This is a Terraform/OpenTofu configuration to deploy an NGINXaaS for Azure instance into a UDF managed Azure account. Infrastructure prerequisites, the NGINXaaS instance itself, and an NGINX configuration are deployed though this config.
This document will use TF to refer to either Terraform or OpenTofu.
To stand up an instance, execute the following:
cd ~/udf-NGINXaaS-for-Azure
source ./populate_creds.sh
tofu init
tofu plan
tofu apply --var="configure=false" --auto-approve
./import_config.sh
tofu apply --auto-approvecd ~/udf-NGINXaaS-for-Azure
source ./populate_creds.sh
terraform init
terraform plan
terraform apply --var="configure=false" --auto-approve
./import_config.sh
terraform apply --auto-approveThe IP address of your NGINXaaS instance is provided as an output. Browse to
https://<ip_address>/ to see your changes in action.
This configuration is broken down into 5 modules:
-
Prerequisites: Deploys the Azure resources needed to deploy NGINXaaS for Azure:
- Public IP Address
- Virtual Network
- Subnet
- NSG
- User Assigned Managed Identity
-
Deployments: Deploys an NGINXaaS for Azure Instance
-
Certificates: Creates resources for using HTTPS:
- Deploys an Azure Key Vault
- Loads a certificate into that vault
- Creates a certificate resource in the NGINXaaS for Azure Instance
-
Configurations: Updates the configuration on the on the NGINXaaS instance to:
- Use HTTPS instead of HTTP
- Change the response from the the default location block
- Adds an additional location block for the
/apiendpoint
-
UDF Shortcuts: Convenience features for working in UDF:
- Creates HTTP and HTTPS shortcuts on the desktop to your deployment
- Creates redirects to your deployment accessible from the bookmarks bar in Chromium
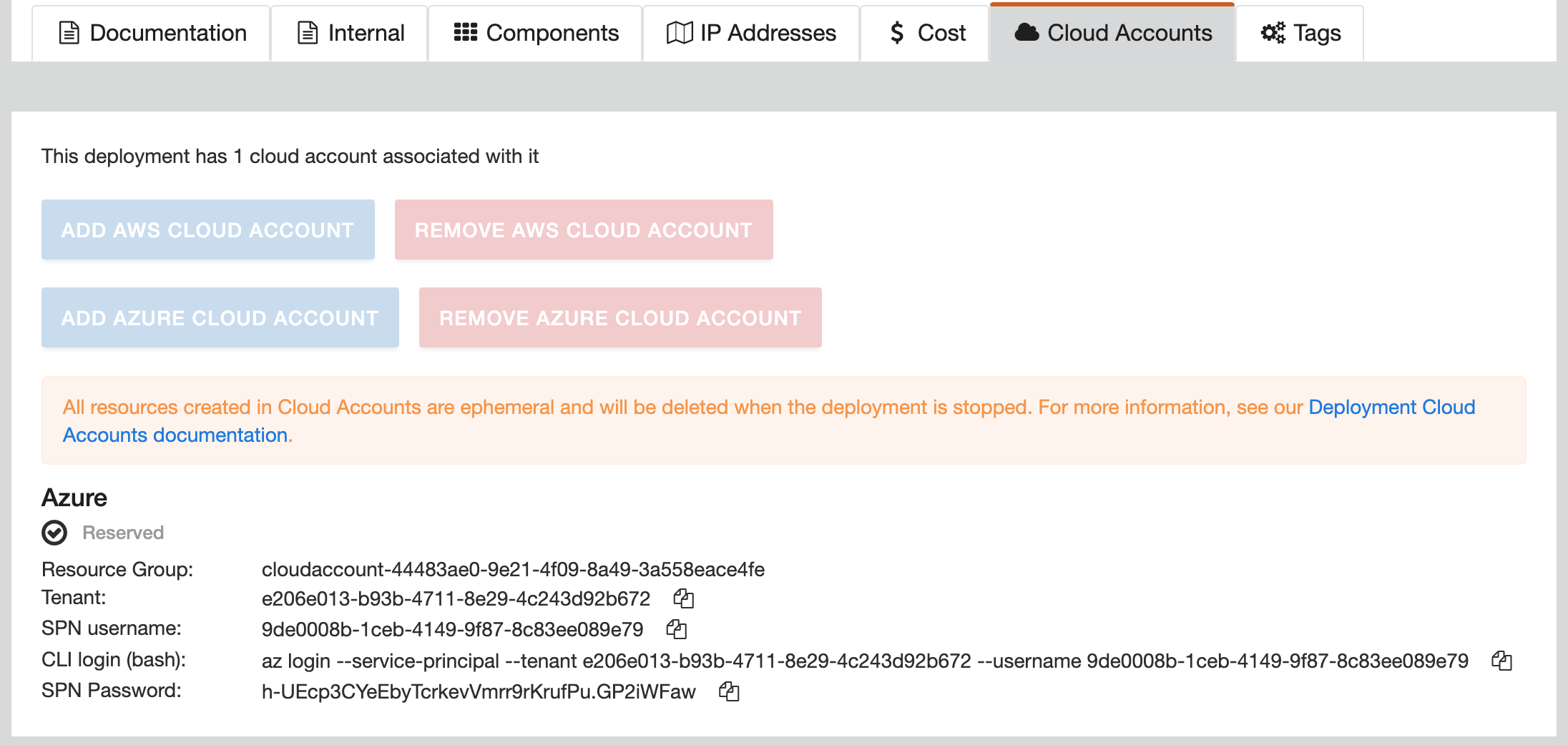
