User-friendly and flexible algorithm for time series segmentation with a regression model governed by a hidden Markov process.
Hidden Markov Model Regression (HMMR) for segmentation of time series with regime changes. The model assumes that the time series is governed by a sequence of hidden discrete regimes/states, where each regime/state has Gaussian regressors as observations. The model parameters are estimated by MLE via the EM algorithm.
You can install the development version of HMMR from GitHub with:
# install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("fchamroukhi/HMMR_r")To build vignettes for examples of usage, type the command below instead:
# install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("fchamroukhi/HMMR_r",
build_opts = c("--no-resave-data", "--no-manual"),
build_vignettes = TRUE)Use the following command to display vignettes:
browseVignettes("HMMR")library(HMMR)# Application to a toy data set
data("toydataset")
x <- toydataset$x
y <- toydataset$y
K <- 5 # Number of regimes (states)
p <- 3 # Dimension of beta (order of the polynomial regressors)
variance_type <- "heteroskedastic" # "heteroskedastic" or "homoskedastic" model
n_tries <- 1
max_iter <- 1500
threshold <- 1e-6
verbose <- TRUE
hmmr <- emHMMR(X = x, Y = y, K, p, variance_type, n_tries,
max_iter, threshold, verbose)
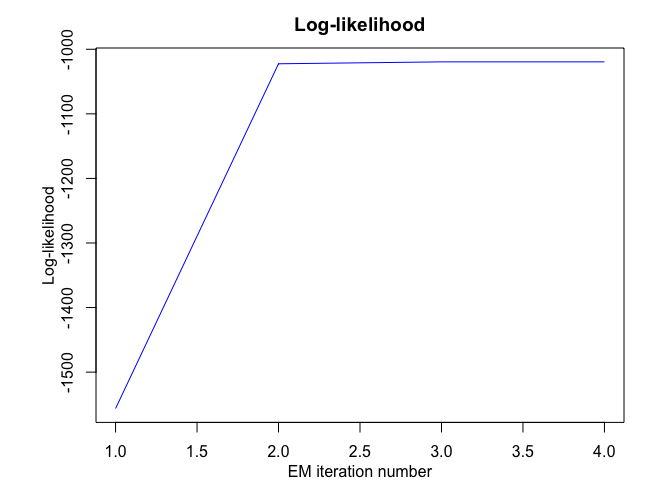
#> EM - HMMR: Iteration: 1 | log-likelihood: -1556.39696825601
#> EM - HMMR: Iteration: 2 | log-likelihood: -1022.47935723687
#> EM - HMMR: Iteration: 3 | log-likelihood: -1019.51830707432
#> EM - HMMR: Iteration: 4 | log-likelihood: -1019.51780361388
hmmr$summary()
#> ---------------------
#> Fitted HMMR model
#> ---------------------
#>
#> HMMR model with K = 5 components:
#>
#> log-likelihood nu AIC BIC
#> -1019.518 49 -1068.518 -1178.946
#>
#> Clustering table (Number of observations in each regimes):
#>
#> 1 2 3 4 5
#> 100 120 200 100 150
#>
#> Regression coefficients:
#>
#> Beta(k = 1) Beta(k = 2) Beta(k = 3) Beta(k = 4) Beta(k = 5)
#> 1 6.031872e-02 -5.326689 -2.65064 120.8612 3.858683
#> X^1 -7.424715e+00 157.189455 43.13601 -474.9870 13.757279
#> X^2 2.931651e+02 -643.706204 -92.68115 598.3726 -34.384734
#> X^3 -1.823559e+03 855.171715 66.18499 -244.5175 20.632196
#>
#> Variances:
#>
#> Sigma2(k = 1) Sigma2(k = 2) Sigma2(k = 3) Sigma2(k = 4) Sigma2(k = 5)
#> 1.220624 1.111487 1.080043 0.9779724 1.028399
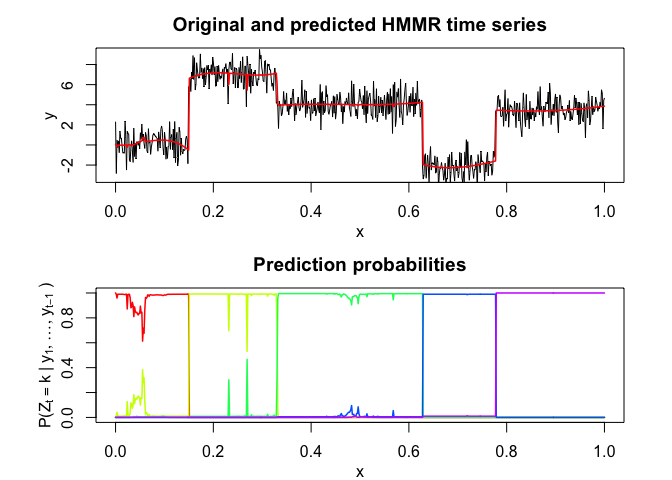
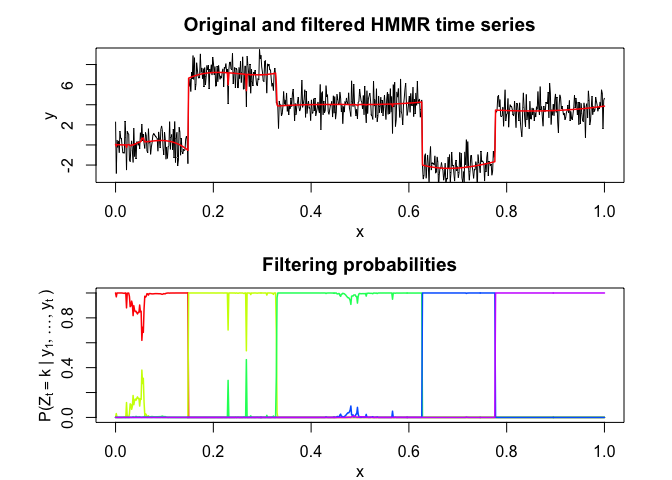
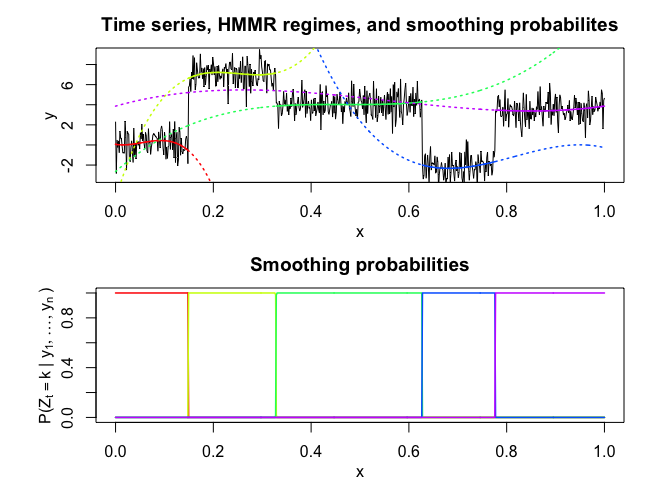
