UPDATE: For official templates, please go to https://github.com/F5Networks/f5-aws-cloudformation repo: https://github.com/F5Networks/f5-aws-cloudformation/tree/master/supported/solutions/autoscale
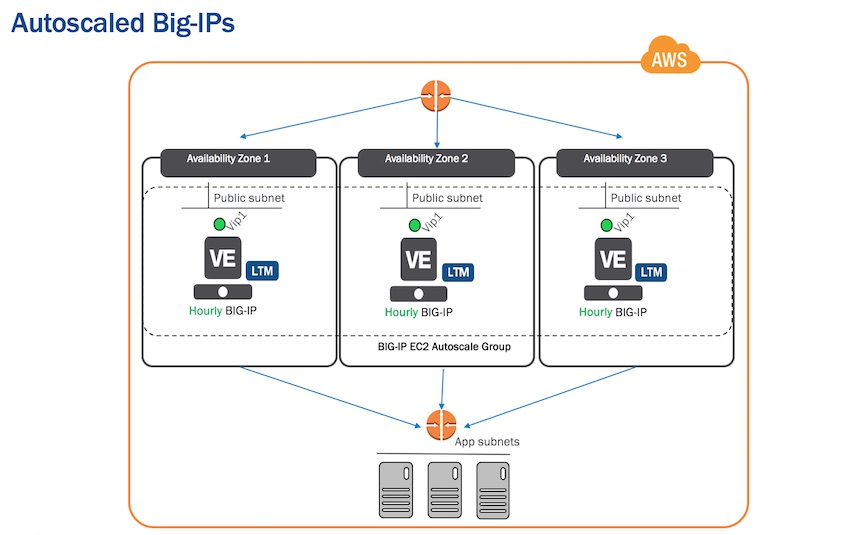
This project contains prototypes of CloudFormation templates which provide an example of how to deploy autoscale instances of BIG-IP in AWS. This project specifically demonstrates autoscaling the Big-IP tier where, as traffic increases, the number of BIG-IPs will increase.
These examples demonstrate leveraging cloudinit in the launch configs to provide the configuration for the autoscaled instances.
Another method is creating custom AMIs. For more information on that method, please see the official documentation on AskF5 (https://support.f5.com):
For service discovery, this example also demonstrates using Big-IPs FQDN Pools (which uses DNS to populate the pool members). For more information, please see:
Another service discovery method available is Big-IP's AWS Autoscale Pool Member Discovery feature:
The individual directories in the /deployments directory contain variations of an autoscaled deployment.
Ex.
L7 Proxy
Example virtual service has a simple URI routing policy. Deploys Big-IP Local Traffic Manager (LTM) images (License = Good).
- SSL-L7proxy-utility-only-immutable (uses DNS LB to distribute traffic to the Big-IPs)
- SSL-L7proxy-sandwich-utility-only-immutable (uses ELB to distribute traffic to the Big-IPs)
- SSL-L7proxy-sandwich-byol-and-utility-immutable (uses ELB to distribute traffic to the Big-IPs)
Web Application Firewall (WAF)
Example virtual service has a simple Web Application Firewall policy. Deploys Big-IP Application Security Manager (ASM) images (License = Best).
- SSL-waf-utility-only-immutable (uses DNS LB)
- SSL-waf-sandwich-utility-only-immutable (uses ELB)
- SSL-waf-sandwich-byol-and-utility-immutable (uses ELB)
Deployment Name Terms:
SSL = Example virtual service terminates SSL. It imports a PKS certificate from a remote location OR uses the default crt.
utility = Big-IP instances use hourly billing licensing.
byol = Deployment includes a Bring Your Own License (BYOL) instance. Requires having a Big-IP registration key. Contact your friendly F5 Account team for "Eval" keys.
immutable = Requires the Big-IP configuration to be managed via the launch config. Any config changes must be entered into the launch config and relaunched.
clustered The Big-IP configuration is managed by syncing the config from an existing member. Changes can be made in traditional operational method of logging into a Big-IP GUI.
For more details about each deployment, please see the README.md in each deployment type directory.
Quickstart: If this is your first time, recommend starting with the deployment below:
SSL-L7proxy-sandwich-utility-only-immutable
ex.
deployments/SSL-L7proxy-sandwich-utility-only-immutable/README.md
- Access to Big-IP images in the Amazon region within which you are working. Make sure that you have accepted the EULA for ALL images used in the AWS marketplace.
- Sign in to your account
- Go to product page for Big-IP selected
- Select "Continue"
- Hit "Accept Software Terms"
Note: If you do not Accept the EULA in the Marketplace, the cloudformation templates may appear to hang (please see events EVENTs tab for information as to why the templates did not "complete")
- Set of AWS Access Keys for use by the BIG-IP, as described here:
These keys will be used to send authenticated messages to AWS (ex. cloudwatch metrics).
ex. The user whose keys are being used should have following policy attached:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"cloudwatch:PutMetricData"
],
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}
-
OPTIONAL: Upload a certificate to a private S3 bucket that the those aws keys have permisson to. Otherwise, the "default" certificate on the Big-IP will be used (recommended for first time). For more information about managing SSL certificates, see the README.md in each deployment type directory (ex. /deployments/deployment_type/README.md).
-
OPTIONAL - If you use the deploy_stacks.py python script per instructions below:
- Install yaml and boto3
pip install pyyaml
pip install boto3
- You will need an AWS Access Key and Secret Access key configured in boto's typical credential locations, ex. ~/.aws/credentials or environment vars like AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID, with appropriate permissions to create all the EC2 objects
To use this example code, you may either
- manually launch the CloudFormation templates directly or
- use the deploy_stacks.py script (recommended).
