A resource allocation application using machine learning technique assisted by cloud computing implemented in Python
An application i've created based on the following paper: "A Machine Learning Framework for Resource Allocation Assisted by Cloud Computing" which is introducing a framework to do resource allocation using Machine Learning techniques and assist Cloud Computing for doing the job(for more details refer to the paper). Please note that this application is a small scale implementaion of the base paper.
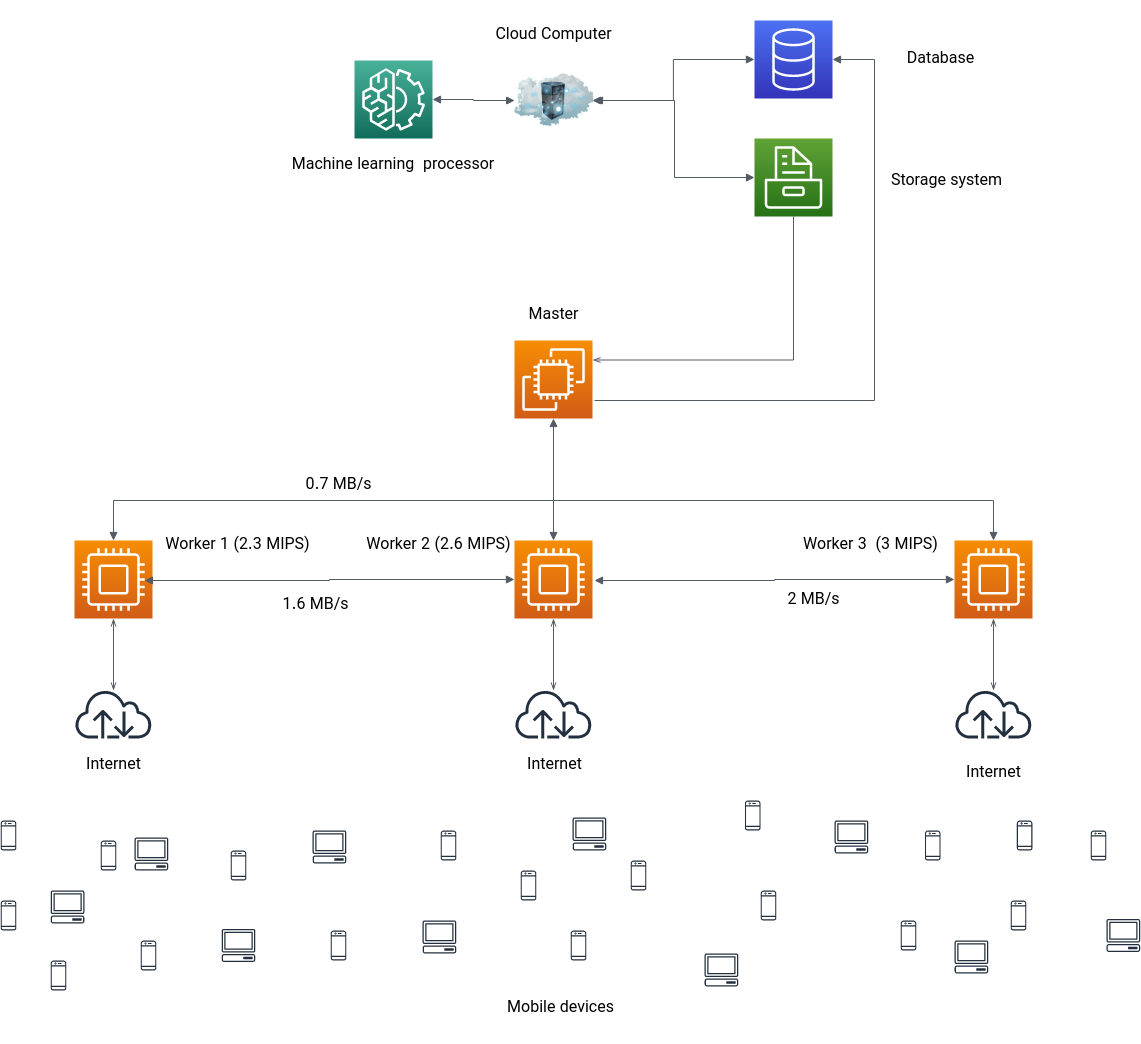
The following imag depicts the geographic system over the network.
Each section of the application documented below:
As the system uses Machine learning to allocate the proper resources, we need data. But finding a prepared and clean data for doing such thing in small scale is not much possible(unless you use Data provided by AWS or Google on massive Data centers). So i created my own Data. The Data Creator module (Seeder module in /Cloud/storage) uses a predefined template(/Cloud/storage/data/seeder_data_template.csv) to create data. description of attributes, classes, values and ... are in the /Cloud/storage/data/data_description.txt file.
