An open source JDBC driver for Elasticsearch released under Apache License 2.0
esqlj is a JDBC driver for Elastic built on top of Elastic Rest High Level API (rel. 7.11). See Elastic licenses in folder licenses/elastic-licenses
esqlj extend SQL syntax with advanced Elastic query capabilities like full text queries, geo queries, shape queries, joining queries etc.
Sql parsing is provided by jsqlparser library JSQLParser. See related licenses in folder licenses/JSqlParser
About SQL implementation see below section 'Support matrix and conventions'
Not production ready
DQL implemented
DDL and DML not implemented (actually not in scope)
JDBC url must to follow this syntax:
jdbc:esqlj:http<s>://<elastic_address_1>:<elastic_port_1>,http://<elastic_address_2>:<elastic_port_2>,...;param1=paramValue1;...
It's possible to declare a pool of connections by comma delimited URLs list.
Optional parameters:
| Name | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
| userName | Credential user name | - |
| password | Credential password | - |
| includeTextFieldsByDefault | Include Elastic text typed fields by default on select * |
false |
| indexMetaDataCache | Cache retrieved indices structure (it's suggested to keep enabled this feature because retrieving these information it could be an heavy operation, especially for alias or starred index queries). Best choice to enable it on unmutable index | true |
| maxGroupByRetrievedElements | Max GROUP BY retrieved elements for selected fields | 500 |
| queryScrollFromRows | Number of rows fetched on first pagination | 500 |
| queryScrollFetchSize | Fetched rows on next pagination | 500 |
| queryScrollTimeoutMinutes | Timeout between pagination expressed in minutes | 3 |
| queryScrollOnlyByScrollApi | If true, pagination will be executed by Elastic Scroll API. If false, it will be applied the scroll strategy that best fit the query (see Pagination paragraph below) | true |
| sharedConnection | If valued true Elastic client internally used by esqlj will be statically shared between all connections (use it if you don't have the requirement to connect to different Elastic clusters inside same JVM) |
true |
Elastic indices are managed like SQL Tables.
Elastic aliases are managed like SQL Views.
Query on indices containing special characters like *, -, . need to be double quoted. Example: 'SELECT * FROM ".test-index*"'
Fields and aliases containing special characters like - must also to be double quoted.
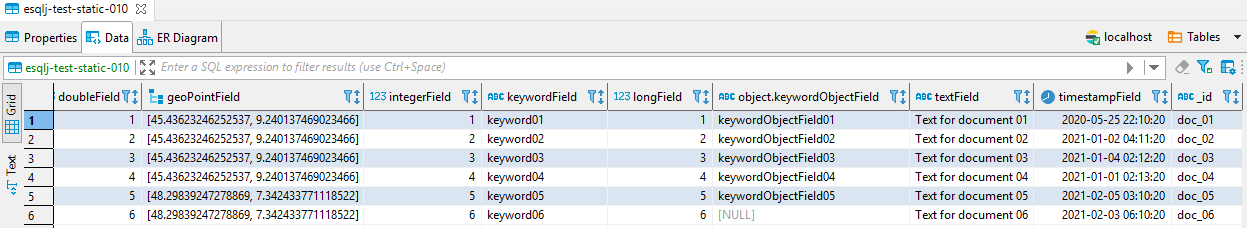
Elastic document identifier "_id" can be fetched in not aggregating query. It's of type string and mapped on MetaData like the index primary key. This column is also available on Where condition for matching query (=, !=).
Search score "_score" is returned like a colum of type float in not aggregating query.
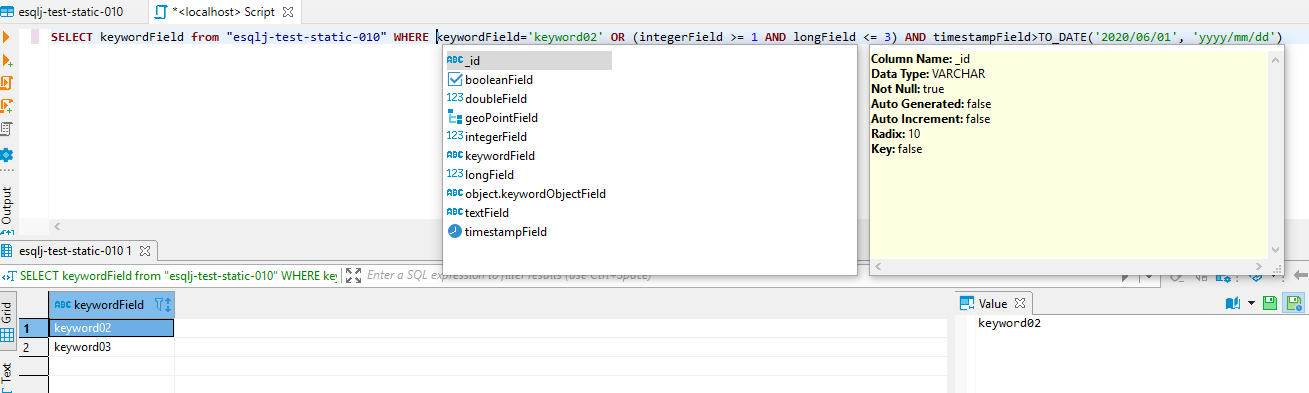
Standard SQL filtering syntax is very limited. Esqlj supports a custom syntax for filtering documents using Elastic API full text queries, geo queries, shape queries...