The TF Azure Resource Manager Provider requires credentials to your Azure subscription in order to manage Azure resources. In UDF, an ephemeral Azure account is created for you, and your credentials are available in the Cloud Accounts tab of your deployment:
You can also access your cloud account metadata from within UDF by accessing
the http://metadata.udf/cloudAccounts URL:
$ curl http://metadata.udf/cloudAccounts
{
"cloudAccounts": [
{
"resourceGroup": "cloudaccount-44483ae0-9e21-4f09-8a49-3a558eace4fe",
"credentials": [
{
"password": "h-UEcp3CYeEbyTcrkevVmrr9rKrufPu.GP2iWFaw",
"tenant": "e206e013-b93b-4711-8e29-4c243d92b672",
"username": "9de0008b-1ceb-4149-9f87-8c83ee089e79",
"type": "AZURE_API_CREDENTIAL"
}
],
"provider": "Azure"
}
]
}The azurerm provider needs to know your tenant ID, SPN username, and password. They can be passed as variables into the provider, or they can be set as the ARM_TENANT_ID, ARM_CLIENT_ID, and ARM_CLIENT_SECRET environment variables, respectively. Because your resource group is also created for you already, we also pass that into TF in the TF_VAR_resource_group_name
environment variable.
The azurerm provider also requires your subscription ID, which isn't included in the UDF metadata, but you can get it by logging in with the Azure CLI:
$ az login --service-principal --username $ARM_CLIENT_ID --password $ARM_CLIENT_SECRET --tenant $ARM_TENANT_ID
[
{
"cloudName": "AzureCloud",
"homeTenantId": "e206e013-b93b-4711-8e29-4c243d92b672",
"id": "614f0527-72db-4e40-adcc-e058a818cae9",
"isDefault": true,
"managedByTenants": [
{
"tenantId": "a21e903b-34f0-45e0-9f73-89c321eeab5b"
}
],
"name": "F5-AZR_1337_UDF_Prod",
"state": "Enabled",
"tenantId": "e206e013-b93b-4711-8e29-4c243d92b672",
"user": {
"name": "9de0008b-1ceb-4149-9f87-8c83ee089e79",
"type": "servicePrincipal"
}
}
]The id attribute contains your subscription ID, which can be passed to the azurerm provider in the ARM_SUBSCRIPTION_ID environment variable.
