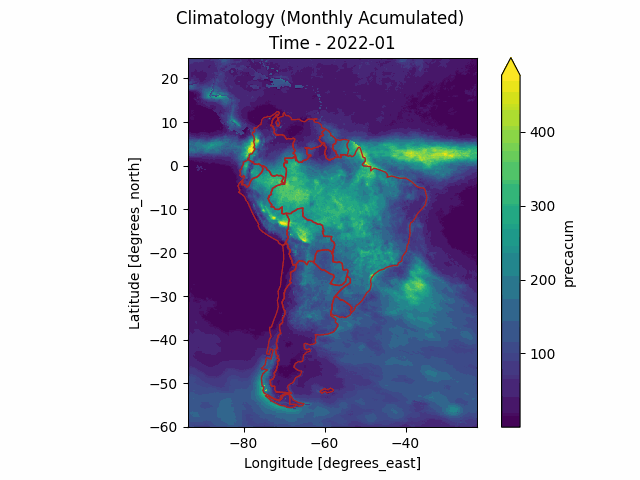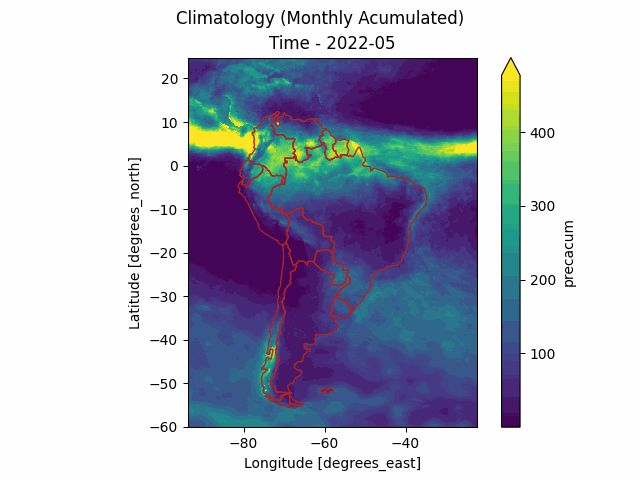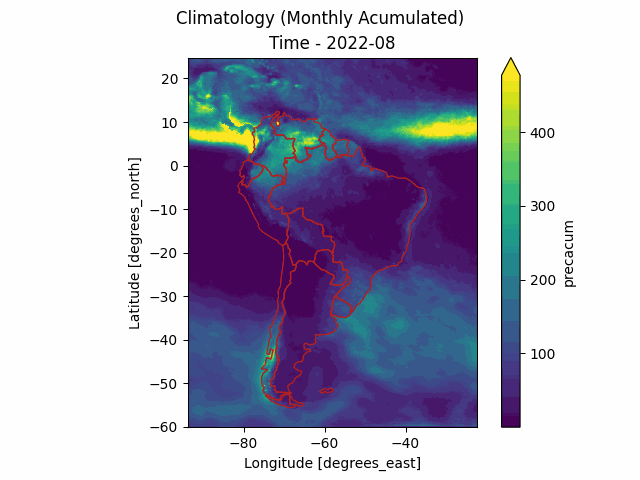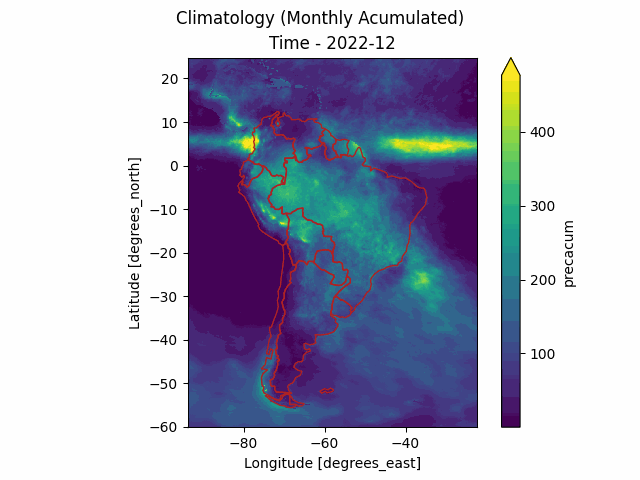
The merge-downloader package is an unofficial Python library to download MERGE products from the Brazilian National Institute for Space Research (INPE). These products include daily precipitation raster files calibrated for South America and obtained from the MERGE model (Rozante et al. 2010), as well as other climatology data.
