Conducting one-vs-all classification on the 'penguins.csv' dataset using both the Naive Bayes classifier implemented from scratch and the one provided by Scikit-Learn's built-in functions.
In the Bayes classifier for L number of features,
Firstly, the dataset undergoes preprocessing where null values are filled with the mean, and numerical values are normalized using the following code. The dataset has been split into a training set and a test set.
def preprocess(data):
df = data.copy()
value = df.drop(df.columns[0], axis=1, inplace=False)
label = df[df.columns[0]]
value = value.apply(lambda col: filling(col))
value = normalize(value)
return value, label
def filling(col):
col = pd.to_numeric(col, errors='coerce').astype('float64')
return col.fillna(col.mean())
def normalize(value):
msc = MinMaxScaler()
return pd.DataFrame(msc.fit_transform(value), columns=value.columns)Below is the implementation of Naive Bayes classification from scratch.
class NaiveBayes():
def __init__(self, X, y):
self.value = train_value
self.label = train_label
self.classes = np.unique(self.label)
self.mean = np.zeros((len(self.classes), len(self.value.columns)))
self.var = np.zeros((len(self.classes), len(self.value.columns)))
self.prior = np.zeros((len(self.classes)))
def train(self):
self.calculate_mean()
self.calculate_var()
self.calculate_prior()
def calculate_mean(self):
for i,cls in enumerate(self.classes):
for j,feature in enumerate(self.value.columns):
self.mean[i][j] = self.value[self.label==cls][feature].mean(axis=0)
def calculate_var(self):
for i,cls in enumerate(self.classes):
for j,feature in enumerate(self.value.columns):
self.var[i][j] = self.value[self.label==cls][feature].var(axis=0)
def calculate_prior(self):
for i ,cls in enumerate(self.classes):
self.prior[i]=sum(self.label==cls)/len(self.label)
def predict(self, test_value, test_label):
df = test_value.copy()
df['y_pred'] = test_value.apply(lambda row: self.posterior(np.array(row)), axis=1)
df = pd.concat([df, test_label], axis=1)
return df
def posterior(self,x):
prob=[]
for i,cls in enumerate(self.classes):
post=np.sum(self.prior[i]*self.likelihood(i,x))
prob.append(post)
max_idx=np.argmax(prob)
return self.classes[max_idx]
def likelihood(self,cls_idx,x):
mean,var=self.mean[cls_idx],self.var[cls_idx]
prob=(np.exp(-(x-mean)**2/(2*var))/np.sqrt(2*np.pi*var))
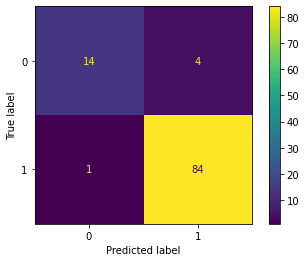
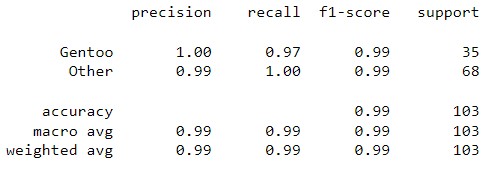
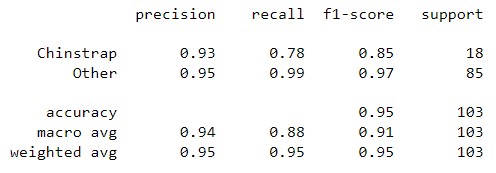
return probWith the given dataset, the penguins need to be classified into three species, namely Adelie, Gentoo, and Chinstrap. This task falls under multi-class classification, and the one-vs-all method is utilized to achieve the classification.
| Result | Adelie vs. All | Gentoo vs. All | Chinstrap vs. All |
|---|---|---|---|
| Confusion Matrix | 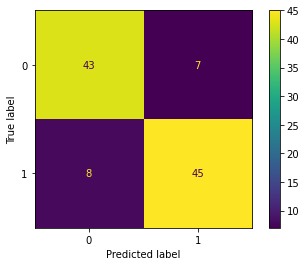 |
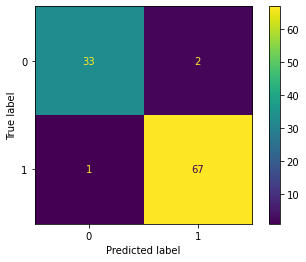 |
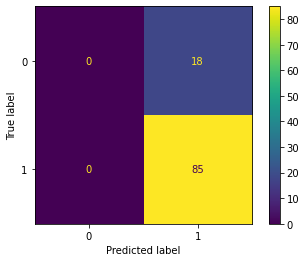 |
| Classification Report | 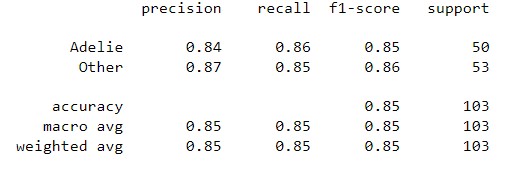 |
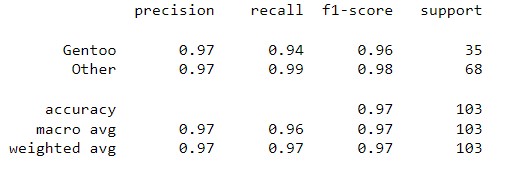 |
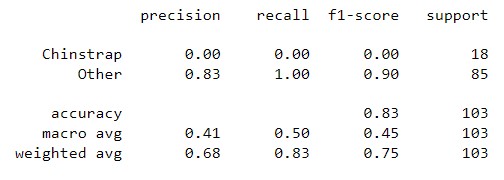 |
In this section, the Naive Bayes classifier is implemented using the Scikit-learn library for classifying penguins into three species: Adelie, Gentoo, and Chinstrap. The one-vs-all method is employed to accomplish this task.
from sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNB| Result | Adelie vs. All | Gentoo vs. All | Chinstrap vs. All |
|---|---|---|---|
| Confusion Matrix | 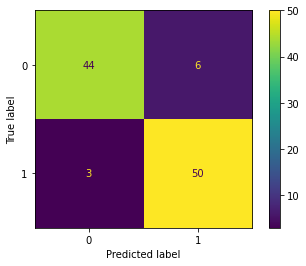 |
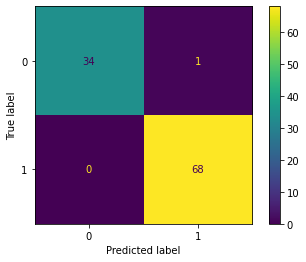 |
 |
| Classification Report | 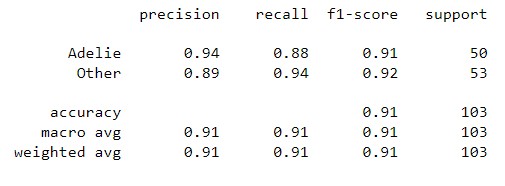 |
 |
 |
- Course: Machine Learning [ECE 501]
- Semester: Spring 2023
- Institution: School of Electrical & Computer Engineering, College of Engineering, University of Tehran
- Instructors: Dr. A. Dehaqani, Dr. Tavassolipour