Node-Red node to receive Server-Sent-Events.
Run the following npm command in your Node-RED user directory (typically ~/.node-red):
npm install node-red-contrib-sse-client
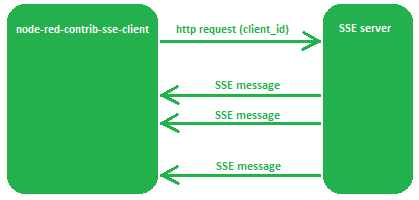
Server-Sent Events allow a client (e.g. a web page in a browser) to get automatically data updates from a server.
This SSE client node sends a single http request to the SSE server, and subscribes for all events at the server. As soon as an event occurs at the SSE server, the server will send the data of the event to this client. This way data streaming is accomplished...
The example flow below is based on this demo SSE stream. By opening the stream with a browser (e.g. Chrome), the content of the stream can be displayed:
[{"id":"87f5d0b2.73f1c","type":"inject","z":"11289790.c89848","name":"Start / Restart / Unpause stream","topic":"","payload":"","payloadType":"date","repeat":"","crontab":"","once":false,"onceDelay":0.1,"x":910,"y":1140,"wires":[["75b9f7f0.4fa048"]]},{"id":"968f88dc.b6b038","type":"inject","z":"11289790.c89848","name":"Pause stream","topic":"","payload":"","payloadType":"date","repeat":"","crontab":"","once":false,"onceDelay":0.1,"x":850,"y":1220,"wires":[["688fcd58.649974"]]},{"id":"55e6b089.e3da4","type":"debug","z":"11289790.c89848","name":"Display event","active":true,"tosidebar":true,"console":false,"tostatus":false,"complete":"true","x":1480,"y":1140,"wires":[]},{"id":"688fcd58.649974","type":"change","z":"11289790.c89848","name":"","rules":[{"t":"set","p":"pause","pt":"msg","to":"true","tot":"bool"}],"action":"","property":"","from":"","to":"","reg":false,"x":1080,"y":1220,"wires":[["75b9f7f0.4fa048"]]},{"id":"3346b21d.2c5c1e","type":"inject","z":"11289790.c89848","name":"Stop stream","topic":"","payload":"","payloadType":"date","repeat":"","crontab":"","once":false,"onceDelay":0.1,"x":850,"y":1180,"wires":[["b11da9d5.f8d938"]]},{"id":"b11da9d5.f8d938","type":"change","z":"11289790.c89848","name":"","rules":[{"t":"set","p":"stop","pt":"msg","to":"true","tot":"bool"}],"action":"","property":"","from":"","to":"","reg":false,"x":1090,"y":1180,"wires":[["75b9f7f0.4fa048"]]},{"id":"75b9f7f0.4fa048","type":"sse-client","z":"11289790.c89848","name":"","url":"https://proxy.streamdata.io/http://stockmarket.streamdata.io/prices/","events":["patch"],"headers":{},"proxy":"","restart":true,"rejectUnauthorized":false,"withCredentials":true,"timeout":"10","x":1290,"y":1140,"wires":[["55e6b089.e3da4"]]}]
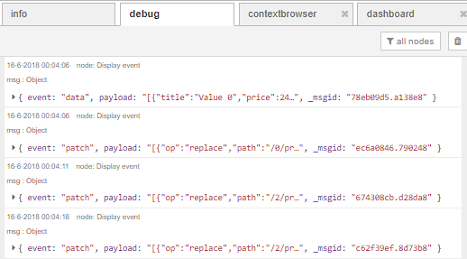
In most cases the server will not specify an event type, which means the client will assign the default event type 'message'. However in this example stream, the sever sends two different event types 'data' and 'patch'.