These products include daily precipitation raster files calibrated for South America and obtained from the MERGE model (Rozante et al. 2010). The MERGE model is built upon the IMERGE/GPM model and calibrated using thousands of in-situ rain gauges to deliver bias-free results. Besides the daily raster precipitation from MERGE, INPE provides also other climatology data such as Year Accumulated, Monthly Average, Daily Average and others according to the following table:
Note: The files are downloaded in the original format provided by INPE (i.e., .nc and .grib2).
Additionally, the merge-downloader automates the procedure of spatial clipping the raster data to geometries of interest, that can be given in spatial formats supported by GeoPandas such as shapefile (i.e., .shp) or GeoJSON (i.e., .geojson).
The easiest way to install the merge-downloader is through pip install merge-downloader.
Alternatively, if you want to contribute to this package, you can clone the repository and install it in edit mode:
git clone https://github.com/cordmaur/merge-downloader.git
cd merge-downloader
pip install -e .
The following libraries are required to run the package:
gdal
geopandas
rioxarray
pystac-client
matplotlib
pytest
cfgrib
netCDF4
contextily
eccodes
adjustText
notebook
Pip will try to install them automatically, however it's recomended to have at least GDAL pre-installed in the environment.
For a seamless experience, I recommend using docker image created specifically for the project. It is available at https://hub.docker.com/r/cordmaur/merge-downloader/ and can be downloaded with docker pull cordmaur/merge-downloader:v1. This image comes with all the necessary libraries.
The following articles brings a quick intro to using docker for geospatial development.
- https://medium.com/towards-data-science/configuring-a-minimal-docker-image-for-spatial-analysis-with-python-dc9970ca8a8a
- https://medium.com/towards-data-science/why-you-should-use-devcontainers-for-your-geospatial-development-600f42c7b7e1
The merge-downloader package offers a CLI that can be used for simple workflows such as downloading a series of files in their original format or exporting a .csv file with a time series. When opening the files through the library, additional post-processing to adjust the coordinates is automatically performed and those are not available in the CLI.
Once installed via pip, the CLI will be accessible through the merge-downloader command:
root@c272deddb0f1:/# merge-downloader
usage: merge-downloader [-h] {reset,init,series,download} ...
Merge Downloader
positional arguments:
{reset,init,series,download}
reset Reset default configuration
init Initialize the environment
series Calculate the rain and create a time-series for the specified period.
download Download raster data
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
Before starting, we need to setup the download folder. This is done through merge-downloader init command. The -f flag is used to specify the folder and the -url flag can be used to change the FTP server that defaults to ftp.cptec.inpe.br.
root@c272deddb0f1:/# merge-downloader init -h
usage: merge-downloader init [-h] -f FOLDER [-url URL]
The init command is used to set the FTP URL to pull the data from and the local download directory.
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-f FOLDER, --folder FOLDER
Local folder to download the files (relative path).
-url URL FTP URL of the server. Defaults to 'ftp.cptec.inpe.br'
root@c272deddb0f1:/# merge-downloader init -f /downloads
Initializing...