To simplify this process, there is a bash script that you can source into your shell that does all of the above for you:
$ source ./populate_creds.sh
Environment Variable | Value
============================+==================================================
TF_VAR_resource_group_name: | cloudaccount-44483ae0-9e21-4f09-8a49-3a558eace4fe
ARM_TENANT_ID: | e206e013-b93b-4711-8e29-4c243d92b672
ARM_CLIENT_ID: | 9de0008b-1ceb-4149-9f87-8c83ee089e79
ARM_CLIENT_SECRET: | <hidden>
ARM_SUBSCRIPTION_ID: | 614f0527-72db-4e40-adcc-e058a818cae9
Azure CLI logged inTo simplify it even further, if you are using the jumphost over RDP, there is a shortcut on the desktop that will open a new terminal window with these values already populated.
Running tofu init and tofu plan will show you the resources that TF is
about to create. See the What it does section for more
details.
At this point, you could simply run tofu apply, but if you do, you'll receive
an error from TF due to a known issue
with the TF provider. If you don't mind seeing the error you can go ahead and apply the configuration. If you'd rather skip the part of the configuration that throws the error, you can pass in the configure variable with a value of false:
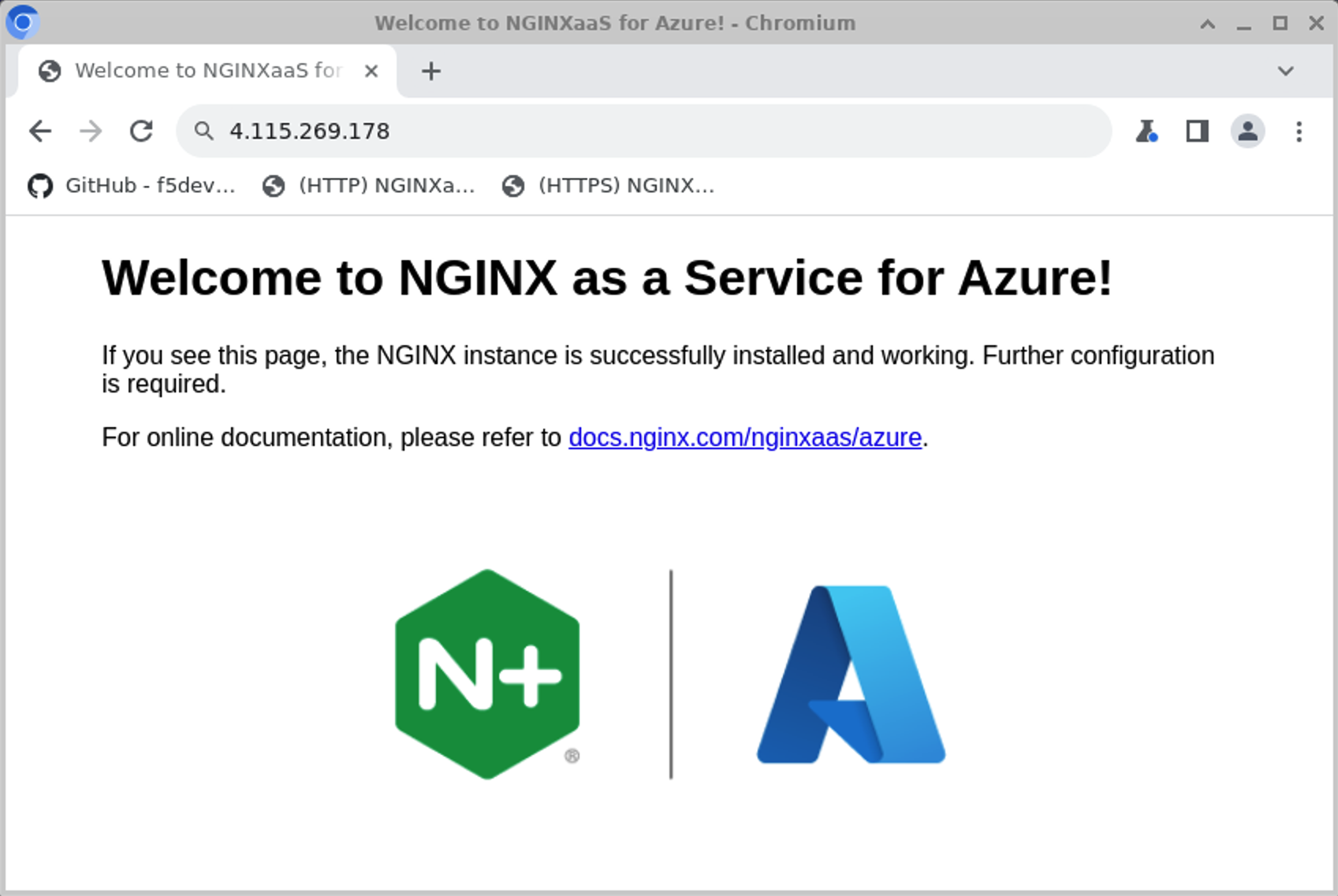
$ tofu apply -var="configure=false"Take a moment to look at the deployment before we apply a configuration. TF will output the IP address of your deployment. Browse to it (or use the http shortcut provided on the jumphost desktop), and you should see the default NGINXaaS for Azure landing page:
After the first apply attempt, you will need to import the default NGINX
configuration back into the TF state using the tofu import command. There is
a bash script, import_config.sh provided that will do this for you:
$ ./import_config.sh
Importing default NGINXaaS configuration into tofu state...
module.certificates.data.azurerm_client_config.current: Reading...
module.certificates.data.azurerm_client_config.current: Read complete after 0s [id=nqMHT6A4xWge0HQxP28K82xgTZZj5euqbxSD5L6WaLRhearNQiKzkHgpWmkAmb5mwXVvRCcJhUh2PT8W4QkegTt9HV2MuaVc12CxUMJcJJG45uWWRNZawZUyFaiuMHmiwGMF2NyyWwufk1h82ix3n7vVKfcrW8NgzdpJTjYAB7cJpuV9x3u1WFNvmwkm015EKgpD2Fwke85M8hS1rNkhRX4A5zJuHvHD3HufX2r7X8ZW9u5bTxzkLMzAMaVrQkYhcekbXGy6KiJNkYd=]