Actually are implemented only a limited set of these advanced filtering techniques. This is an example that uses Query string ELastic API (query-dsl-query-string-query):
SELECT _id, _score FROM indexName WHERE query_string('(new york city) OR (big apple) OR name:/joh?n(ath[oa]n)/', 'field1, field2,city.*', 'minimum_should_match:2')
By default the maximum number of document fields / columns that can be retrieved is set to 100.
This explains - for example - because by default .kibana_* index containing almost 500 fields return an error on 'select *'.
For increasing this configuration threshold change this Elastic setting according to your needs: 'index.max_docvalue_fields_search'
Change max doc threshold on indices that start with 'my-index':
PUT /my-index*/_settings
{
"index" : {
"max_docvalue_fields_search" : 500
}
}
Change max doc threshold on all indices:
PUT /*/_settings
{
"index" : {
"max_docvalue_fields_search" : 500
}
}
In the future there will no longer be possible query system indices.
Elastic boolean fields are typed BOOLEAN on resultset. Use constants true and false to express conditions on these fields. Example:
SELECT * from \"esqlj-test-static-010\" WHERE booleanField=true
A sample usage of esqlj in DBeaver:
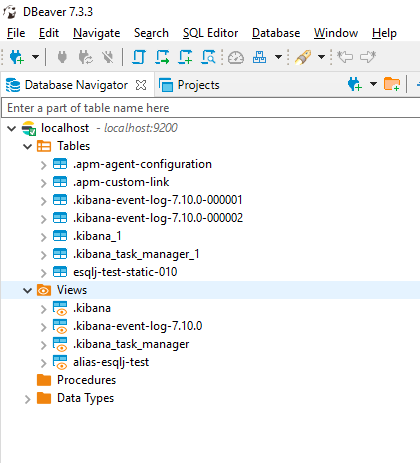
Tables are Elasticsearch indices. Views are Elasticsearch aliases
- Create a new connection of type Elasticsearch
- Click "Edit Driver Settings"
- Change:
- Class Name:
org.fpasti.jdbc.esqlj.EsDriver - URL Template:
jdbc:esqlj:http://{host}:{port} - Remove all jars and add
esqlj-<rel>-shaded.jar(available from project build) - Click "OK" to confirm
- Class Name:
- Change if required host and port and Test Connection
- OK
Add driver dependency in pom.xml:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.fpasti</groupId>
<artifactId>esqlj</artifactId>
<version>0.2.0</version>
</dependency>
DriverManager.registerDriver(new EsDriver());
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:esqlj:http://localhost:9200");
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
stmt = connection.createStatement();
rs = stmt.executeQuery("SELECT * from \"esqlj-test-static-010\" WHERE booleanField=true");
// print out column & fields
ResultSetMetaData rsm = rs.getMetaData();
for(int i = 1; i <= rs.getMetaData().getColumnCount(); i++) {
System.out.println(String.format("%d: Column: %s, Column Alias: %s, Type: %s", i, rsm.getColumnName(i), rsm.getColumnLabel(i), rsm.getColumnTypeName(i)));
}
// iterate over query res
while (rs.next()) {
System.out.println(String.format("_id: %s : doubleField: %f - keywordField: %s - textField: %s - score: %f", rs.getString(10), rs.getDouble(2), rs.getObject(5), rs.getString(8), rs.getFloat(11)));
}
} catch (SQLException ex) {
System.out.println("SQLException: " + ex.getMessage());
} finally {
if(stmt != null) {
stmt.close();
}
if(connection != null) {
connection.close();
}
}
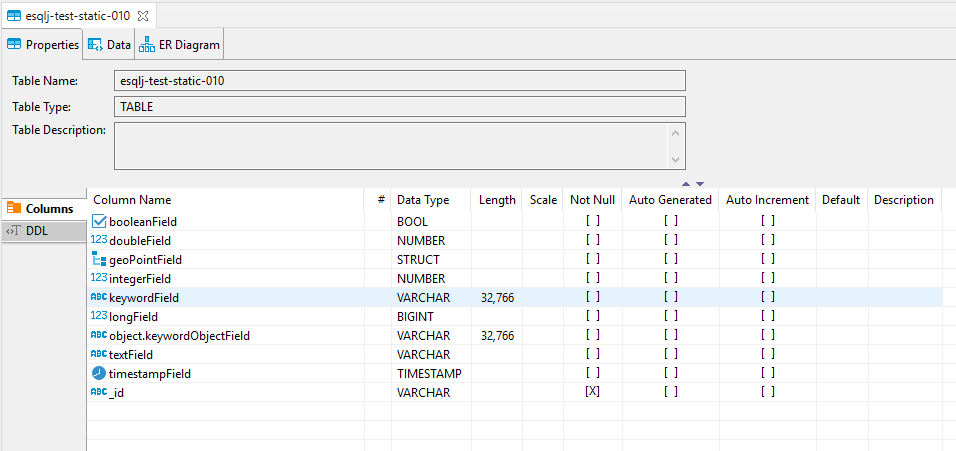
Mapping of supported Elastic types to SQL types:
| Elastic on index type | Metadata declared SQL Type | Java effective type |
|---|---|---|
| boolean | BOOL | Boolean |
| date | TIMESTAMP | LocalDateTime |
| date_nanos | TIMESTAMP | LocalDateTime |
| doc_id | VARCHAR | String |
| double | NUMBER | Double |
| flattened | STRUCT | Object |
| float | NUMBER | Float |
| geo_point | STRUCT | EsGeoPoint |
| half_float | NUMBER | Float |
| integer | NUMBER | Integer |
| ip | VARCHAR | String |
| keyword | VARCHAR | String |
| long | BIGINT | Long |
| object | STRUCT | Object |
| scaled_float | NUMBER | Float |
| short | NUMBER | Byte |
| text | VARCHAR | String |
| unsigned_long | NUMBER | Long |
| wildcard | VARCHAR | String |