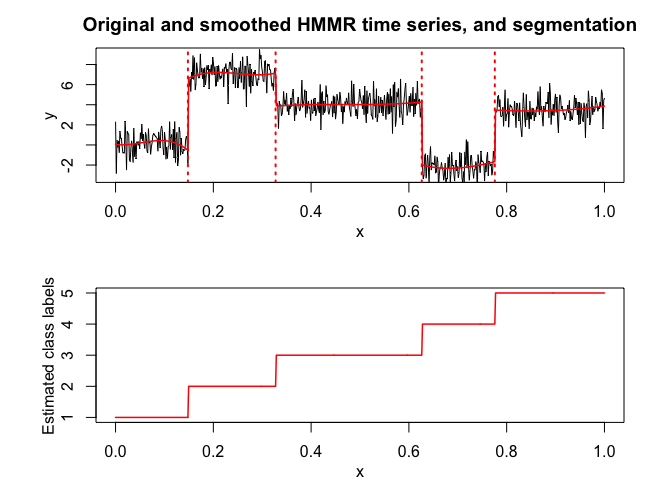
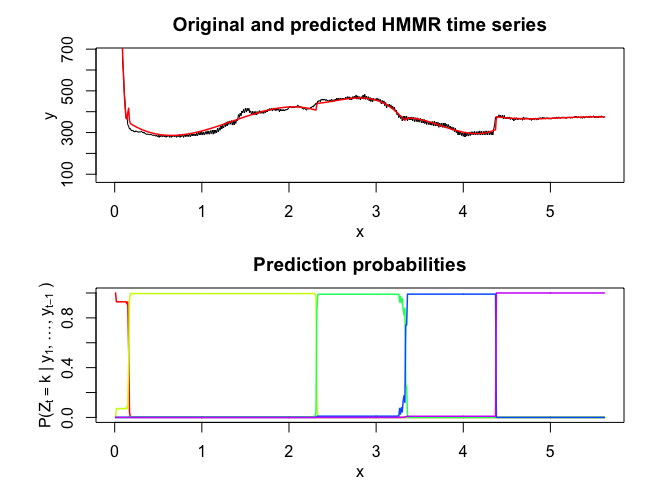
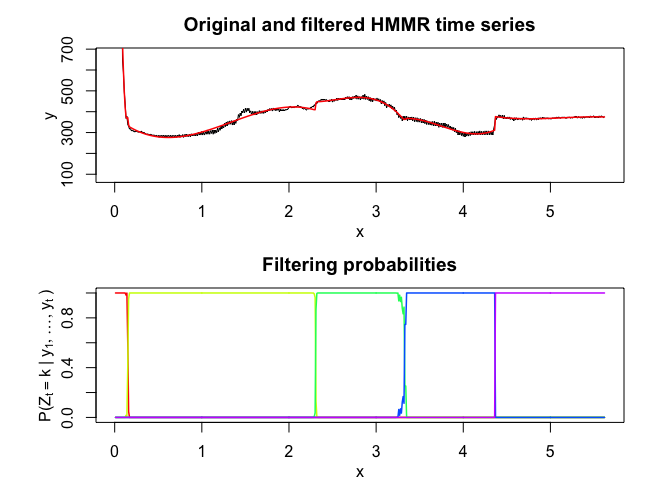
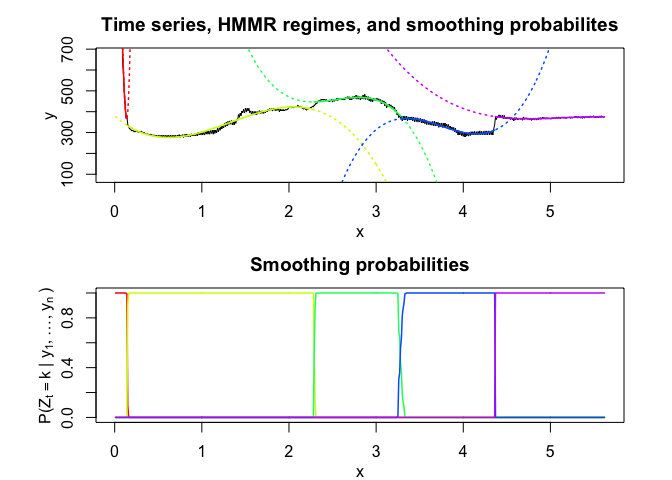
hmmr$plot()# Application to a real data set
data("realdataset")
x <- realdataset$x
y <- realdataset$y2
K <- 5 # Number of regimes (states)
p <- 3 # Dimension of beta (order of the polynomial regressors)
variance_type <- "heteroskedastic" # "heteroskedastic" or "homoskedastic" model
n_tries <- 1
max_iter <- 1500
threshold <- 1e-6
verbose <- TRUE
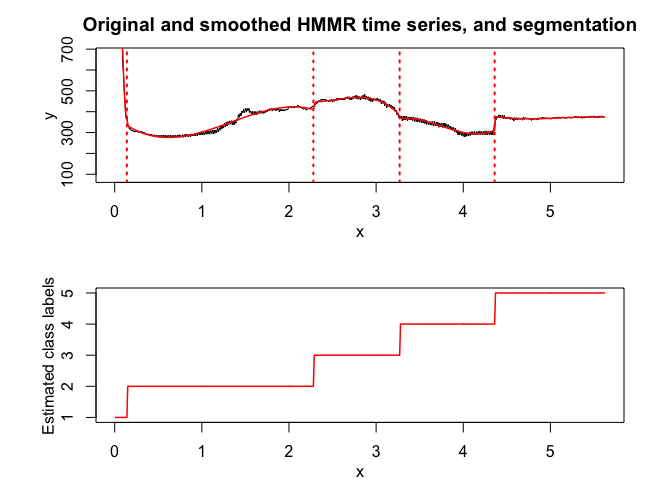
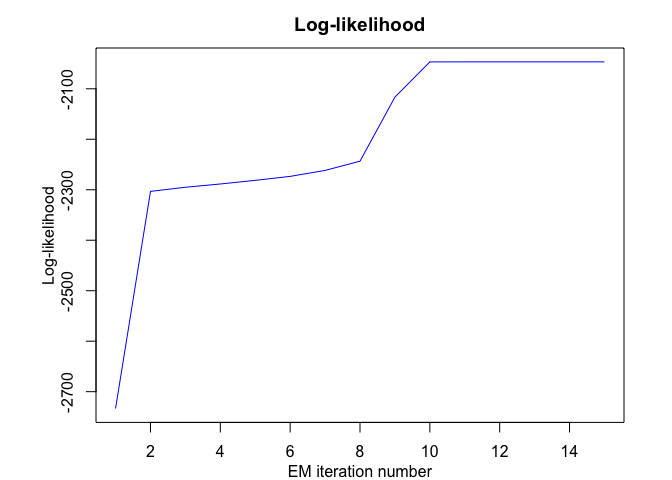
hmmr <- emHMMR(X = x, Y = y, K, p, variance_type,
n_tries, max_iter, threshold, verbose)
#> EM - HMMR: Iteration: 1 | log-likelihood: -2733.41028643114
#> EM - HMMR: Iteration: 2 | log-likelihood: -2303.24018378559
#> EM - HMMR: Iteration: 3 | log-likelihood: -2295.0470677529
#> EM - HMMR: Iteration: 4 | log-likelihood: -2288.57866215726
#> EM - HMMR: Iteration: 5 | log-likelihood: -2281.36756202518
#> EM - HMMR: Iteration: 6 | log-likelihood: -2273.50303676091
#> EM - HMMR: Iteration: 7 | log-likelihood: -2261.70334656117
#> EM - HMMR: Iteration: 8 | log-likelihood: -2243.43509121433
#> EM - HMMR: Iteration: 9 | log-likelihood: -2116.4610801575