module.prerequisites.data.azurerm_resource_group.example: Reading...
module.prerequisites.data.azurerm_resource_group.example: Read complete after 0s [id=/subscriptions/614f0527-72db-4e40-adcc-e058a818cae9/resourceGroups/cloudaccount-44483ae0-9e21-4f09-8a49-3a558eace4fe]
module.configurations.azurerm_nginx_configuration.example[0]: Importing from ID "/subscriptions/614f0527-72db-4e40-adcc-e058a818cae9/resourceGroups/cloudaccount-44483ae0-9e21-4f09-8a49-3a558eace4fe/providers/Nginx.NginxPlus/nginxDeployments/example-nginx-9b7965b3fb/configurations/default"...
module.configurations.azurerm_nginx_configuration.example[0]: Import prepared!
Prepared azurerm_nginx_configuration for import
module.configurations.azurerm_nginx_configuration.example[0]: Refreshing state... [id=/subscriptions/614f0527-72db-4e40-adcc-e058a818cae9/resourceGroups/cloudaccount-44483ae0-9e21-4f09-8a49-3a558eace4fe/providers/Nginx.NginxPlus/nginxDeployments/example-nginx-9b7965b3fb/configurations/default]
Import successful!
The resources that were imported are shown above. These resources are now in
your OpenTofu state and will henceforth be managed by OpenTofu.
Re-run tofu apply to apply the new configurationNow you can re-run tofu apply (without the -var="configure=false" option),
and TF will apply the new configuration to your deployment. The NGINX config
files are located in the files/https directory; take a look at them and see what
they do.
Once the configuration is applied, try connecting to your instance again via HTTP. Your connection should fail, because the instance is now listening only for HTTPS. Change your browser to connect to https://<ip_address> (or use the https shortcut on the jumphost desktop), click past the certificate warning, and you should see the new "Hello world" page. Navigate to the /api endpoint to see the effect of the additional location block.
tofu destroy will tear down the entire configuration.
