KoboldCpp is an easy-to-use AI text-generation software for GGML and GGUF models. It's a single self contained distributable from Concedo, that builds off llama.cpp, and adds a versatile Kobold API endpoint, additional format support, Stable Diffusion image generation, backward compatibility, as well as a fancy UI with persistent stories, editing tools, save formats, memory, world info, author's note, characters, scenarios and everything Kobold and Kobold Lite have to offer.
- Download the latest .exe release here or clone the git repo.
- Windows binaries are provided in the form of koboldcpp.exe, which is a pyinstaller wrapper for a few .dll files and koboldcpp.py. You can also rebuild it yourself with the provided makefiles and scripts.
- Weights are not included, you can use the official llama.cpp
quantize.exeto generate them from your official weight files (or download them from other places such as TheBloke's Huggingface. - To run, simply execute koboldcpp.exe.
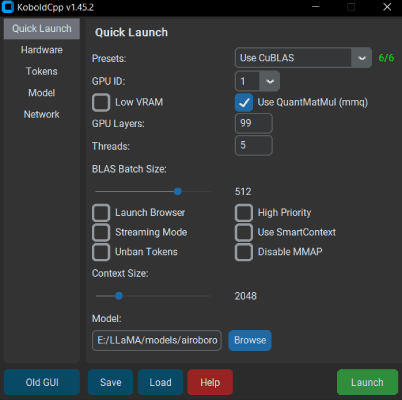
- Launching with no command line arguments displays a GUI containing a subset of configurable settings. Generally you dont have to change much besides the
PresetsandGPU Layers. Read the--helpfor more info about each settings. - By default, you can connect to http://localhost:5001
- You can also run it using the command line. For info, please check
koboldcpp.exe --help
- (Nvidia Only) GPU Acceleration: If you're on Windows with an Nvidia GPU you can get CUDA support out of the box using the
--usecublasflag, make sure you select the correct .exe with CUDA support. - Any GPU Acceleration: As a slightly slower alternative, try CLBlast with
--useclblastflags for a slightly slower but more GPU compatible speedup. - GPU Layer Offloading: Want even more speedup? Combine one of the above GPU flags with
--gpulayersto offload entire layers to the GPU! Much faster, but uses more VRAM. Experiment to determine number of layers to offload, and reduce by a few if you run out of memory. - Increasing Context Size: Try
--contextsize 4096to 2x your context size! without much perplexity gain. Note that you'll have to increase the max context in the Kobold Lite UI as well (click and edit the number text field). - If you are having crashes or issues, you can try turning off BLAS with the
--noblasflag. You can also try running in a non-avx2 compatibility mode with--noavx2. Lastly, you can try turning off mmap with--nommap.
For more information, be sure to run the program with the --help flag, or check the wiki.
- KoboldCpp now has an official Colab GPU Notebook! This is an easy way to get started without installing anything in a minute or two. Try it here!.
- Note that KoboldCpp is not responsible for your usage of this Colab Notebook, you should ensure that your own usage complies with Google Colab's terms of use.
On Linux, we provide a koboldcpp-linux-x64-cuda1150 PyInstaller prebuilt binary on the releases page for modern systems. Simply download and run the binary.
Alternatively, you can also install koboldcpp to the current directory by running the following terminal command:
curl -fLo koboldcpp https://github.com/LostRuins/koboldcpp/releases/latest/download/koboldcpp-linux-x64-cuda1150 && chmod +x koboldcpp
After running this command you can launch Koboldcpp from the current directory using ./koboldcpp in the terminal (for CLI usage, run with --help).
when you can't use the precompiled binary directly, we provide an automated build script which uses conda to obtain all dependencies, and generates (from source) a ready-to-use a pyinstaller binary for linux users. Simply execute the build script with ./koboldcpp.sh dist and run the generated binary. (Not recomended for systems that already have an existing installation of conda. Dependencies: curl, bzip2)
./koboldcpp.sh # This launches the GUI for easy configuration and launching (X11 required).
