[The library is still in development. The doc is not completed yet. You can contribute to improve the library.]
capslock is a high level utility library written in python for writing certain frequently needed task in faster & efficient way. For example, if you want to keep track of the execution time of one of your method while optimizing it, witing code for tracking execution time can be done easily using capslock.
Install using the following command -
pip install capslockUninstall using the following command -
pip uninstall capslockCapslock defines different decorators that can be used out of the box for certain frequent tasks. E.g. getting the run time of certain function over the period of optimization in development phase.
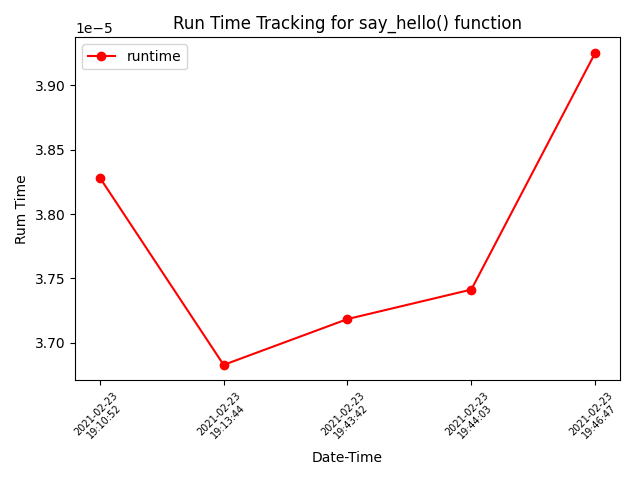
To keep track of the execution time of a function in your project for optimizing it over the time, just put the "timing" decorator in your desired function. Capslock will keep track of different run of that function and will plot a well visualized graph for last five execution time of that function.
from capslock import timing
@timing(plot=True)
def say_hello():
print("Hello World")
if __name__ == '__main__':
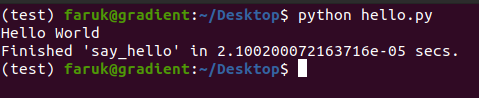
say_hello()This will generate output like bellow:
And it will also keep track of runtime for different runs of the say_hello() function. and will plot a graph in the same directory of your python script if you set plot=True, otherwise the plot flag is by default False.
To get debug information of anyof your function, follow the bellow instruction-
from capslock import debug
@debug
def add(number1, number2):
return number1 + number2
if __name__ == '__main__':
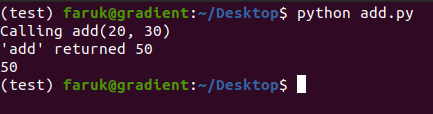
print(add(20, 30))will provide you the following output with some debug information-
To run a function multiple times, use the run_multiple_times decorator from capslock package.
from datetime import datetime
from capslock import run_multiple_times
@run_multiple_times(times=10)
def current_time():
now = datetime.now()
return now.strftime("%H:%M:%S.%f")
if __name__ == '__main__':
print(current_time())will run the current time function 10 times.
If you want to prevent some accidental execution of a certain part of code
that might cause system-wide changes and you wish the user to have root
previllege before running that part of the python code, just use the
require_root decorator from capslock.
from capslock import require_root
@require_root
def say_hello():
for _ in range(10):
print("Hello World")
if __name__ == '__main__':
say_hello()Now, say_hello() will only run, if the user is root.
If you want to see your function output as colorful this method might help you to color your function output.
At present this method support these colors BLUE, CYAN, GREEN, YELLOW, RED, BOLD, UNDERLINE
from capslock import color_output
@color_output("RED")
def hello_color():
return "Hey! How are you!"
if __name__ == '__main__':
hello_color()If you have a memory intensive workload function and you know the minimum memory requriement, you can restrict the fucntion execution by checking the available memory in that system beforehand by using this decorator.
from capslock import requires_ram
@requires_ram(8)
def memory_intensive_task():
print("Running a memory-intensive task...")
if __name__ == '__main__':
memory_intensive_task()If the system has less memory than mentioned in the decorator, the function will not execute. E.g., in the above example, if the system has 8 GB or more RAM, then the function will execute.
You can contribute in different ways. You can add more decorators for frequently used tasks in day to day development works.