There are three factors that come together to cause issues with Key Vaults and ephemeral UDF accounts:
- Key Vault names are globally unique.
- Key Vaults are only soft-deleted when they are destroyed.
- Only subscription owners can purge a soft-deleted Key Vault before the retention period expires (minimum 7 days)
To prevent collisions from occurring between UDF deployments that don't change the default name, a random suffix is appended to the name variable used for all the resources created by this configuration. This suffix will change if you re-apply the configuration after destroying it, so that you don't collide with your own soft-deleted vault.
Ephemeral Azure accounts don't have access to the Azure Portal, but you can still use the Azure CLI to see what has been deployed in your tenant:
az resource list --output tableExample output
$ az resource list --output table
Name ResourceGroup Location Type Status
------------------------ ------------------------------------------------- ---------- ------------------------------------------------ --------
example-nginx-9b7965b3fb cloudaccount-44483ae0-9e21-4f09-8a49-3a558eace4fe westus2 Microsoft.KeyVault/vaults
example-nginx-9b7965b3fb cloudaccount-44483ae0-9e21-4f09-8a49-3a558eace4fe westus2 Microsoft.ManagedIdentity/userAssignedIdentities
example-nginx-9b7965b3fb cloudaccount-44483ae0-9e21-4f09-8a49-3a558eace4fe westus2 Microsoft.Network/networkSecurityGroups
example-nginx-9b7965b3fb cloudaccount-44483ae0-9e21-4f09-8a49-3a558eace4fe westus2 Microsoft.Network/publicIPAddresses
example-nginx-9b7965b3fb cloudaccount-44483ae0-9e21-4f09-8a49-3a558eace4fe westus2 Microsoft.Network/virtualNetworks
example-nginx-9b7965b3fb cloudaccount-44483ae0-9e21-4f09-8a49-3a558eace4fe westus2 Nginx.NginxPlus/nginxDeploymentsaz nginx deployment show \
--resource-group $TF_VAR_resource_group_name \
--deployment-name <NGINXaaS Deployment Name from TF output>Example output
$ az nginx deployment show --resource-group $TF_VAR_resource_group_name --deployment-name example-nginx-9b7965b3fb
{
"id": "/subscriptions/614f0527-72db-4e40-adcc-e058a818cae9/resourceGroups/cloudaccount-44483ae0-9e21-4f09-8a49-3a558eace4fe/providers/Nginx.NginxPlus/nginxDeployments/example-nginx-9b7965b3fb",
"identity": {
"type": "UserAssigned",
"userAssignedIdentities": {
"/subscriptions/614f0527-72db-4e40-adcc-e058a818cae9/resourceGroups/cloudaccount-44483ae0-9e21-4f09-8a49-3a558eace4fe/providers/Microsoft.ManagedIdentity/userAssignedIdentities/example-nginx-9b7965b3fb": {
"clientId": "b95361c0-bb82-46df-bb56-99567ca73929",
"principalId": "b5143fb6-23c8-4042-9bd6-90fe1e793875"
}
}
},
"location": "westus2",
"name": "example-nginx-9b7965b3fb",
"properties": {
"enableDiagnosticsSupport": true,
"ipAddress": "20.69.120.9",
"managedResourceGroup": "NGX_cloudaccount-44483ae0-9e21-4f09-8a49-3a558eace4fe_example-nginx-9b7965b3fb_westus2",
"networkProfile": {
"frontEndIPConfiguration": {
"publicIPAddresses": [
{
"id": "/subscriptions/614f0527-72db-4e40-adcc-e058a818cae9/resourceGroups/cloudaccount-44483ae0-9e21-4f09-8a49-3a558eace4fe/providers/Microsoft.Network/publicIPAddresses/example-nginx-9b7965b3fb",