./koboldcpp.sh --help # List all available terminal commands for using Koboldcpp, you can use koboldcpp.sh the same way as our python script and binaries.
./koboldcpp.sh rebuild # Automatically generates a new conda runtime and compiles a fresh copy of the libraries. Do this after updating Koboldcpp to keep everything functional.
./koboldcpp.sh dist # Generate your own precompiled binary (Due to the nature of Linux compiling these will only work on distributions equal or newer than your own.)
-
Otherwise, you will have to compile your binaries from source. A makefile is provided, simply run
make. -
If you want you can also link your own install of OpenBLAS manually with
make LLAMA_OPENBLAS=1 -
If you want you can also link your own install of CLBlast manually with
make LLAMA_CLBLAST=1, for this you will need to obtain and link OpenCL and CLBlast libraries.- For Arch Linux: Install
cblasopenblasandclblast. - For Debian: Install
libclblast-devandlibopenblas-dev.
- For Arch Linux: Install
-
You can attempt a CuBLAS build with
LLAMA_CUBLAS=1. You will need CUDA Toolkit installed. Some have also reported success with the CMake file, though that is more for windows. -
For a full featured build (all backends), do
make LLAMA_OPENBLAS=1 LLAMA_CLBLAST=1 LLAMA_CUBLAS=1 LLAMA_VULKAN=1 -
After all binaries are built, you can run the python script with the command
koboldcpp.py [ggml_model.bin] [port] -
Note: Many OSX users have found that the using Accelerate is actually faster than OpenBLAS. To try, you may wish to run with
--noblasand compare speeds.
There are some community made AUR packages (Maintained by @AlpinDale) available: CUBLAS, and HIPBLAS. They are intended for users with NVIDIA GPUs, and users with a supported AMD GPU. Note that these packages may be outdated, and it's probably better to use official KoboldCpp binaries.
- You're encouraged to use the .exe released, but if you want to compile your binaries from source at Windows, the easiest way is:
- Use the latest release of w64devkit (https://github.com/skeeto/w64devkit). Be sure to use the "vanilla one", not i686 or other different stuff. If you try they will conflit with the precompiled libs!
- Make sure you are using the w64devkit integrated terminal, then run 'make' at the KoboldCpp source folder. This will create the .dll files.
- If you want to generate the .exe file, make sure you have the python module PyInstaller installed with pip ('pip install PyInstaller').
- Run the script make_pyinstaller.bat at a regular terminal (or Windows Explorer).
- The koboldcpp.exe file will be at your dist folder.
- If you wish to use your own version of the additional Windows libraries (OpenCL, CLBlast and OpenBLAS), you can do it with:
- OpenCL - tested with https://github.com/KhronosGroup/OpenCL-SDK . If you wish to compile it, follow the repository instructions. You will need vcpkg.
- CLBlast - tested with https://github.com/CNugteren/CLBlast . If you wish to compile it you will need to reference the OpenCL files. It will only generate the ".lib" file if you compile using MSVC.
- OpenBLAS - tested with https://github.com/xianyi/OpenBLAS .
- Move the respectives .lib files to the /lib folder of your project, overwriting the older files.
- Also, replace the existing versions of the corresponding .dll files located in the project directory root (e.g. libopenblas.dll).
- You can attempt a CuBLAS build with using the provided CMake file with visual studio. If you use the CMake file to build, copy the
koboldcpp_cublas.dllgenerated into the same directory as thekoboldcpp.pyfile. If you are bundling executables, you may need to include CUDA dynamic libraries (such ascublasLt64_11.dllandcublas64_11.dll) in order for the executable to work correctly on a different PC. - Make the KoboldCPP project using the instructions above.
