MRHLP is an R package for flexible and user-friendly probabilistic joint segmentation of multivariate time series (or multivariate structured longitudinal data) with smooth and/or abrupt regime changes by a mixture model-based multiple regression approach with a hidden logistic process (Multiple Regression model with a Hidden Logistic Process (MRHLP)). The model is fitted by the EM algorithm.
You can install the MRHLP package from GitHub with:
# install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("fchamroukhi/MRHLP")To build vignettes for examples of usage, type the command below instead:
# install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("fchamroukhi/MRHLP",
build_opts = c("--no-resave-data", "--no-manual"),
build_vignettes = TRUE)Use the following command to display vignettes:
browseVignettes("MRHLP")library(MRHLP)# Application to a toy data set
data("toydataset")
x <- toydataset$x
y <- toydataset[,c("y1", "y2", "y3")]
K <- 5 # Number of regimes (mixture components)
p <- 1 # Dimension of beta (order of the polynomial regressors)
q <- 1 # Dimension of w (order of the logistic regression: to be set to 1 for segmentation)
variance_type <- "heteroskedastic" # "heteroskedastic" or "homoskedastic" model
n_tries <- 1
max_iter <- 1500
threshold <- 1e-6
verbose <- TRUE
verbose_IRLS <- FALSE
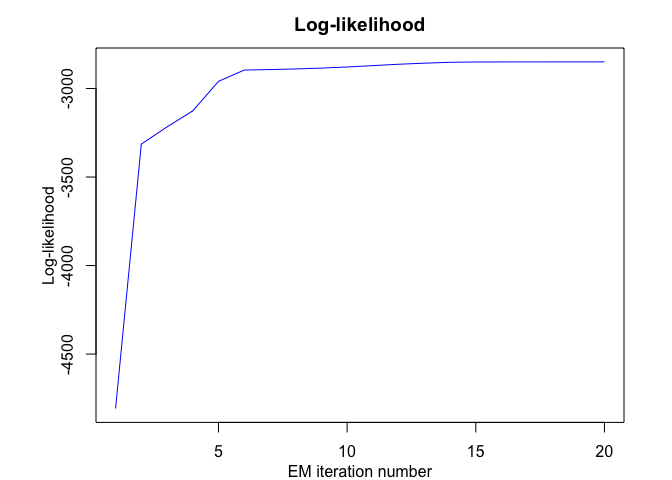
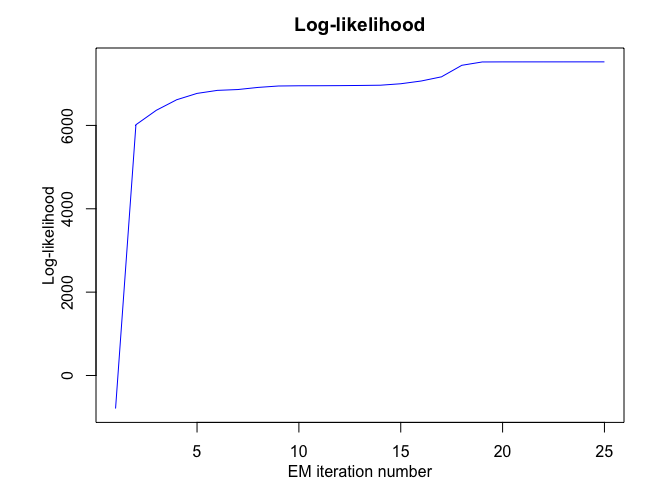
mrhlp <- emMRHLP(X = x, Y = y, K, p, q, variance_type, n_tries,
max_iter, threshold, verbose, verbose_IRLS)
#> EM - MRHLP: Iteration: 1 | log-likelihood: -4807.6644322901
#> EM - MRHLP: Iteration: 2 | log-likelihood: -3314.25165556383
#> EM - MRHLP: Iteration: 3 | log-likelihood: -3216.8871750704
#> EM - MRHLP: Iteration: 4 | log-likelihood: -3126.33556053822
#> EM - MRHLP: Iteration: 5 | log-likelihood: -2959.59933830667
#> EM - MRHLP: Iteration: 6 | log-likelihood: -2895.65953485704
#> EM - MRHLP: Iteration: 7 | log-likelihood: -2892.93263500326
#> EM - MRHLP: Iteration: 8 | log-likelihood: -2889.34084959654
#> EM - MRHLP: Iteration: 9 | log-likelihood: -2884.56422084139