First the seeder module reads the seeder_data_template.csv file and creates a data based on it in /Cloud/storage/data/dat.csv file. Attributes, classes and values are manipulatable but needs coding also.
To execute the seeder and create the data, run python3 Cloud/seeder.py. change the '/' to '\' in case you are using a non-unix based system.
the command outputs the data.csv file
The Cloud Module is Responsible for Storing Raw data, Preprocessing the Data, Managing the Warehouses, Learn based on the Data and Create ML model based on it and finally Sending Model To Edges. We can Consider it as the Brain of our system.
Data is stored in it's storage system and in here, we do the whole learning process in the cloud.py module (in Cloud/Storage/cloud.py, Not a Python Class). the code is fully commented in Docstring format so there is no need for details description but an overview. the Module reads the Data, splits it on 70 percent for training and 30 percent testing, Trains it's model using Decision Tree Classifier Technique, Tests it's model and persists it's model in the storage system. The Classifier Technique is chosen using Cross validation Technique which showed that Decision Tree can classify the Data with 85 percent Accuracy which is a good number for resource allocation. other techniques like KNN had about 65 percents accuracy on out data
The cloud module is executable using python3 Cloud/cloud.py command. it outputs a model with joblib format on our storage.
Cloudlets are just Tasks, a name chosen by Cloudsim framework. Tasks are generated on different areas (in our application we have 3 different position).
Attributes, values and classes are listed bellow. the raw Data Created are all in numbers categorizes or continues, but we preprocess them to categorized values, for example a task with 120 mi is considered as a task with high level instruction (more than 100). the thresholds are calculated using test and trial process. values af each tasks are Generated randomly. What we need to do is to find best Worker for Each Task
| Attributes | Position | Instructions (million instructions) | Size (MB) | High Priority | Allocated Worker (Class) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| values | area 1 | High (1 to 100) | High (1 to 10) | True | Worker in Area 1 |
| area 2 | Low (101 to 300) | Low (11 to 30) | False | Worker in Area 2 | |
| area 3 | Worker in area 3 | ||||
| Type | Categorized | Continues | Continues | Categorized | Categorized |
Cloudlet is a Class Generated in edges so i placed it in Edges/Cloudlet.py. creating object of the Class initializes it's attributes. Code is fully commented.
Worker is our Resources, machines which does the jobs. all workers are Inheriting the Mother Worker Class (Edges/workers/worker.py file) which has all the functionalities and attributes. each worker can override these properties by their own. my application has 3 workers. each worker has some attributes:
- Position: position of the worker server
- Power: Power of the worker server in million instructions per seconds
- Bandwidth: Bandwidth Between the worker server and other Workers in MB/s
- Makespan (timer): the time the worker consumed to do the jobs in seconds
Worker is a class, so creating a class with optional name and inheriting the Worker Class would create a worker server.
If we name the Cloud module as the Brain of our system, Master Node of the system is it's heart. It's responsible for getting information of each Cloudlet and finding the best Worker for it using the trained model in the cloud storage. for instance web have a task, the metadata of the task is being sent to the Master Node, it choses best Worker by considering all attributes of Cloudlet and Workers, then Attaching The Cloudlet To The Worker. Worker then gets the Cloudlet through the Network and does the job. In this application i've implemented a greedy approach to compare the functionality and performance of the ML model with it. the Greedy algorithm considers Size and Instructions of the Task not it's priority.
Master Class declares itself and does the job. following command: python3 Edges/Master.py would do it all and prints the outputs.
i chose values for attributes in Cloudlets and workers using Test and Trial. my purpose was that the Worker 3 have more power than Worker 2 and Worker 2 than 3. but the bandwidth between 1 and 3 is very low , between 1 and 2 is high and between 2 and 3 is the highest. Running the resource allocation process using the application had following results average on 40 time of execution:
Using Machine learning Technique:
- Worker 1 Makespan: 221.5 s
- Worker 2 Makespan: 569 s
- Worker 3 Makespan: 982.5 s
Using Greedy Algorithm
- Worker 1 Makespan: 322.2 s
- Worker 2 Makespan: 248.4 s
- Worker 3 Makespan: 1050.5 s
Which shows the ML model does a better job spreading the tasks on workers and lowering the overall makespan. As you can see the Greedy algorithm Sends most of the Tasks To Worker 3. but ML balances the loads as we wanted it to be. although the Data was Generated but a human so the result has to be what we. In real world Application the process of training the mode is not once and can even be in intervals so that it can find the best way to allocate resources.