concourse-gitlab-flow
This repository has two concourse pipeline examples supporting two Gitlab flow model below:
Production branch with GitLab flow
Production branch with Gitlab flow assumes two major branches.
mainbranch: This branch is for tracking production 'grade' code, it can be seen as release candidates. Not as github flow, master branch is not for tracking production codes.- features branch: as standard git flow and github flow, this is for developing each feature and will be merged to master.
productionbranch: This is the branch for tracking production code. Every commit on the branch will be shipped to the production environment.
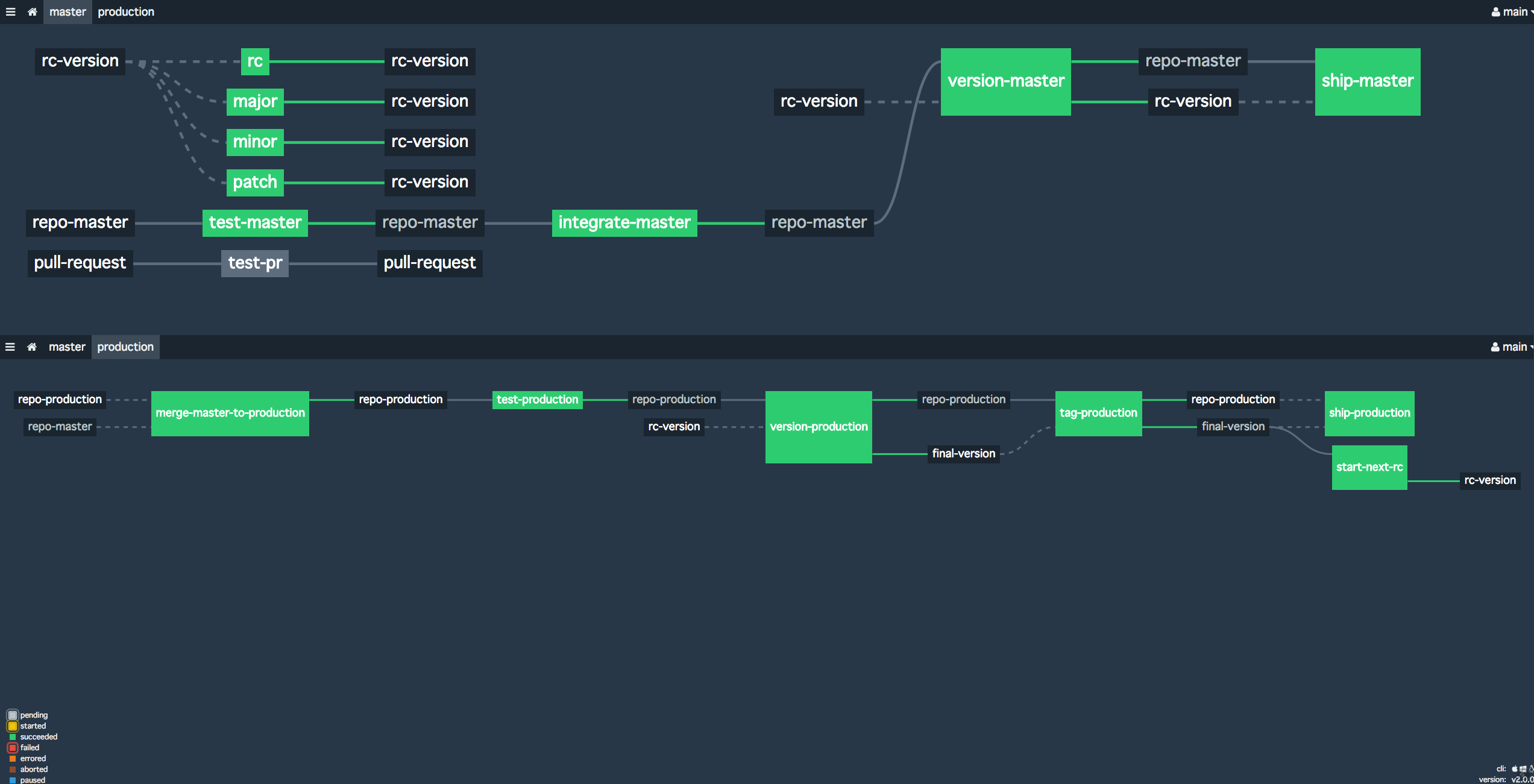
Concourse pipeline to support "Production branch with Gitlab flow"
2-envs.yml supports that:
- Semantic versioning by semver-resource
- Continuous Integration(CI) for pull requests.