#> EM - MRHLP: Iteration: 10 | log-likelihood: -2878.29772085061
#> EM - MRHLP: Iteration: 11 | log-likelihood: -2870.61242183846
#> EM - MRHLP: Iteration: 12 | log-likelihood: -2862.86238149363
#> EM - MRHLP: Iteration: 13 | log-likelihood: -2856.85351443338
#> EM - MRHLP: Iteration: 14 | log-likelihood: -2851.74642203885
#> EM - MRHLP: Iteration: 15 | log-likelihood: -2850.00381259526
#> EM - MRHLP: Iteration: 16 | log-likelihood: -2849.86516522686
#> EM - MRHLP: Iteration: 17 | log-likelihood: -2849.7354103643
#> EM - MRHLP: Iteration: 18 | log-likelihood: -2849.56953544124
#> EM - MRHLP: Iteration: 19 | log-likelihood: -2849.40322468732
#> EM - MRHLP: Iteration: 20 | log-likelihood: -2849.40321381274
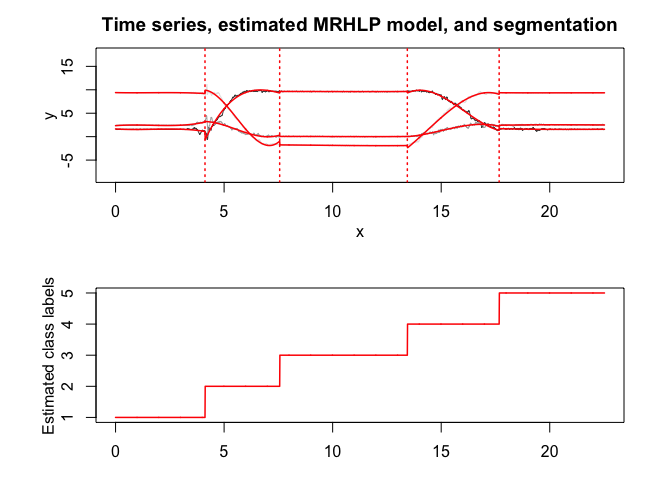
mrhlp$summary()
#> ----------------------
#> Fitted MRHLP model
#> ----------------------
#>
#> MRHLP model with K = 5 regimes
#>
#> log-likelihood nu AIC BIC ICL
#> -2849.403 68 -2917.403 -3070.651 -3069.896
#>
#> Clustering table:
#> 1 2 3 4 5
#> 100 120 200 100 150
#>
#>
#> ------------------
#> Regime 1 (k = 1):
#>
#> Regression coefficients:
#>
#> Beta(d = 1) Beta(d = 2) Beta(d = 3)
#> 1 0.11943184 0.6087582 -2.038486
#> X^1 -0.08556857 4.1038126 2.540536
#>
#> Covariance matrix:
#>
#> 1.19063336 0.12765794 0.05537134
#> 0.12765794 0.87144062 -0.05213162
#> 0.05537134 -0.05213162 0.87885166
#> ------------------
#> Regime 2 (k = 2):
#>
#> Regression coefficients:
#>
#> Beta(d = 1) Beta(d = 2) Beta(d = 3)
#> 1 6.924025 4.9368460 10.288339
#> X^1 1.118034 0.4726707 -1.409218
#>
#> Covariance matrix:
#>
#> 1.0690431 -0.18293369 0.12602459
#> -0.1829337 1.05280632 0.01390041
#> 0.1260246 0.01390041 0.75995058
#> ------------------
#> Regime 3 (k = 3):
#>
#> Regression coefficients:
#>
#> Beta(d = 1) Beta(d = 2) Beta(d = 3)
#> 1 3.6535241 6.3654379 8.488318
#> X^1 0.6233579 -0.8866887 -1.126692
#>
#> Covariance matrix:
#>
#> 1.02591553 -0.05445227 -0.02019896
#> -0.05445227 1.18941700 0.01565240
#> -0.02019896 0.01565240 1.00257195
#> ------------------
#> Regime 4 (k = 4):
#>
#> Regression coefficients:
#>