-
Go to the Cloudformation page of the AWS console. Select "Create Stack"
-
Choose "Upload a template to Amazon S3" and navigate to the cft directory of the deployment you would like launch.
ex. Recommend:
deployments/SSL-L7proxy-sandwich-utility-only-immutable/cfts
Launch the following CFTs in the following order:
-
common.template
-
application.template
-
autoscale-bigip.template
-
byol-bigip.template (if deployment type contains it)
-
ubuntu-client.template ( Optional )
DISCLAIMER: the reference diagram above shows three Availability Zones to further illustrate scale-out. However, many regions only contain two Availibility Zones so common template creates VPC with two zones.
This ordering is necessary because "output" values from previous templates are used as "input" parameters for later templates. Note that "output" variables names are the same for all matching input parameters. For example, the outputs from the common.template include vpc, subnets, availabilityZones, bigipSecurityGroup, etc. so when creating later templates, you should "copy" some outputs from previous templates and "paste" them into input parameters of the next.
Although this method may allow you to develop a deeper understanding of the autoscaled deployments, due to numerous inputs and outputs, it is more error prone.
This will be the easiest and least error prone method by far. The script will launch each of the CloudFormation templates in the correct order.
To use this script:
- Clone or download this repoistory to a secure host running this python script and confirm the prerequisite libraries mentioned above (boto3 and pyyaml) are installed.
Note: If you have never used boto before, type "aws configure" to enter your AWS credentials. That will populate ~/.aws/credentials.
If you don't have access to a host with with these libraries, as a further convenience, we have also included cloud formation templates in this directory which launch an ubuntu host that downloads all the necessary libraries, clones this repository, etc.
Requirements: This automation host requires sufficient admin privledges to provision the AWS resources mentioned in this deployment. AWS does not recommend using AWS Access/Secret Keys on instances in AWS and using IAM roles instead.
With IAM role:
These templates also create and apply an IAM Role ( based on the AWS example "AmazonEC2FullAccess" policy ) to give the automation host the necessary privledges.
Without IAM role:
If you would like create a more restricted custom IAM role (recommended), you can launch a template below and attach the IAM role to the instance post deployment (ex. Instance -> Instance Settings -> Attach/Replace IAM role).
After launch, go to the output tab of the cloudformation template, obtain the publicIP or publicDNS, ssh to the host:
ssh -i ~/.ssh/YOUR-AWS-KEY.pem ubuntu@X.X.X.X
Disclaimer: The host needs a few minutes to build. When complete, your login should have the virtualenv (venv) setup and prompt should look like:
(venv) ubuntu@ip-10-0-0-115:~$
Otherwise, wait a little bit longer and re-login.
- Find config.yaml.example located in the top directory of the repository, copy this to a new file named "config.yaml" ( which is excluded in .gitignore to avoid publishing credentials ).
cd f5-aws-autoscale
cp config.yaml.example config.yaml
In this config.yaml file, use the editor of your choice to configure the variables for your scenario.
If you didn't deploy the optional automation host above, the last flag in the script 'deploy_jmeter_host' should be given a value of 'true' if you wish to test scale out using JMeter as documented below.
- Then run the script:
python ./deploy_stacks.py -d <deployment_type>
ex.
$python deploy_stacks.py -d SSL-L7proxy-sandwich-utility-only-immutable
Use the output of the script and/or go the "Outputs" tab of each cloudformation template (after status = "CREATE_COMPLETE") to get login or additional information about the deployment.
To trigger a scale out event:
- Go to AWS Console. Go to EC2 -> Autoscale Groups. Select the autoscale group. Select the "Details" tab, hit "Edit" and adjust the "Desired" or "Min" values
or
for your convenience, you can use the JMeter script included with these examples to generate traffic:
- If you have launched the "automation-host" or "ubuntu-client" instance, copy or paste the simple_jmeter_load.xml file to the ubuntu host.
scp -i <path to key pair you provided in config.yaml> simple_jmeter_load.xml ubuntu@<ip address of the ubuntu instance>:/home/ubuntu
- SSH to it:
ssh -i <path to key pair you provided in config.yaml> ubuntu@<ip address of the ubuntu instance>
- Find and replace all instances of string "AUTOSCALE-DNS" in the simple_jmeter_load.xml script with the WIDEIP OR ELB name associated with your BIG-IP Autoscale group using editor of choice (ex. vim,nano, pico, sed, etc)
sed -i.bak 's/AUTOSCALE-DNS/<NEW_DNS_NAME>/g' simple_jmeter_load.xml
ex.
ubuntu@ip-10-0-1-232:~$ sed -i.bak 's/AUTOSCALE-DNS/gtm-wideip.example.com/g' simple_jmeter_load.xml
or
ubuntu@ip-10-0-1-232:~$ sed -i.bak 's/AUTOSCALE-DNS/BigipElasticLoadBalancer-1263232202.us-east-1.elb.amazonaws.com/g' simple_jmeter_load.xml
- Run the script from the Ubuntu host:
nohup jmeter -n -t simple_jmeter_load.xml &
To stop traffic
killall java
- A CloudWatch alarm will be triggered, and EC2 Autoscale will launch another BIG-IP instance.
Author: Alex Applebaum (a.applebaum@f5.com)