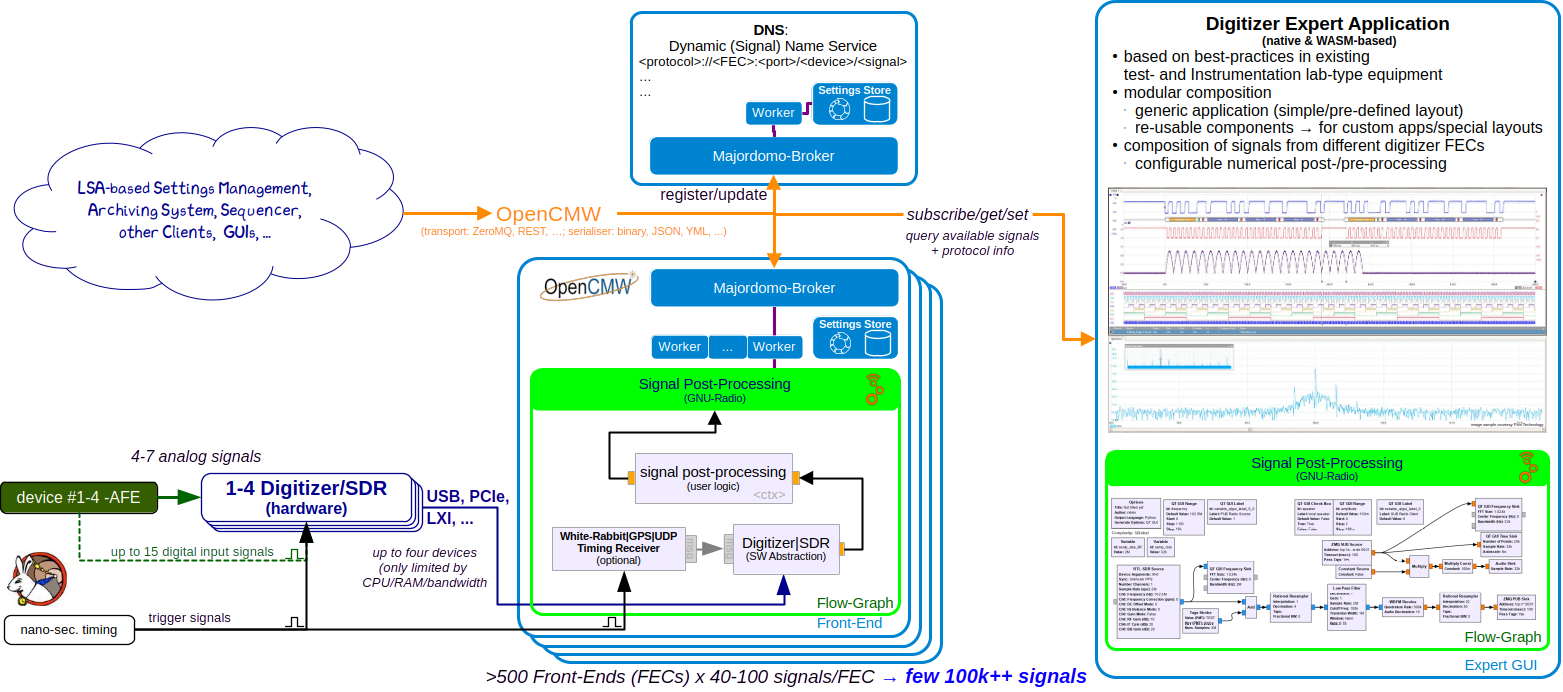
OpenDigitizer is an open-source project modernising FAIR’s time- and frequency-domain digitizer infrastructure embracing modern C++20 standards and uses the OpenCMW, GNU Radio (version 4.0), ImGUI and WebAssembly ecosystems.
While initially designed for the FAIR facility, the expressed intent is to be highly adaptable also for use by other research facilities, industry, academia, as well as private users.