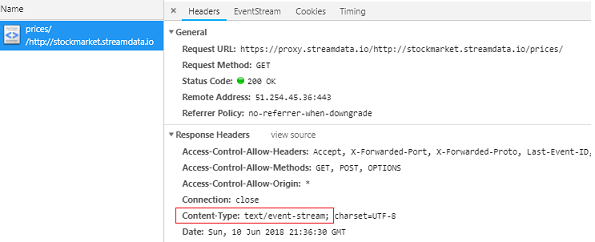
P.S. If you are wondering whether your data stream is an SSE stream (or perhaps some other streaming type), have a look at the 'content-type' of the http response. In case of SSE streaming, the content-type should contain 'event-stream'. For example in Chrome this can be visualised in the Developer Tools (Network tab):
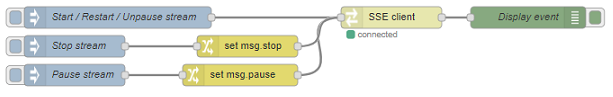
The following example flow explains how this node works:
[{"id":"715e407a.e85bf","type":"inject","z":"11289790.c89848","name":"Start / Restart / Unpause stream","topic":"","payload":"","payloadType":"date","repeat":"","crontab":"","once":false,"onceDelay":0.1,"x":910,"y":1060,"wires":[["c901454e.b1d798"]]},{"id":"8b7134c9.554938","type":"inject","z":"11289790.c89848","name":"Pause stream","topic":"","payload":"","payloadType":"date","repeat":"","crontab":"","once":false,"onceDelay":0.1,"x":850,"y":1140,"wires":[["2994d674.bab3fa"]]},{"id":"9b17cec2.d676b","type":"debug","z":"11289790.c89848","name":"Display event","active":true,"tosidebar":true,"console":false,"tostatus":false,"complete":"true","x":1480,"y":1060,"wires":[]},{"id":"2994d674.bab3fa","type":"change","z":"11289790.c89848","name":"","rules":[{"t":"set","p":"pause","pt":"msg","to":"true","tot":"bool"}],"action":"","property":"","from":"","to":"","reg":false,"x":1080,"y":1140,"wires":[["c901454e.b1d798"]]},{"id":"f6380689.8056d8","type":"inject","z":"11289790.c89848","name":"Stop stream","topic":"","payload":"","payloadType":"date","repeat":"","crontab":"","once":false,"onceDelay":0.1,"x":850,"y":1100,"wires":[["9804188f.b94b18"]]},{"id":"9804188f.b94b18","type":"change","z":"11289790.c89848","name":"","rules":[{"t":"set","p":"stop","pt":"msg","to":"true","tot":"bool"}],"action":"","property":"","from":"","to":"","reg":false,"x":1090,"y":1100,"wires":[["c901454e.b1d798"]]},{"id":"c901454e.b1d798","type":"sse-client","z":"11289790.c89848","name":"","url":"https://proxy.streamdata.io/http://stockmarket.streamdata.io/prices/","events":["patch"],"headers":{},"proxy":"","restart":true,"rejectUnauthorized":false,"withCredentials":true,"timeout":"10","x":1290,"y":1060,"wires":[["9b17cec2.d676b"]]}]
The node will be controlled by the input messages it receives:
- Start the stream by sending a message to the node (which doesn't contain msg.stop or msg.pause). The node will send a http request to the server, to subscribe for all event types. This can be used to:
- Start a new stream in the beginning, when no stream has been started yet.
- Stop the current active stream and immediately start a new stream.
- Resume a paused stream.
- Stop the current (active or paused) stream by sending a message with
msg.stop = trueto the node. The connection to the server will be disconnected entirely, and no events will be streamed anymore to our client node. Start the stream again afterwards by sending a new input message, to reconnect again to the server. - Pause the current active stream by sending a message with
msg.pause = trueto the node. The connection to the server will stay open, and the events will keep coming from the server! However the client will skip all those events, as long as the client is paused. Resume the stream again afterwards by sending a new (arbitrary) input message, so the client will stop ignoring events from the server.
When controlling this node, the node will be in one of the following statusses:
When you don't know which event types are being streamed from the server, then following way of working is advised:
-
Start by specifying no event types in the node's config screen.
-
As a result, ALL event types will be received from the server.
-
Determine which event types are interesting for your purpose.
-
Specify those indiviual event types (that you want to keep receiving) in the node's config screen.
This URL refers to the resource (e.g. php file) on the SSE server, which will be able to respond by pushing SSE events to this client.