"resourceGroup": "cloudaccount-44483ae0-9e21-4f09-8a49-3a558eace4fe"
}
]
},
"networkInterfaceConfiguration": {
"subnetId": "/subscriptions/614f0527-72db-4e40-adcc-e058a818cae9/resourceGroups/cloudaccount-44483ae0-9e21-4f09-8a49-3a558eace4fe/providers/Microsoft.Network/virtualNetworks/example-nginx-9b7965b3fb/subnets/example-nginx-9b7965b3fb"
}
},
"nginxVersion": "1.25.1 (nginx-plus-r30-p1)",
"provisioningState": "Succeeded"
},
"resourceGroup": "cloudaccount-44483ae0-9e21-4f09-8a49-3a558eace4fe",
"sku": {
"name": "standard_Monthly"
},
"systemData": {
"createdAt": "2024-01-19T17:03:30.2182174Z",
"createdBy": "9de0008b-1ceb-4149-9f87-8c83ee089e79",
"createdByType": "Application",
"lastModifiedAt": "2024-01-19T17:03:30.2182174Z",
"lastModifiedBy": "9de0008b-1ceb-4149-9f87-8c83ee089e79",
"lastModifiedByType": "Application"
},
"tags": {
"env": "Production"
},
"type": "nginx.nginxplus/nginxdeployments"
}az nginx deployment configuration show \
--resource-group $TF_VAR_resource_group_name \
--deployment-name <NGINXaaS Deployment Name from TF output> \
--name defaultExample output
$ az nginx deployment configuration show --resource-group $TF_VAR_resource_group_name --deployment-name example-nginx-9b7965b3fb --name default
{
"id": "/subscriptions/614f0527-72db-4e40-adcc-e058a818cae9/resourceGroups/cloudaccount-44483ae0-9e21-4f09-8a49-3a558eace4fe/providers/NGINX.NGINXPLUS/nginxDeployments/example-nginx-9b7965b3fb/configurations/default",
"name": "default",
"properties": {
"files": [
{
"content": "bG9jYXRpb24gL2FwaSB7CiBkZWZhdWx0X3R5cGUgdGV4dC9odG1sOwogcmV0dXJuIDIwMCAnSGVsbG8gZnJvbSBBUEknOwp9Cg==",
"virtualPath": "/etc/nginx/site/api.conf"
},
{
"content": "aHR0cCB7CiAgICBzZXJ2ZXIgewogICAgICAgIGxpc3RlbiA0NDMgc3NsOwogICAgICAgIHNzbF9jZXJ0aWZpY2F0ZSAvZXRjL25naW54L3NzbC90ZXN0LmNydDsKICAgICAgICBzc2xfY2VydGlmaWNhdGVfa2V5IC9ldGMvbmdpbngvc3NsL3Rlc3Qua2V5OwogICAgICAgIGxvY2F0aW9uIC8gewogICAgICAgICAgICByZXR1cm4gMjAwICdIZWxsbyBXb3JsZCc7CiAgICAgICAgfQogICAgICAgIGluY2x1ZGUgc2l0ZS8qLmNvbmY7CiAgICB9Cn0K",
"virtualPath": "/etc/nginx/nginx.conf"
}
],
"package": {},
"provisioningState": "Succeeded",
"rootFile": "/etc/nginx/nginx.conf"
},
"resourceGroup": "cloudaccount-44483ae0-9e21-4f09-8a49-3a558eace4fe",
"type": "NGINX.NGINXPLUS/nginxDeployments/configurations"
}There is a known issue with applying a configuration to a newly-deployed NGINXaaS instance using TF. This is because deploying the NGINXaaS instance automatically creates a default configuration, but TF doesn't know about it yet. To work around this issue, the default NGINXaaS configuration needs to be imported into the TF state, and the configuration re-applied.
To avoid seeing this error the first time you apply the TF configuration, you
can call plan or apply with the configure variable set to false. This
will skip creating the NGINX configuration resource, at which point you can
import the default NGINXaaS config using ./import_config.sh, and then re-apply
the TF configuration without the configure=false variable.
You only need to do this the first time you deploy a new instance; once the configuration is part of TF's state, subsequent deployment will update it correctly.