#> EM - HMMR: Iteration: 10 | log-likelihood: -2046.73194777839
#> EM - HMMR: Iteration: 11 | log-likelihood: -2046.68328282973
#> EM - HMMR: Iteration: 12 | log-likelihood: -2046.67329222076
#> EM - HMMR: Iteration: 13 | log-likelihood: -2046.66915144265
#> EM - HMMR: Iteration: 14 | log-likelihood: -2046.66694236131
#> EM - HMMR: Iteration: 15 | log-likelihood: -2046.66563379017
hmmr$summary()
#> ---------------------
#> Fitted HMMR model
#> ---------------------
#>
#> HMMR model with K = 5 components:
#>
#> log-likelihood nu AIC BIC
#> -2046.666 49 -2095.666 -2201.787
#>
#> Clustering table (Number of observations in each regimes):
#>
#> 1 2 3 4 5
#> 14 214 99 109 126
#>
#> Regression coefficients:
#>
#> Beta(k = 1) Beta(k = 2) Beta(k = 3) Beta(k = 4) Beta(k = 5)
#> 1 2152.64 379.75158 5211.1759 -14306.4654 6417.62823
#> X^1 -12358.67 -373.37266 -5744.7879 11987.6666 -3571.94086
#> X^2 -103908.33 394.49359 2288.9418 -3233.8021 699.55894
#> X^3 722173.26 -98.60485 -300.7686 287.4567 -45.42922
#>
#> Variances:
#>
#> Sigma2(k = 1) Sigma2(k = 2) Sigma2(k = 3) Sigma2(k = 4) Sigma2(k = 5)
#> 9828.793 125.3346 58.71053 105.8328 15.66317
hmmr$plot()In this package, it is possible to select models based on information criteria such as BIC, AIC and ICL.