When the URL is not specified in the config screen, it has to be specified in the msg.url field:
[{"id":"6c4db38d.c9d5ac","type":"inject","z":"11289790.c89848","name":"Start / Restart / Unpause stream","topic":"","payload":"","payloadType":"date","repeat":"","crontab":"","once":false,"onceDelay":0.1,"x":830,"y":940,"wires":[["77c2e6d.3e19a18"]]},{"id":"5d134fb6.0f921","type":"debug","z":"11289790.c89848","name":"Display event","active":true,"tosidebar":true,"console":false,"tostatus":false,"complete":"true","x":1500,"y":940,"wires":[]},{"id":"77c2e6d.3e19a18","type":"change","z":"11289790.c89848","name":"","rules":[{"t":"set","p":"url","pt":"msg","to":"https://proxy.streamdata.io/http://stockmarket.streamdata.io/prices/","tot":"str"}],"action":"","property":"","from":"","to":"","reg":false,"x":1090,"y":940,"wires":[["fc36aac.4889158"]]},{"id":"fc36aac.4889158","type":"sse-client","z":"11289790.c89848","name":"","url":"","events":["patch"],"headers":{},"proxy":"","restart":true,"rejectUnauthorized":false,"withCredentials":true,"timeout":"10","x":1290,"y":940,"wires":[["5d134fb6.0f921"]]}]
Specify a list of event types that needs to be received. When no events types are specified, this means that ALL events will be handled. When a single incorrect event name is specified, no events will be received in the Node-Red flow (without having an error)!
Optionally http headers can be specified, which will be send to the SSE server in the initial http request. This can be used for example to send cookies to the server.
When the Http headers are not specified in the config screen, they can be specified in the msg.headers field.
Optionally a proxy url can be specified, in case a (corporate) firewall is isolating the Node-Red flow from the SSE server.
When this checkbox is selected, a timeout interval (in seconds) can be specified. When no event is received in that timeout interval, the connection to the SSE server will be disconnected and reconnected again automatically.
Remark: this option has no effect if the node is being paused! Indeed when the node is paused, no events will be received anyway ...
In case of a https based URL, a secure SSL connection will be setup based on the server certificate that this node will receive.
As soon as the server certificate arrives, it will be validated (validity period, hostname and CA certificate chain):
When the validation fails, the connection will automatically be aborted. By deselecting this option, the server certificate will not be validated anymore and the connection will be accepted automatically.
CAUTION: don't used this feature for secure information, because malicous services could have been tempering with the certificate to intercept the event stream information!
When this checkbox is selected, the credentials (cookies, authorization headers or TLS client certificates) will be passed to cross-domain Access-Control requests. Then on the server side, the 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' header can be set to a wildcard '*'.
Similar to some other nodes in Node-RED, this node also allows URL's with Mustache syntax. Such a syntax allows the URL to be constructed dynamically, using values of the incoming message.
For example, if the URL is set to example.com/{{{some_field}}}, then the value of msg.some_field will automatically be inserted into this placeholder. So if msg.some_field contains '123456', then the URL will become example.com/123456.
[{"id":"72d804d4.e27f3c","type":"inject","z":"11289790.c89848","name":"Start stream","topic":"","payload":"","payloadType":"date","repeat":"","crontab":"","once":false,"onceDelay":0.1,"x":950,"y":1140,"wires":[["7ce97ec6.e5095"]]},{"id":"440cfc8c.aa48f4","type":"debug","z":"11289790.c89848","name":"Display event","active":true,"tosidebar":true,"console":false,"tostatus":false,"complete":"true","x":1560,"y":1140,"wires":[]},{"id":"5bd574da.a75a7c","type":"sse-client","z":"11289790.c89848","name":"","url":"example.com/{{{some_field}}}","events":["patch"],"headers":{},"proxy":"","restart":true,"rejectUnauthorized":false,"withCredentials":true,"timeout":"10","x":1350,"y":1140,"wires":[["440cfc8c.aa48f4"]]},{"id":"7ce97ec6.e5095","type":"change","z":"11289790.c89848","name":"","rules":[{"t":"set","p":"some_field","pt":"msg","to":"\"123456\"","tot":"str"}],"action":"","property":"","from":"","to":"","reg":false,"x":1150,"y":1140,"wires":[["5bd574da.a75a7c"]]}]
P.S. Mustache allows double brackets {{...}} to be used. However by using triple brackets {{{...}}}, we will prevent Mustache from escaping characters like / and & ...
To simplify the usage of this contribution, a user should be able to receive all events. Indeed this is very handy if the user doesn't know which event types are being send by the SSE server. However the SSE protocol doesn't support listening to all events! That is the reason why I couldn't get this functionality implemented in the EventSource. So unfortunately I had to create a fork of the EventSource node, and copy it to this project. When a new version of EventSource is needed for some reason, my fork needs to be updated ...