- Continuous Deployment(CD) of
masterbranch- deployment to
stagingenvironment bumps release candidate version (stored inrc-versionresource)- release candidate version will be of the form
x.y.z-rc.n
- release candidate version will be of the form
- deployment to
- CI/CD of
productionbranchmerge-master-to-productionjob is the trigger to start deployment to production.- Succeeding jobs performs CI/CD
version-productionjob always computes final version fromrc-versionresource and stores it tofinal-versionresource.- If release candidate version was
x.y.z-rc.n, final version will bex.y.z start-next-rcis executed aftertag-production. This stores next release candidate version torc-versionresource.- If
x.y.zwill be tagged,start-next-rcbumped patch version. i.e. in this case, next release candidate version will bex.y.(z+1)-dev.1 - Team can manually bump minor/major version when big changes happened on master branch.
- If
- tagging commits and actual shipment jobs are separated. This enables you to ship the latest commit on production branch to production environment without bumping versions. This would be useful for deployment failure or network issues.
Please note that this pipeline does NOT support hotfix-ing on production branch. This means you need to commits those fixes to master branch and start over release process. See 2-envs.yml for implementation details.
Environment branches with GitLab flow
In Environment branches with GitLab flow, it assumes three environment. They are staging, pre-production, production environments. It also assumes git repository have three major branches whose are corresponding to environments. Please note that master branch is the only branch whose name is different from environment name.
mainbranch: This branch is for tracking codes which are deployed continuously tostagingenvironment.- features branch: as standard git flow and github flow, this is for developing each feature and will be merged to master.
pre-productionbranch: This branch if for tracking codes which are deployed topre-productionenvironment. Every commit on the branch will be shipped to the pre-production environment. These shipment can be seen as release candidates.produtionbranch: This is the branch for tracking production code. Every commit on the branch will be shipped to the production environment.
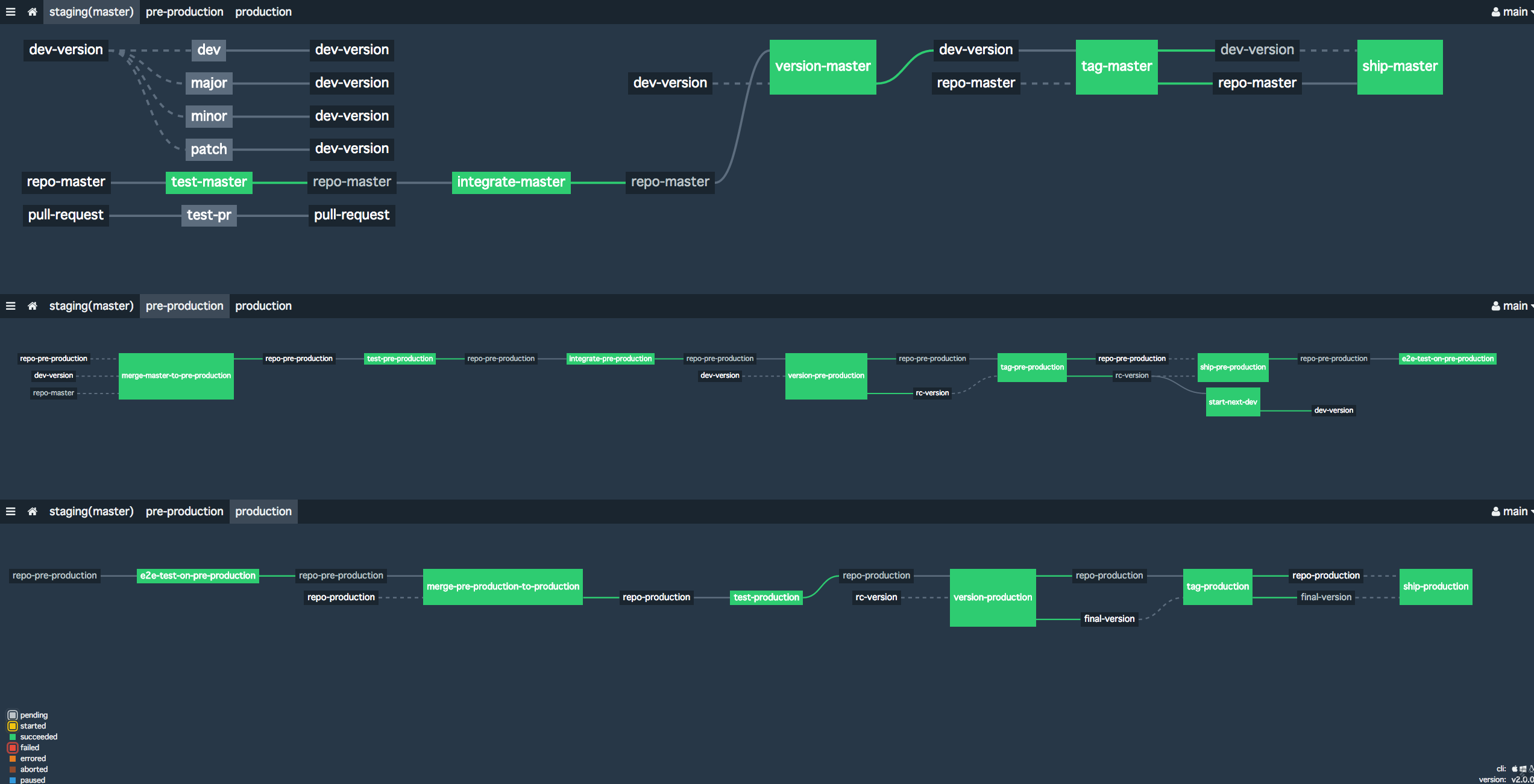