#> Beta(d = 1) Beta(d = 2) Beta(d = 3)
#> 1 -1.439637 -4.463014 2.952470
#> X^1 0.703211 3.649717 -4.187703
#>
#> Covariance matrix:
#>
#> 0.88000190 -0.03249118 -0.03411075
#> -0.03249118 1.12087583 -0.07881351
#> -0.03411075 -0.07881351 0.86060127
#> ------------------
#> Regime 5 (k = 5):
#>
#> Regression coefficients:
#>
#> Beta(d = 1) Beta(d = 2) Beta(d = 3)
#> 1 3.4982408 2.5357751 7.652113
#> X^1 0.0574791 -0.7286824 -3.005802
#>
#> Covariance matrix:
#>
#> 1.13330209 0.25869951 0.03163467
#> 0.25869951 1.21230741 0.04746018
#> 0.03163467 0.04746018 0.80241715
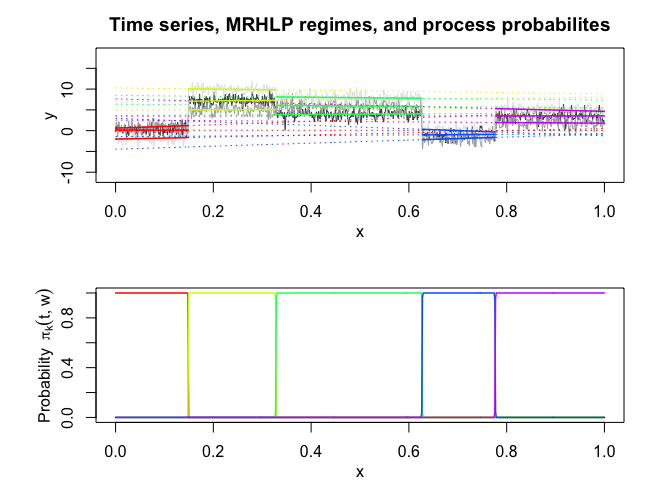
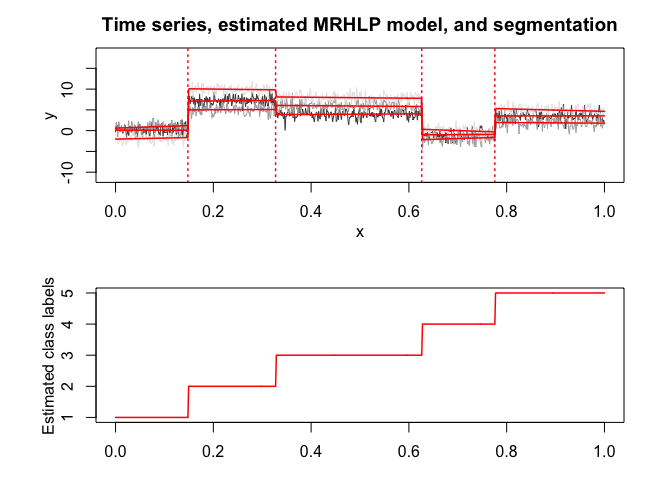
mrhlp$plot()# Application to a real data set (human activity recogntion data)
data("realdataset")
x <- realdataset$x
y <- realdataset[,c("y1", "y2", "y3")]
K <- 5 # Number of regimes (mixture components)
p <- 3 # Dimension of beta (order of the polynomial regressors)
q <- 1 # Dimension of w (order of the logistic regression: to be set to 1 for segmentation)
variance_type <- "heteroskedastic" # "heteroskedastic" or "homoskedastic" model
n_tries <- 1
max_iter <- 1500
threshold <- 1e-6
verbose <- TRUE
verbose_IRLS <- FALSE
mrhlp <- emMRHLP(X = x, Y = y, K, p, q, variance_type, n_tries,
max_iter, threshold, verbose, verbose_IRLS)
#> EM - MRHLP: Iteration: 1 | log-likelihood: -792.888668727036
#> EM - MRHLP: Iteration: 2 | log-likelihood: 6016.45835957306
#> EM - MRHLP: Iteration: 3 | log-likelihood: 6362.81791662824
#> EM - MRHLP: Iteration: 4 | log-likelihood: 6615.72233403002
#> EM - MRHLP: Iteration: 5 | log-likelihood: 6768.32107943849
#> EM - MRHLP: Iteration: 6 | log-likelihood: 6840.97339565987
#> EM - MRHLP: Iteration: 7 | log-likelihood: 6860.97262839295
#> EM - MRHLP: Iteration: 8 | log-likelihood: 6912.25605673784
#> EM - MRHLP: Iteration: 9 | log-likelihood: 6945.96718258737
#> EM - MRHLP: Iteration: 10 | log-likelihood: 6951.28584396645
#> EM - MRHLP: Iteration: 11 | log-likelihood: 6952.37644678517
#> EM - MRHLP: Iteration: 12 | log-likelihood: 6954.80510338749
#> EM - MRHLP: Iteration: 13 | log-likelihood: 6958.99033092484