The selection can be done for the two following parameters:
- K: The number of regimes;
- p: The order of the polynomial regression.
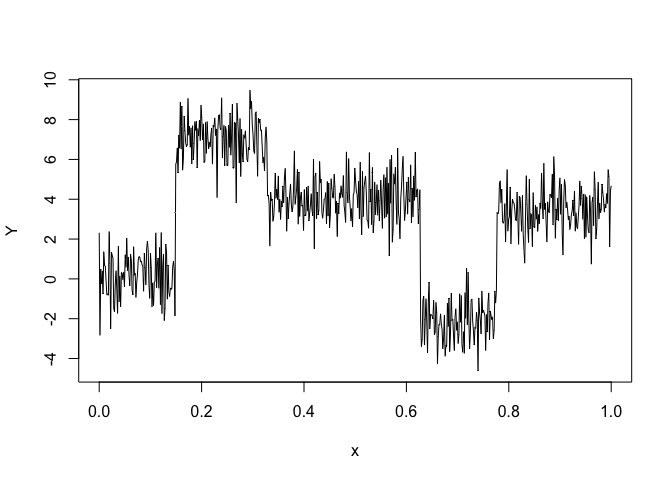
Let’s select a HMMR model for the following time series Y:
data("toydataset")
x <- toydataset$x
y <- toydataset$y
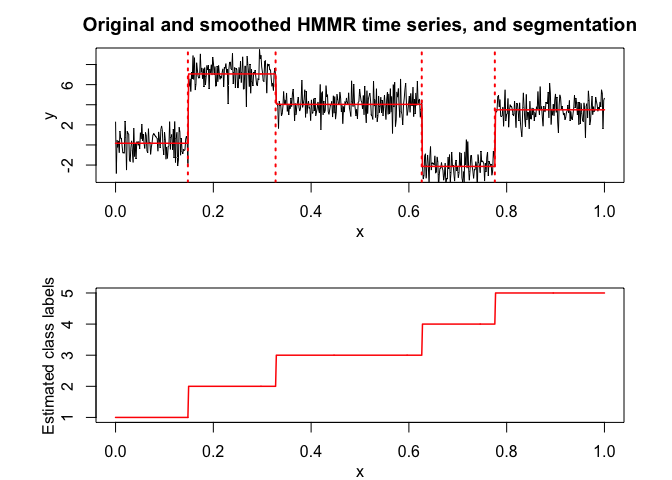
plot(x, y, type = "l", xlab = "x", ylab = "Y")selectedhmmr <- selectHMMR(X = x, Y = y, Kmin = 2, Kmax = 6, pmin = 0, pmax = 3)
#> The HMMR model selected via the "BIC" has K = 5 regimes
#> and the order of the polynomial regression is p = 0.
#> BIC = -1136.39152222095
#> AIC = -1059.76780111041
selectedhmmr$plot(what = "smoothed")