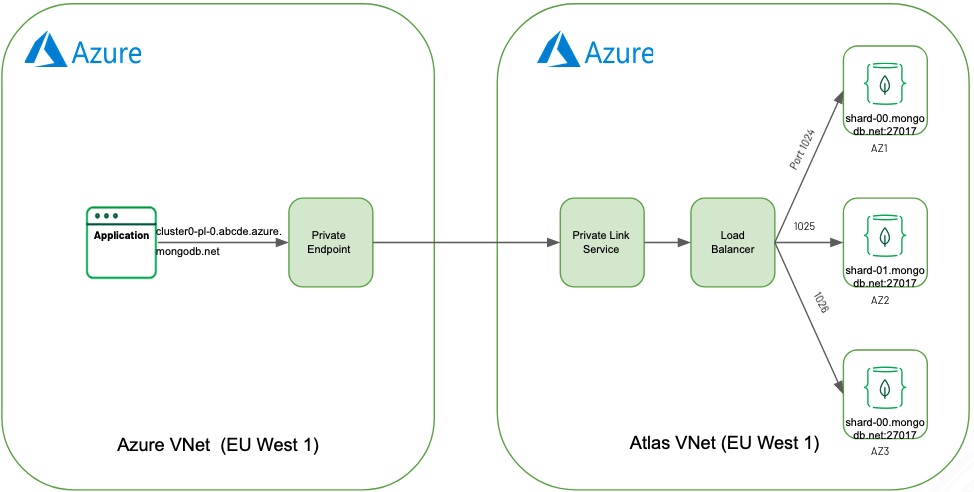
Based on an small Proof of Concept to make Atlas available via Private endpoint in Azure in the same region, this script automates all steps. The documentation on how to do this manually: https://docs.atlas.mongodb.com/security-private-endpoint
The end result of the Terraform script is a project in Atlas + a Cluster + provisioned user, private linked to Azure with a 1 vm with public interface (ssh/key). The vm has already MongoDB client tools installed.
- Authenticate into Azure via CLI with: az login
- Have Terraform 0.13+ installed
- Run: terraform init
Initializing provider plugins...
- Checking for available provider plugins...
- Downloading plugin for provider "azurerm" (hashicorp/azurerm) 2.1.0...
- Downloading plugin for provider "mongodbatlas" (terraform-providers/mongodbatlas) 0.8
- Set up credential, as in section: "Configure Script - Credentials"
- Change basic parameters, as in file : locals.tf
- Run: terraform apply
- Test with terrafrom 14.
- mongodbatlas_project, creates an empty project in your Atlas account
- mongodbatlas_privatelink_endpoint, create privatelink endpoint
- mongodbatlas_privatelink_endpoint_service, create private link service in Atlas
- mongodbatlas_private_ip_mode, switches new project to private IP mode so it can be used for peering
- azurerm_resource_group, create a Azure resource group to hold vnet and other resources
- azurerm_virtual_network, create a Azure Virtual Network to peer into
- azurerm_private_endpoint, creates the endpoint in Azure
- azurerm_subnet,
- azurerm_public_ip,
- azurerm_network_security_group,
- azurerm_network_interface,
- azurerm_network_interface_security_group_association,
- azurerm_linux_virtual_machine,
- mongodbatlas_advanced_cluster, finally create cluster
To configure the providers, such as Atlas and Azure, one needs credentials to gain access. In case of MongoDB Atlas a public and private key pair is required. How to create an API key pair for an existing Atlas organization can be found here: https://docs.atlas.mongodb.com/configure-api-access/#programmatic-api-keys These keys are read in environment variables for safety. Alternatively these parameters can be provide on the command line of the terraform invocation. The MONGODBATLAS provider will read the 2 distinct variable, as below:
- MONGODB_ATLAS_PUBLIC_KEY=
- MONGODB_ATLAS_PRIVATE_KEY=
Second a Azure subscription is required. The primary attributes are also expected as environment variables. Values need to be provided in TF_VAR_ format.
- TF_VAR_azure_subscription_id=<SUBSCRIPTION_ID>
- TF_VAR_azure_tenant_id=<DIRECTORY_ID>
Third there are several other parameters that are trusted, which should be provided via environment variables.
variable "atlas_organization_id" {
description = "Atlas organization id where to create project & link & project"
type = string
}
variable "azure_subscription_id" {
description = "Azure subscription for peering with ..."
type = string
}
variable "azure_tenant_id" {
description = "Azure subscription Directory ID"
type = string
}
variable "public_key_path" {
description = "Access path to public key"
type = string
}
variable "private_key_path" {
description = "Access path to private key"
type = string
}
variable "admin_password" {
description = "Generic password for demo resources"
type = string
}
variable "source_ip" {
description = "Limit vm access to this ip_address"
type = string
}
In the locals resource of the locals.tf file, several parameters should be adapted to your needs
locals {
# New empty Atlas project name to create in organization
project_id = "Azure-Linked-Project"
# Atlas region, https://docs.atlas.mongodb.com/reference/microsoft-azure/#microsoft-azure
region = "EUROPE_WEST"
# Atlas cluster name
cluster_name = "Sample"
# Atlas Public providor
provider_name = "AZURE"
# Provider Region
provider_region = "westeurope"
# A Azure resource group
resource_group_name = "atlas-demo-link"
# Associated Azure vnet
vnet_name = "atlas-link-vnet"
# Azure location
location = "West Europe"
# Azure cidr block for vnet
address_space = ["10.12.4.0/23"]
# Azure subnet in vnet
subnet = "subnet2"
# Azure subnet cidr
subnet_address_space = "10.12.4.192/26"
# Azure vm admin_user
admin_username = "testuser"
# Azure vm size
azure_vm_size = "Standard_F2"
# Azure vm_name
azure_vm_name = "demo-link"
}
terraform {
required_version = ">= 0.13.5"
}
In you favorite shell, run terraform apply and review the execution plan on what will be added, changed and detroyed. Acknowledge by typing: yes
%> terraform apply
Your final result should look like:
Apply complete! Resources: 0 added, 0 changed, 0 destroyed.
Outputs:
atlasclusterstring = mongodb+srv://sample-pl-0.xrbqa.mongodb.net
public_ip_address = 42.71.150.20
user1 = testuser
>$ ssh testuser@42.71.150.20
...
Last login: Mon Feb 8 09:47:34 2021 from **************************
testuser@demo-link:~$ mongo mongodb+srv://sample-pl-0.xrbqa.mongodb.net --username testuser
MongoDB shell version v4.4.3
Enter password:
connecting to: mongodb://pl-0-westeurope-azure.xrbqa.mongodb.net:1026,pl-0-westeurope-azure.xrbqa.mongodb.net:1025,pl-0-westeurope-azure.xrbqa.mongodb.net:1024/?authSource=admin&compressors=disabled&gssapiServiceName=mongodb&replicaSet=atlas-zmjsri-shard-0&ssl=true
Implicit session: session { "id" : UUID("8ee43f82-3da4-41c7-a36a-3baf93ca7464") }
MongoDB server version: 4.2.12
WARNING: shell and server versions do not match
MongoDB Enterprise atlas-zmjsri-shard-0:PRIMARY>
- let me know