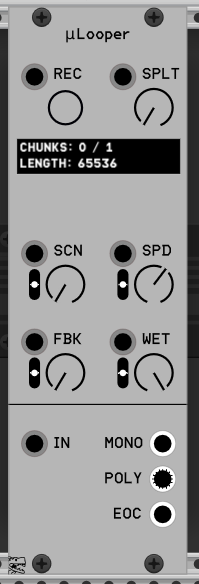
Recording looper for very short (4096 ~ 65536 samples length) recordings.
- REC: Record. Push button to fill the buffer.
- SPLT: Split. Split the whole buffer (65536 samples for number of chunks).
- SCN: Scan. Lineary interpolates between chunks.
- SPD: Speed. playback speed. Use negative values to play backwards.
- FBK: Feedback. Overdub previous buffer.
- WET: Dry/Wet. Mix input and recorded signals.
- IN: Recording signal input.
- MONO: Play current chunk (with interpolation between it and the next one).
- POLY: Up to 16 chunks distributed across channels.
- EOC: Trigger in the end of the record.
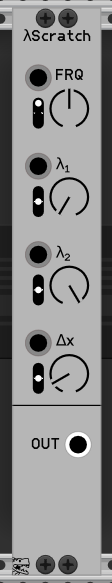
Glitchy and scratchy oscillator. Based on https://www.mathematica-journal.com/2013/05/27/using-the-logistic-map-to-generate-scratching-sounds/ algorithm.
- FRQ: Playback frequency with CV input below.
- λ1: Coefficient for the logistic equation
x = λx(1-x) - λ2: Second coefficient for the logistic equation. Oscillator oscillates between λ1 and λ2 with playback frequency.
- Δx: See article above for explanation.
NB! Due to chaotic nature of this oscillator it's nearly impossible to keep the steady pitch. Use lower λ1, λ2 values and higher Δx values for more mellow results or use it as exciter for physical modelling resonators (see the Pluck module below).
8-bit Linear Feedback Shift Register (LFSR) sequencer. Consider it like fully deterministic Turing Machine sequencer*
* Random values in Turing Machine are generated using LFSR under the hood, so Turing Machine sequencer is fully deterministic as well.
- COEF: Decimal representation of LFSR coefficients.
- Small buttons to the right are LFSR coefficients.
- Small square lights are shift register bits.
- LEN: Sequence length.
- NOT: Use
XNORinstead ofXORfor LFSR. - V/OCT: Black knobs are used to generate pitch information from the shift register bits. The result is scaled with the corresponding input.
- CLK: Input trigger.
- GATE: Polyphonic gate output from the shift register bits.
- CV: CV output from the shift register bits.
NB! Register may be emptied and sequence will be stuck. You can use NOT button to feed 1-bit to the sequence.
16-bit Linear Feedback Shift Register (LFSR) sequencer which can be splitted for two independent sequences.
- Small buttons are LFSR coefficients.
- Small square white and black lights are shift registers' bits.
- COEF: Decimal representation of LFSR coefficients (for both sequences combined).
- SPLT: Split one register for two with the total length of 16 bits.
- NOT1, NOT2: Use
XNORinstead ofXOR.
- CLK1, CLK2: Triggers to run corresponding sequence.
- GATE
- 1: Polyphonic gate output from the 1st shift register bits.
- 2: Polyphonic gate output from the 2nd shift register bits.
- XY: XOR the bit sequence in the row (channels 1-4) or the column (channels 5-8) to open the gate.
- CV
- 1: Output from the 1st shift register bits (using bits as binary representation of the float number).
- 2: Output from the 2nd shift register bits (using bits as binary representation of the float number).
- XY: Use the bit sequence in the row (channels 1-4) or the column (channels 5-8) as binary representation of the float CV value.
Experiment in hydrodynamics. Model of the liquid flow in the leaky faucet.
- FLOW: The pressure of the incoming liquid.
- VISC: The liquid viscosity.
- Square lights are represents the pipe. The brightness in the cell corresponds to the amount of liquid in the cell.
- CLK: Trigger to process one liquid flow cycle.
- DROP: Each time the amount of liquid in the cell is large enough to overcome viscosity the drop occurs and the gate is open.
- CV: Polyphonic output. 8 channels, each for one cell.
Sequencer based on chaotic maps (logistic and tent).
- MAP: Switch between Logistic and Tent map.
- R: Map coefficient.
- RST: Reset button.
- CLK: Sequencer clock.
- GATE: Open the gate if the previous iteration value is bigger than the current one. Not very useful but whatever.
- CV: Current iteration value mapped to CV.
Venerable Karplus-Strong algorithm with the extensions. See https://ccrma.stanford.edu/realsimple/faust_strings/faust_strings.pdf
- PLK: Pluck the string.
- FRQ: Base oscillator frequency.
- DMP: Damping coefficient. More is duller, less is brighter.
- DCY: Audio decay time in seconds (t60).
- DIR: Pluck direction. Up or down or some angle inbetween.
- POS: Pluck position. Closer to the bridge or to the string middle.
- LVL: Pluck velocity.
- EXC: Exciter input. You can use any sound to excite the pluck, white noise is used by default.
- OUT: Polyphonic output. You can play chords, yay!
There are some main building blocks for the modules, e.g.
The input above the knobs sets the value without the attenuation.
The input above the knobs sets the value with the attenuation given by slider. So the middle slider position (0) does nothing.