Concourse pipeline to support "Environment branches with Gitlab flow"
3-envs.yml supports that:
- Semantic versioning by semver-resource
- Continuous Integration(CI) for pull requests.
- Continuous Deployment(CD) to
stagingenvironment of master branch.- deployment to
stagingenvironment bumps development version (dev-versionresource)- development version will be of the form
x.y.z-dev.n
- development version will be of the form
- deployment to
- CI/CD of
pre-productionbranchmerge-master-to-pre-productionjob is the trigger to start deployment topre-productionenvironment.- Succeeding jobs performs CI/CD to
pre-productionenvironment. version-pre-productionjob always computes release candidate version fromdev-versionresource and stores it torc-versionresource.- If development version was
x.y.z-dev.n, release candidate version will bex.y.z-rc.1 start-next-devis executed aftertag-pre-production. This stores next development version todev-versionresource.- If
x.y.z-rc.1will be tagged,start-next-devbumped patch version. Next dev version will bex.y.(z+1)-dev.1 - This means release candidate version will never be bumped to
rc.2. Team needs to fix commits on mater branch and start over CI/CD flow frommerge-master-to-pre-production - Team can manually bump patch/minor/master branch when big changes happened on master branch.
- If
e2e-test-on-pre-productionperforms end-to-end test onpre-productionenvironment. This would work as the final gate to promote pre-production branch to production branch.
- CI/CD of
productionbranch- When
e2e-test-on-pre-productionpassed, CI/CD process of production branch will be triggered automatically.merge-pre-production-to-productionwill be kicked. - Succeeding jobs performs CI/CD to
productionenvironment. version-productionjob always computes final version fromrc-versionresource and stores it tofinal-versionresource.- If release candidate version was
x.y.z-rc.1, final version will bex.y.z
- When
- tagging and actual shipment jobs are separated. This enables you to ship the latest commit on production branch to production environment without bumping versions. This would be useful for deployment failure or network issues.
Please note that this pipeline does NOT support hotfix-ing on pre-production and production branch. This means you need to commits those fixes to master branch and start over release process. See 3-envs.yml for detailed.