By default esqlj implements a scrolling strategy on query through Elastic Scroll API. Optionally it's possibile to activate the less expensive scroll by order, but if you want to activate this functionality pay attention to include in every query a sorting on at least one tiebreaker field (in future it's no longer possible to query by doc id, it could be a best practice to store identifier also in document field). It's in discussion an RFC on Elastic product about the introduction of an automatic tiebreaker in query result. But for now if you enable this feature and miss to add a sorting on a tiebreaker fields some rows could be skipped between paginations of data.
Still on the subject of scrolling by order, the driver doesn't use Point in Time API (it seems missing the support in Elastic Rest High level API).
Pay attention: Scroll API consume resources on server. It's a best practice to fetch all required data as soon as possible. The scroll link will be automatically released from esqlj at the end of data retrieve.
Most of test units require a live Elastic instance.
The activation of these units is commanded by a system variable named "ESQLJ_TEST_CONFIG".
The environment variabile must concatenate a valid esqlj JDBC url connection string and the load strategy of the documents requested by query inside units:
ESQLJ_TEST_CONFIG=jdbc:esqlj:http://<elastic_address>:<elastic_port>|<createAndDestroy or createOnly>
| Parameters | Actions | Scope |
|---|---|---|
| createAndDestroy | Test units create index 'esqlj-test-volatile-<uuid>' on start and delete it on finish | Continuous Delivery/Deployment |
| createOnly | Test units create index 'esqlj-test-static-<release.version>' and not delete it on finish. If it's just present on Elasticsearch it will be preserved. (Will be required a manual delete of it from system). | Development stage |
Sample configuration: ESQLJ_TEST_CONFIG="jdbc:esqlj:http://10.77.154.32:9080|createOnly"
If ESQLJ_TEST_CONFIG isn't declared, all tests depending from live connection will be skipped.
Actually supported SELECT [...] elements:
| Select element | Notes |
|---|---|
column |
Elastic document field |
column alias or column AS alias |
Alias for field in query result |
* |
All document fields |
_id |
document identifier (string) |
_score |
document query search score (float) |
TO_CHAR(field, mask_date) |
Format date field. Example: TO_CHAR(timestampField, 'YYYY/MM/DD HH:MI:SS'). Supported mask: YEAR, YYYY, YY, MM, MONTH, MON, DDD, DD, HH24, HH12, HH, MI, SS, DAY, XFF, FFF, FF, F, PM, TZR, TZH. |
LATITUDE |
Extract latitude from EsGeoPoint field (not orderable) |
LONGITUDE |
Extract longitude from EsGeoPoint field (not orderable) |
COUNT(*) |
Number of documents in index: SELECT COUNT(*) FROM index |
COUNT(field) |
Number of documents in index where specified field is present and not null: SELECT COUNT("object.keywordObjectField") FROM index |
COUNT(DISTINCT field) |
Number of distinct values of specified field in index: SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT keywordField) FROM index |
Supported GROUP BY query functions:
| Function | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
AVG |
Average of values | SELECT AVG(integerField) FROM index |
COUNT(*) |
Number of documents | Number of documents in group: SELECT COUNT(*) FROM index |
COUNT(field) |
Number of documents with specified field | Number of documents in group where specified field is present and not null: SELECT COUNT("object.keywordObjectField") FROM index |
COUNT(DISTINCT field) |
Number of distinct values | Number of distinct values of specified field: SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT keywordField) FROM index |
MAX |
Max column value | SELECT MAX(integerField) FROM index |
MIN |
Min column value | SELECT MIN(integerField) FROM index |
SUM |
Sum of values | SELECT SUM(integerField) FROM index |
It's possibile to query distinct values using DISTINCT clause.