#> EM - MRHLP: Iteration: 14 | log-likelihood: 6964.81099837456
#> EM - MRHLP: Iteration: 15 | log-likelihood: 6999.90358068156
#> EM - MRHLP: Iteration: 16 | log-likelihood: 7065.39327246318
#> EM - MRHLP: Iteration: 17 | log-likelihood: 7166.23398344994
#> EM - MRHLP: Iteration: 18 | log-likelihood: 7442.73330846285
#> EM - MRHLP: Iteration: 19 | log-likelihood: 7522.65416438396
#> EM - MRHLP: Iteration: 20 | log-likelihood: 7524.41524338024
#> EM - MRHLP: Iteration: 21 | log-likelihood: 7524.57590110924
#> EM - MRHLP: Iteration: 22 | log-likelihood: 7524.73808801417
#> EM - MRHLP: Iteration: 23 | log-likelihood: 7524.88684996651
#> EM - MRHLP: Iteration: 24 | log-likelihood: 7524.9753964817
#> EM - MRHLP: Iteration: 25 | log-likelihood: 7524.97701548847
mrhlp$summary()
#> ----------------------
#> Fitted MRHLP model
#> ----------------------
#>
#> MRHLP model with K = 5 regimes
#>
#> log-likelihood nu AIC BIC ICL
#> 7524.977 98 7426.977 7146.696 7147.535
#>
#> Clustering table:
#> 1 2 3 4 5
#> 413 344 588 423 485
#>
#>
#> ------------------
#> Regime 1 (k = 1):
#>
#> Regression coefficients:
#>
#> Beta(d = 1) Beta(d = 2) Beta(d = 3)
#> 1 1.64847721 2.33823068 9.40173242
#> X^1 -0.31396583 0.38235782 -0.10031616
#> X^2 0.23954454 -0.30105177 0.07812145
#> X^3 -0.04725267 0.06166899 -0.01586579
#>
#> Covariance matrix:
#>
#> 0.0200740364 -0.004238036 0.0004011388
#> -0.0042380363 0.006082904 -0.0012973026
#> 0.0004011388 -0.001297303 0.0013201963
#> ------------------
#> Regime 2 (k = 2):
#>
#> Regression coefficients:
#>
#> Beta(d = 1) Beta(d = 2) Beta(d = 3)
#> 1 -106.0250571 -31.4671946 -107.9697464
#> X^1 45.2035210 21.2126134 72.0220177
#> X^2 -5.7330338 -4.1285514 -13.9857795
#> X^3 0.2343552 0.2485377 0.8374817
#>
#> Covariance matrix:
#>
#> 0.11899225 -0.03866052 -0.06693441
#> -0.03866052 0.17730401 0.04036629
#> -0.06693441 0.04036629 0.11983979
#> ------------------
#> Regime 3 (k = 3):
#>
#> Regression coefficients:
#>
#> Beta(d = 1) Beta(d = 2) Beta(d = 3)
#> 1 9.0042249443 -1.247752962 -2.492119515
#> X^1 0.2191555621 0.418071041 0.310449523