Setting downloading folder to '/downloads'
To download raw data, we use the download command. We need to specify the start and end dates through the -d flag. It accepts common ISO formats that can be parsed by dateutils library (e.g., -d 20230501 20230515). Additionally, it's necessary to specify the data type to be downloaded. The list of currently available types is available in the help and contains:
DAILY_RAIN,
MONTHLY_ACCUM_YEARLY,
DAILY_AVERAGE,
MONTHLY_ACCUM,
MONTHLY_ACCUM_MANUAL,
YEARLY_ACCUM,
HOURLY_WRF,
DAILY_WRF
So, to download the daily rain, from 1st to 10th of June 2023, we can use the following command. Once the download is complete, it will display the list of files available.
root@c272deddb0f1:/# merge-downloader download -d 20230601 20230610 -t DAILY_RAIN
Downloading INPETypes.DAILY_RAIN series for range: ['01-06-2023', '10-06-2023']
The following files are available:
/downloads/DAILY_RAIN/MERGE_CPTEC_20230601.grib2
/downloads/DAILY_RAIN/MERGE_CPTEC_20230602.grib2
/downloads/DAILY_RAIN/MERGE_CPTEC_20230603.grib2
/downloads/DAILY_RAIN/MERGE_CPTEC_20230604.grib2
/downloads/DAILY_RAIN/MERGE_CPTEC_20230605.grib2
/downloads/DAILY_RAIN/MERGE_CPTEC_20230606.grib2
/downloads/DAILY_RAIN/MERGE_CPTEC_20230607.grib2
/downloads/DAILY_RAIN/MERGE_CPTEC_20230608.grib2
/downloads/DAILY_RAIN/MERGE_CPTEC_20230609.grib2
/downloads/DAILY_RAIN/MERGE_CPTEC_20230610.grib2
When creating a time-series, the merge-downloader will automatically reduce the X (i.e., longitude) and Y (i.e., latitude) axes through the mean operator to have the value alongside the time dimension. If a geometry is given (e.g., shapefile or geojson), the computation will be performed within the given geometries, otherwise the values will be computed for the entire raster.
Similarly to download, the series command requires the flags -d and -t for dates and data type, as well as the optional -s for the geometry and -f to specify the output file. Besides, one can also use the flags --anim and --chart to output a simple .png chart and an animated GIF automatically.
For example, in the following code we compute the monthly rain occurred in 2022 in the Amazonas Brazlilian state and output it to a file named amazon.csv (the sample .geojson files are located inside the data/ folder of the project.
root@c272deddb0f1:/workspaces/merge-downloader# merge-downloader series -d 2022-01 2022-12 -t MONTHLY_ACCUM_YEARLY -s ./data/amazon.geojson -f tmp/amazon.csv --anim --chart
Downloading INPETypes.MONTHLY_ACCUM_YEARLY series for range: ['26-01-2022', '26-12-2022']
Cutting raster to: data/amazon.geojson
Coverting shp CRS to EPSG:4326
Series exported to: tmp/amazon.csv
Creating bar chart: tmp/amazon.png
Creating animation file: tmp/amazon.gif
Appending: 2022-01-01T12:00:00.000000000
Appending: 2022-02-01T12:00:00.000000000
Appending: 2022-03-01T12:00:00.000000000
Appending: 2022-04-01T12:00:00.000000000
Appending: 2022-05-01T12:00:00.000000000
Appending: 2022-06-01T12:00:00.000000000
Appending: 2022-07-01T12:00:00.000000000
Appending: 2022-08-01T12:00:00.000000000
Appending: 2022-09-01T12:00:00.000000000
Appending: 2022-10-01T12:00:00.000000000
Appending: 2022-11-01T12:00:00.000000000
Appending: 2022-12-01T12:00:00.000000000
The series (.csv) and the chart (.png) can be seen in the following picture.

To use the package from a Jupyter or a python script, you can refer to the notebooks available in the nbs/ folder.
Rozante, José Roberto, Demerval Soares Moreira, Luis Gustavo G. De Goncalves, and Daniel A. Vila. “Combining TRMM and Surface Observations of Precipitation: Technique and Validation over South America.” Weather and Forecasting 25, no. 3 (June 1, 2010): 885–94. https://doi.org/10.1175/2010WAF2222325.1.