Example:SELECT DISTINCT keywordField, booleanField FROM index ORDER BY keywordField, booleanField DESC
You can use both column name or column alias in expression.
| Expression condition | Notes |
|---|---|
left expression = value |
|
left expression != value |
|
left expression > numeric_value |
|
left expression >= numeric_value |
|
left expression < numeric_value |
|
left expression <= numeric_value |
|
left expression LIKE expression |
Implemented by Wildcard Elasticsearch filter. See Elasticsearch documentation about its usage (query-dsl-wildcard-query) |
left expression IS NULL |
|
left expression IS NOT NULL |
|
left expression BETWEEN a AND b |
a and b could be NUMBER, STRING, date expressed by TO_DATE('date', 'mask_date'), EXTRACT function |
left expression IN (value1, value2, ...) |
|
query_string(...) |
Elastic raw query. See below for reference |
geo_bounding_box(...) |
Elastic raw query. See below for reference |
| Expression |
|---|
column |
alias |
EXTRACT(period from column) |
value=column expression is for example considered invalid from esqlj
esqlj allow you to use specific Elastic query API.
Syntax usage is query_type(param1,param2,...), where query_type maps specific Elastic query; and param1,param2,... allows you to pass parameters to that query.
There are a set of mandatory parameters for every implemented custom query. It's possible also to set optional parameters for changing low level configuration query behaviour, like for example analyze_wildcard, fuzzy_max_expansions etc. These configuration settings must to be declared in this way:
query_string('search criteria','field1,field2,object.*','analyze_wildcard:true','fuzzy_max_expansions:15').
Esqlj will dynamically cast params value type according to expected parameter Elastic query object.
Currently implemented raw Elastic queries:
| Elastic query | query_type | Parameters | Elastic reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Query string | query_string | 1: query expression, 2: search on fields (* for all), 3..x: additional query parameters (see Elastic documentation) | string_query |
| Geo bounding box | geo_bounding_box | 1: geopoint field, 2: top left latitude, 3: top left: longitude, 4: bottom right latitude, 5: bottom right longitude, 6..x extra params | geo_bounding_box |
Specific Elastic query functions samples
| Query type | Sample |
|---|---|
| query_string | SELECT id, _score FROM indexName WHERE query_string('(new york city) OR (big apple) OR name:/joh?n(ath[oa]n)/', 'field1, field2,city.*', 'minimum_should_match:2') |
| geo_bounding_box | SELECT _id, _score FROM indexName WHERE geo_bounding_box('geoPointField', 50, 8, 40.1, 10.2) |
| Function name | Admitted on | Notes |
|---|---|---|
SYSDATE |
Right expression | Current date time |
SYSDATE() |
Right expression | Current date time |
NOW() |
Right expression | Current date time |
GETDATE() |
Right expression | Current date time |
TRUNC(SYSDATE|SYSDATE()) |
Right expression | Current date |
TO_DATE(date, mask_date) |
Right expression | Supported mask: YEAR, YYYY, YY, MM, MONTH, MON, DDD, DD, HH24, HH12, HH, MI, SS, DAY, XFF, FFF, FF, F, PM, TZR, TZH. Example TO_DATE('2020/01/01', 'YYYY/MM/DD') |
EXTRACT(PERIOD FROM column) |
Left expression | PERIOD can be valued with YEAR, MONTH, DAY, HOUR, MINUTE, SECOND. Usage example: EXTRACT(YEAR FROM timestamp)!=2020 |
It's possible to aggregate values using GROUP BY clause.
Example: SELECT booleanField, AVG(integerField) test, SUM(longField), COUNT(doubleField), COUNT(*) from testIndex GROUP BY booleanField
It's possible to apply filtering on Group by expressions.
Example:
SELECT booleanField, AVG(integerField) test, SUM(longField), COUNT(*) from testIndex GROUP BY booleanField HAVING AVG(integerField)>=4 OR SUM(longField)>=19
Example:
SELECT * FROM column ORDER BY keywordField, integerField DESC
Example:
SELECT * FROM column LIMIT 100
Tested on 7.4.2 and 7.10.0 Elasticsearch release
Fabrizio Pasti
fabrizio.pasti@gmail.com
https://www.linkedin.com/in/fabrizio-pasti-2340a627