- Install and run Termux from F-Droid
- Enter the command
termux-change-repoand chooseMirror by BFSU - Install dependencies with
pkg install wget git python(plus any other missing packages) - Install dependencies
apt install openssl(if needed) - Clone the repo
git clone https://github.com/LostRuins/koboldcpp.git - Navigate to the koboldcpp folder
cd koboldcpp - Build the project
make - Grab a small GGUF model, such as
wget https://huggingface.co/concedo/KobbleTinyV2-1.1B-GGUF/resolve/main/KobbleTiny-Q4_K.gguf - Start the python server
python koboldcpp.py --model KobbleTiny-Q4_K.gguf - Connect to
http://localhost:5001on your mobile browser - If you encounter any errors, make sure your packages are up-to-date with
pkg up - GPU acceleration for Termux may be possible but I have not explored it. If you find a good cross-device solution, do share or PR it.
- Please check out https://github.com/YellowRoseCx/koboldcpp-rocm
- The official docker can be found at https://hub.docker.com/r/koboldai/koboldcpp
- KoboldCpp also has a few unofficial third-party community created docker images. Feel free to try them out, but do not expect up-to-date support:
- If you're building your own docker, remember to set CUDA_DOCKER_ARCH or enable LLAMA_PORTABLE
- First, please check out The KoboldCpp FAQ and Knowledgebase which may already have answers to your questions! Also please search through past issues and discussions.
- If you cannot find an answer, open an issue on this github, or find us on the KoboldAI Discord.
- For Windows: No installation, single file executable, (It Just Works)
- Since v1.0.6, requires libopenblas, the prebuilt windows binaries are included in this repo. If not found, it will fall back to a mode without BLAS.
- Since v1.15, requires CLBlast if enabled, the prebuilt windows binaries are included in this repo. If not found, it will fall back to a mode without CLBlast.
- Since v1.33, you can set the context size to be above what the model supports officially. It does increases perplexity but should still work well below 4096 even on untuned models. (For GPT-NeoX, GPT-J, and LLAMA models) Customize this with
--ropeconfig. - Since v1.42, supports GGUF models for LLAMA and Falcon
- Since v1.55, lcuda paths on Linux are hardcoded and may require manual changes to the makefile if you do not use koboldcpp.sh for the compilation.
- Since v1.60, provides native image generation with StableDiffusion.cpp, you can load any SD1.5 or SDXL .safetensors model and it will provide an A1111 compatible API to use.
- I plan to keep backwards compatibility with ALL past llama.cpp AND alpaca.cpp models. But you are also encouraged to reconvert/update your models if possible for best results.
- The original GGML library and llama.cpp by ggerganov are licensed under the MIT License
- However, Kobold Lite is licensed under the AGPL v3.0 License
- The other files are also under the AGPL v3.0 License unless otherwise stated
- Generation delay scales linearly with original prompt length. If OpenBLAS is enabled then prompt ingestion becomes about 2-3x faster. This is automatic on windows, but will require linking on OSX and Linux. CLBlast speeds this up even further, and
--gpulayers+--useclblastor--usecublasmore so. - I have heard of someone claiming a false AV positive report. The exe is a simple pyinstaller bundle that includes the necessary python scripts and dlls to run. If this still concerns you, you might wish to rebuild everything from source code using the makefile, and you can rebuild the exe yourself with pyinstaller by using
make_pyinstaller.bat - API documentation available at
/apiand https://lite.koboldai.net/koboldcpp_api - Supported GGML models (Includes backward compatibility for older versions/legacy GGML models, though some newer features might be unavailable):
- All up-to-date GGUF models are supported (Mistral/Mixtral/QWEN/Gemma and more)
- LLAMA and LLAMA2 (LLaMA / Alpaca / GPT4All / Vicuna / Koala / Pygmalion 7B / Metharme 7B / WizardLM and many more)
- GPT-2 / Cerebras
- GPT-J
- RWKV
- GPT-NeoX / Pythia / StableLM / Dolly / RedPajama
- MPT models
- Falcon (GGUF only)
- Stable Diffusion and SDXL models