Simple and highly effective algorithm project : sorting data ( numbers)
You have at your disposal a set of int values, 2 stacks and a set of instructions to manipulate both stacks.
Those 2 stacks are named a and b.
- a contains a random number of either positive or negative numbers without any duplicates.
- b is empty
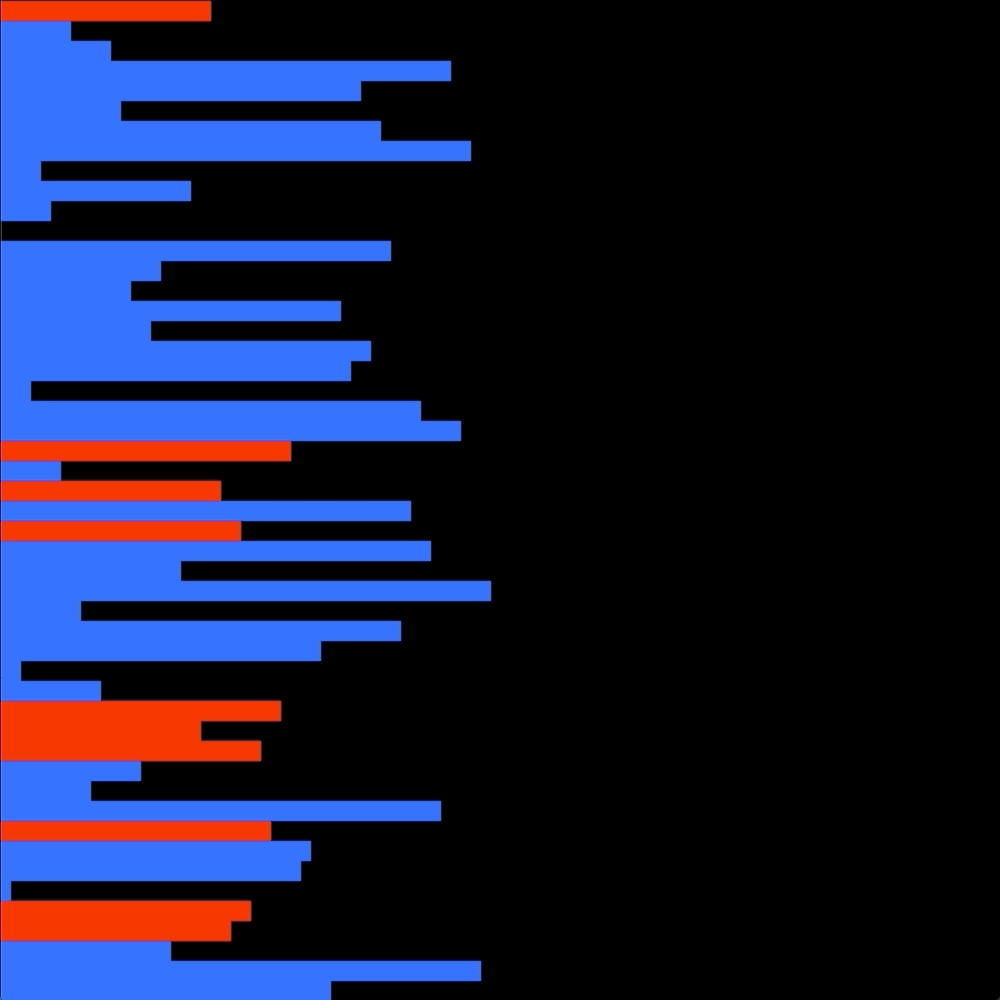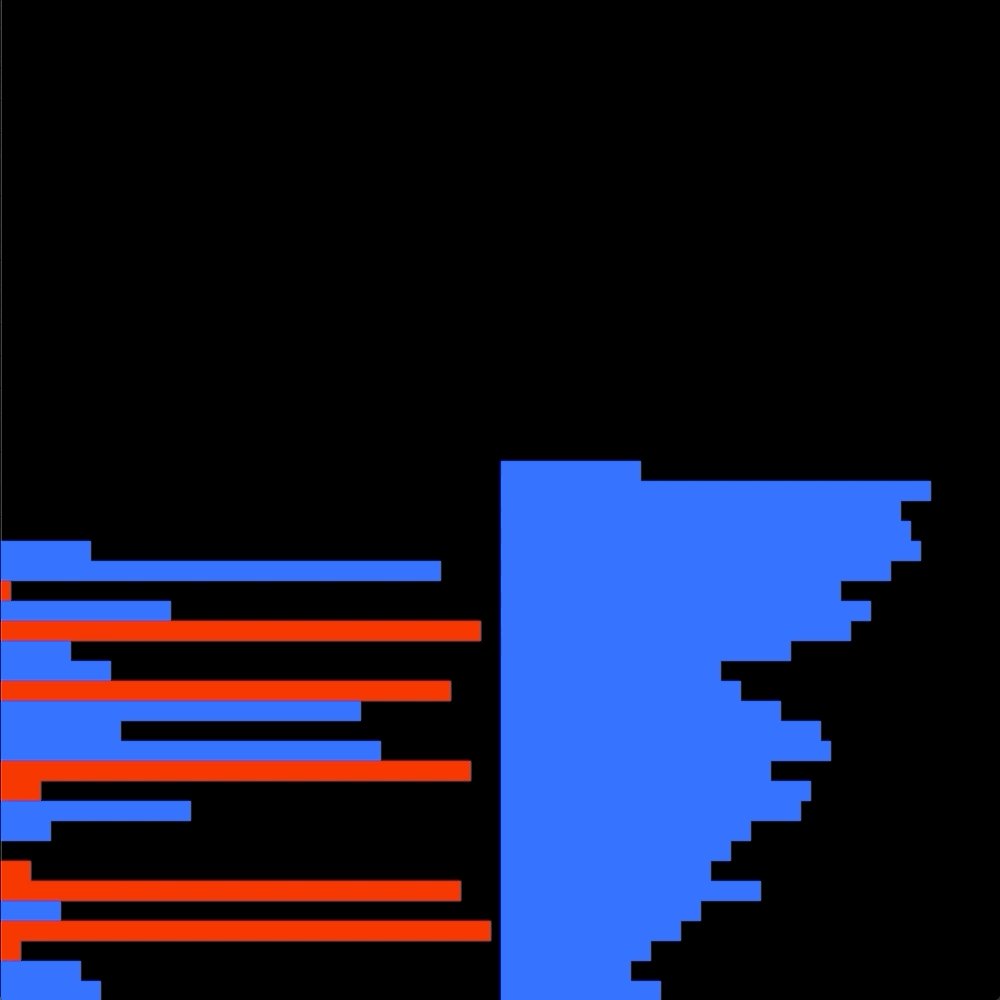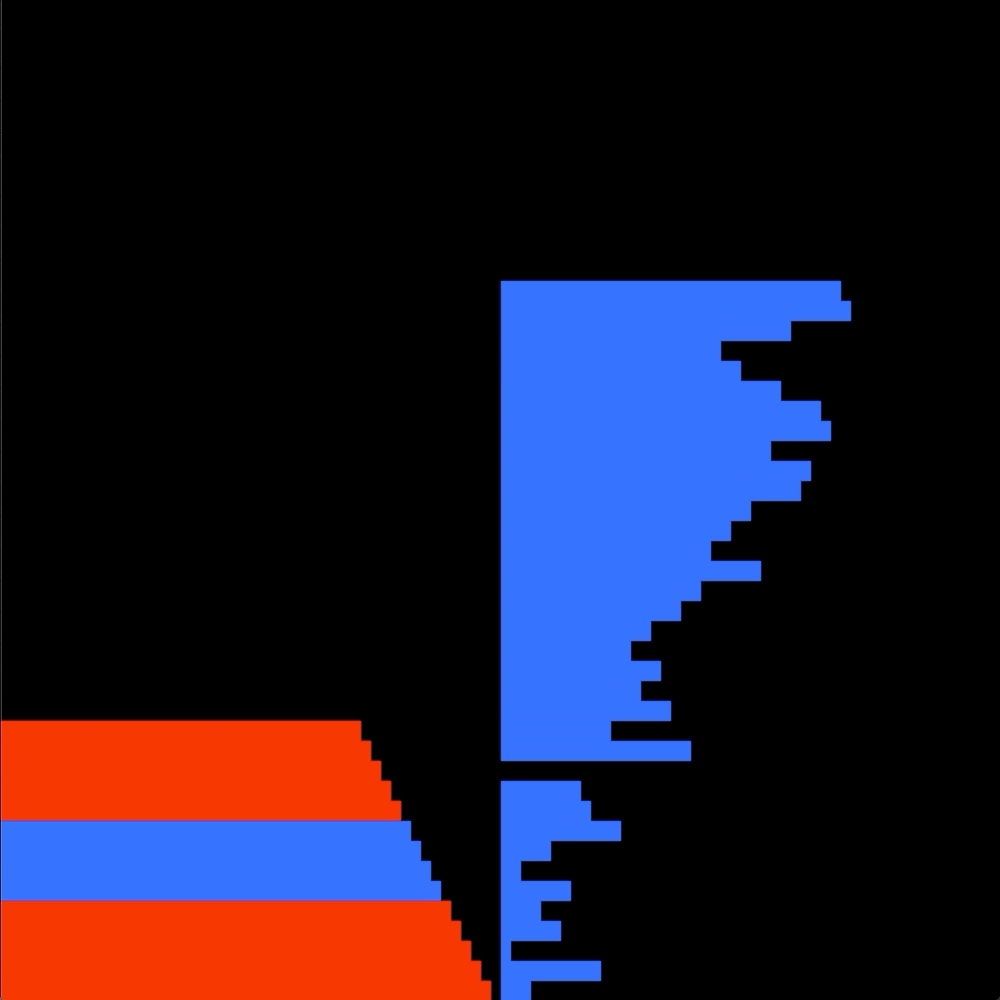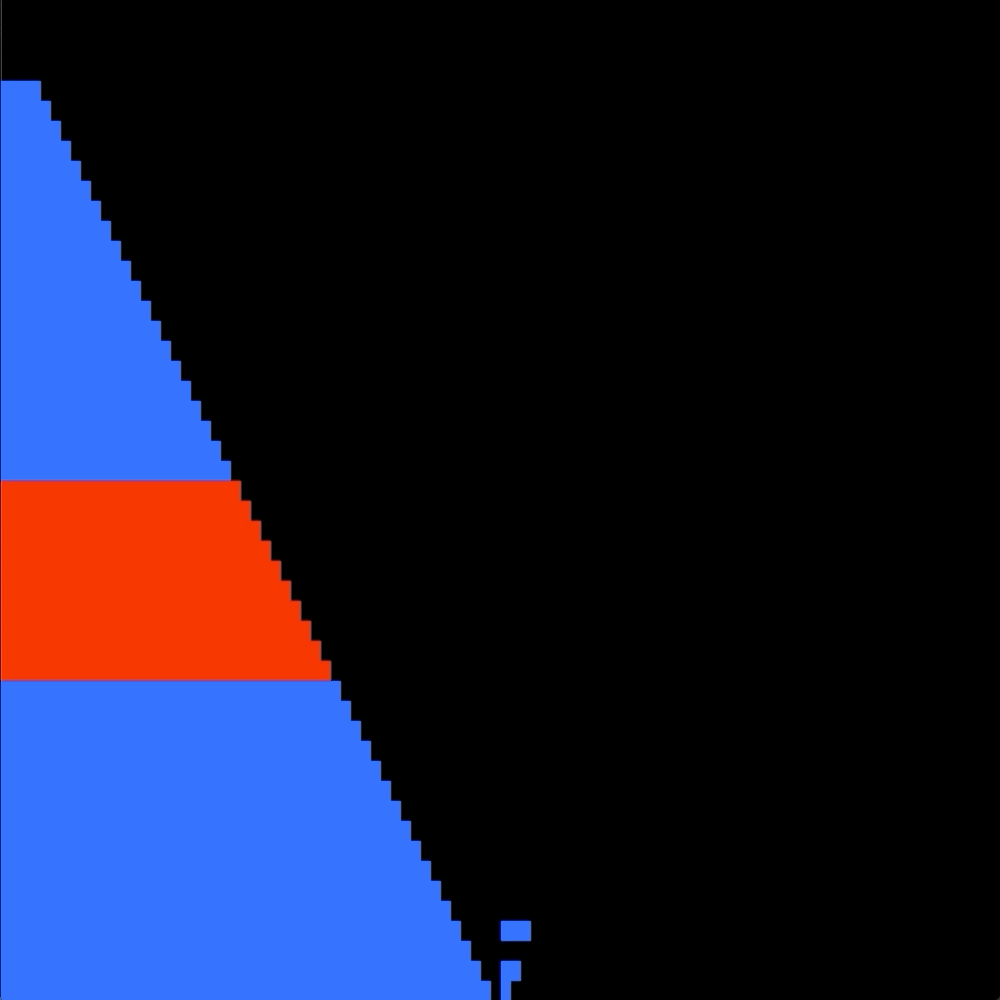
The goal is to sort in ascending order numbers into stack a.
 To do this you have the following operations at your disposal:
To do this you have the following operations at your disposal:
- sa : swap a - swap the first 2 elements at the top of stack a.
- sb : swap b - swap the first 2 elements at the top of stack b.
- ss : sa and sb at the same time.
- pa : push a - take the first element at the top of b and put it at the top of a.