The primary applications of OpenDigitizer include:
- First-line diagnostics and fault identification, serving as a distributed diagnostic tool for accelerator equipment with nanosecond-level synchronization, offering functionalities similar to oscilloscopes, software-defined-radios, spectrum analyzers, VNAs, and other hardware.
- Providing building blocks for higher-level diagnostics and monitoring tools, assisting equipment experts, operators, and scientist in developing basic to advanced top-level diagnostics and feedback control loops
- Supporting a rapid prototyping R&D environment for quick adaptation, testing, and integration of solutions developed on lab test stands or during machine studies into the 24/7 operation of the facility.
The key components are:
- OpenCMW, an open-source middleware solution developed at GSI and FAIR providing flexible data transport, efficient data serialisation, and intuitive domain objects based on compile-time reflection
- GNU Radio (version 4.0), a powerful software toolkit designed for signal processing and software-defined radios. GNU Radio uses directed signal flow graphs for efficient expression of post-processing and feedback control loop logic. This feature makes it easy for domain experts with minimal programming experience to inspect and reconfigure existing systems, while at the same time keeping the internal C++ components clean, lean, and maintainable by RSE experts.
- ImGUI and WebAssembly (WASM, through Emscripten) are used for the user interfaces, enabling cross-platform compatibility, and native deployment on the desktop, mobile, as well as other browser-based platforms supporting flexible use during commissioning and troubleshooting.
Follow these instructions in the subdirectories to compile the individual parts of the project. The top-level CMakeList can be used to compile the complete project in one go:
cmake -S . -B build -DEMCMAKE_COMMAND=`which emcmake` && cmake --build buildThis will compile the native UI, the WebAssemblyUI (in a subbuild), and the service which includes the wasm artifacts in its assets.
export DIGITIZER_CHECK_CERTIFICATES=0 # to disable certificate checking, if wanted
export DIGITIZER_HOSTNAME=localhost # set a custom host
export OPENCMW_REST_CERT_FILE=${BUILD_DIR}/_deps/opencmw-cpp-src/src/client/test/assets/server-cert.pem
export OPENCMW_REST_PRIVATE_KEY_FILE=${BUILD_DIR}/_deps/opencmw-cpp-src/src/client/test/assets/server-key.pem
build/src/service/opendigitizer & # launches the service
build/src/ui/opendigitizer-ui & # launches the native digitizer UI
xdg-open https://localhost:8080/web/index.html # launches the webassembly UI
xdg-open https://localhost:8080/flowchart # launches the html based web ui for the flowgraph property
xdg-open https://localhost:8080/acquisition # launches the html based web ui for the acquisition propertyWe are committed to:
-
Clean & Lean Code (Muda 無駄 & Kaizen 改善 )
Boost maintainability and adaptability through concise, modular code, eliminating waste and fostering continuous improvement
-
Test-Driven & Extreme Programming
Ensure software reliability, accelerate, and keep developing applications fit-for-purpose
-
Bus Factor & Knowledge Distribution
Foster collaborative environments and respect for people to enhance team resilience by sharing knowledge and responsibilities
-
FAIR Principles (see here and here for details)
Improve the discoverability, accessibility, interoperability, and reusability of digital assets, benefiting the research community and wider public through standardisation
-
Automation & Efficiency
Streamline processes and improve productivity with continuous integration/deployment, optimising resource usage and promoting continuous improvement
-
Scalability & Resource Optimisation
Ensure software longevity and efficient resource usage by designing with future growth in mind, eliminating waste, and optimizing delivery
-
Security & Long-Term Planning
Safeguard data and software by prioritizing security, while fostering sustainable development through long-term planning and continuous improvement
-
Develop People & Teams
Capitalise on the inverse of 'Conway's Law' by nurturing skilled engineers, create opportunities for experimentation, inspiring and guiding them towards sound solutions, allowing them to continuously adapt organisational structures that support producing better technical outcomes
- Digitization of Analog Signals
- OpenCMW repo and specification