#> X^2 -0.0242080660 -0.043802827 -0.039012607
#> X^3 0.0008494208 0.001474635 0.001427627
#>
#> Covariance matrix:
#>
#> 4.103351e-04 -0.0001330363 5.289199e-05
#> -1.330363e-04 0.0006297205 2.027763e-04
#> 5.289199e-05 0.0002027763 1.374405e-03
#> ------------------
#> Regime 4 (k = 4):
#>
#> Regression coefficients:
#>
#> Beta(d = 1) Beta(d = 2) Beta(d = 3)
#> 1 -1029.9071752 334.4975068 466.0981076
#> X^1 199.9531885 -68.7252041 -105.6436899
#> X^2 -12.6550086 4.6489685 7.6555642
#> X^3 0.2626998 -0.1032161 -0.1777453
#>
#> Covariance matrix:
#>
#> 0.058674116 -0.017661572 0.002139975
#> -0.017661572 0.047588713 0.007867532
#> 0.002139975 0.007867532 0.067150809
#> ------------------
#> Regime 5 (k = 5):
#>
#> Regression coefficients:
#>
#> Beta(d = 1) Beta(d = 2) Beta(d = 3)
#> 1 27.247199195 -14.393798357 19.741283724
#> X^1 -3.530625667 2.282492947 -1.511225702
#> X^2 0.161234880 -0.101613670 0.073003292
#> X^3 -0.002446104 0.001490288 -0.001171127
#>
#> Covariance matrix:
#>
#> 6.900384e-03 -0.001176838 2.966199e-05
#> -1.176838e-03 0.003596238 -2.395420e-04
#> 2.966199e-05 -0.000239542 5.573451e-04
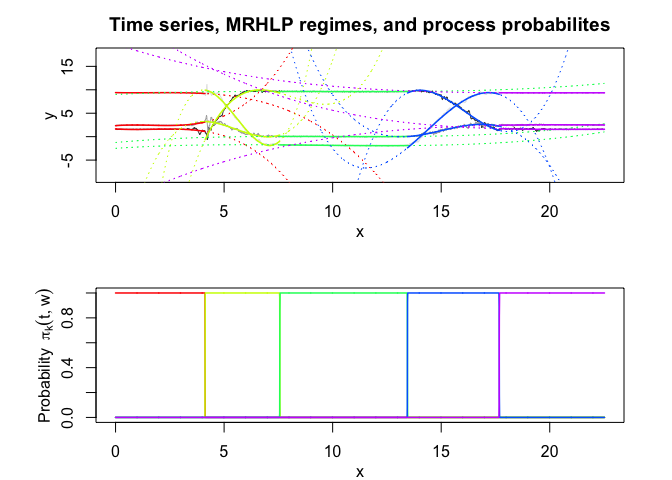
mrhlp$plot()In this package, it is possible to select models based on information criteria such as BIC, AIC and ICL.
The selection can be done for the two following parameters:
- K: The number of regimes;
- p: The order of the polynomial regression.
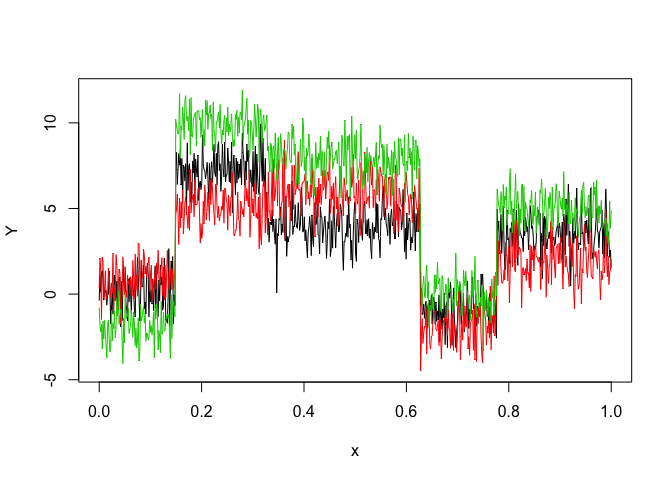
Let’s select a MRHLP model for the following multivariate time series Y:
data("toydataset")
x <- toydataset$x
y <- toydataset[, c("y1", "y2", "y3")]
matplot(x, y, type = "l", xlab = "x", ylab = "Y", lty = 1)selectedmrhlp <- selectMRHLP(X = x, Y = y, Kmin = 2, Kmax = 6, pmin = 0, pmax = 3)
#> Warning in emMRHLP(X = X1, Y = Y1, K, p): EM log-likelihood is decreasing
#> from -3105.78591044952to -3105.78627830471!
#> The MRHLP model selected via the "BIC" has K = 5 regimes
#> and the order of the polynomial regression is p = 0.
#> BIC = -3033.20042397111
#> AIC = -2913.75756459291
selectedmrhlp$plot(what = "estimatedsignal")