- pb : push b - take the first element at the top of a and put it at the top of b.
- ra : rotate a - shift up all elements of stack a by 1. The first element becomes the last one.
- rb : rotate b - shift up all elements of stack b by 1. The first element becomes the last one.
- rr : ra and rb at the same time.
- rra : reverse rotate a - shift down all elements of stack a by 1. The last element becomes the first one.
We needed to write 2 programs in C:
• The first, named checker which takes integer arguments and reads instructions on the standard output. Once read, checker executes them and displays OK if integers are sorted. Otherwise, it will display KO.
• The second one called push_swap which calculates and displays on the standard output the smallest progam using Push_swap instruction language that sorts integer arguments received.
I chose to first see if there is a "bruteforce" solution where i look if there is a way wich doesn't involve the B stack, so only using the sa, ra, and rra operation.
If there is no easy bruteforce solution my alorithm performs a enhanced quicksort to push every integers on the B stack.
Then a simple selection sort push everything back in order on the A stack.
You need to install sdl2
brew sdl2
Then do
make
You will first choose an ARG composed by integers. Example :
ARG="4 67 3 87 23";
100 shuffled numbers :
ARG=`ruby -e "puts (0..99).to_a.shuffle.join(' ')"`
Then if you want to see the number of operations required:
./push_swap $ARG | wc -l
Now do everything :
ARG=`ruby -e "puts (0..99).to_a.shuffle.join(' ')"`; ./push_swap $ARG | ./checker $ARG
With visualiation :
ARG=`ruby -e "puts (0..99).to_a.shuffle.join(' ')"`; ./push_swap $ARG | ./checker -v $ARG
