This repository provides scripts that leverage the roofline model to compare the performance of Large Language Model (LLM) inference tasks across various hardware platforms.
In LLM inference tasks, several factors can influence performance on different hardware. These factors include:
-
Batch Size: The batch size usually refers to the number of requests forward at the same time.
-
KV Cache Length: In Transformer models, the KV cache length refers to the length of the cache used to store key-value pairs.
-
Hidden Size: The hidden size refers to the dimension of the hidden layers in the model.
-
Intermediate Size: The intermediate size refers to the dimension of the fully connected layers in the model.
-
GQA: the group number of the Grouped Query Attention.
-
MoE : Mixture of Experts configurations.
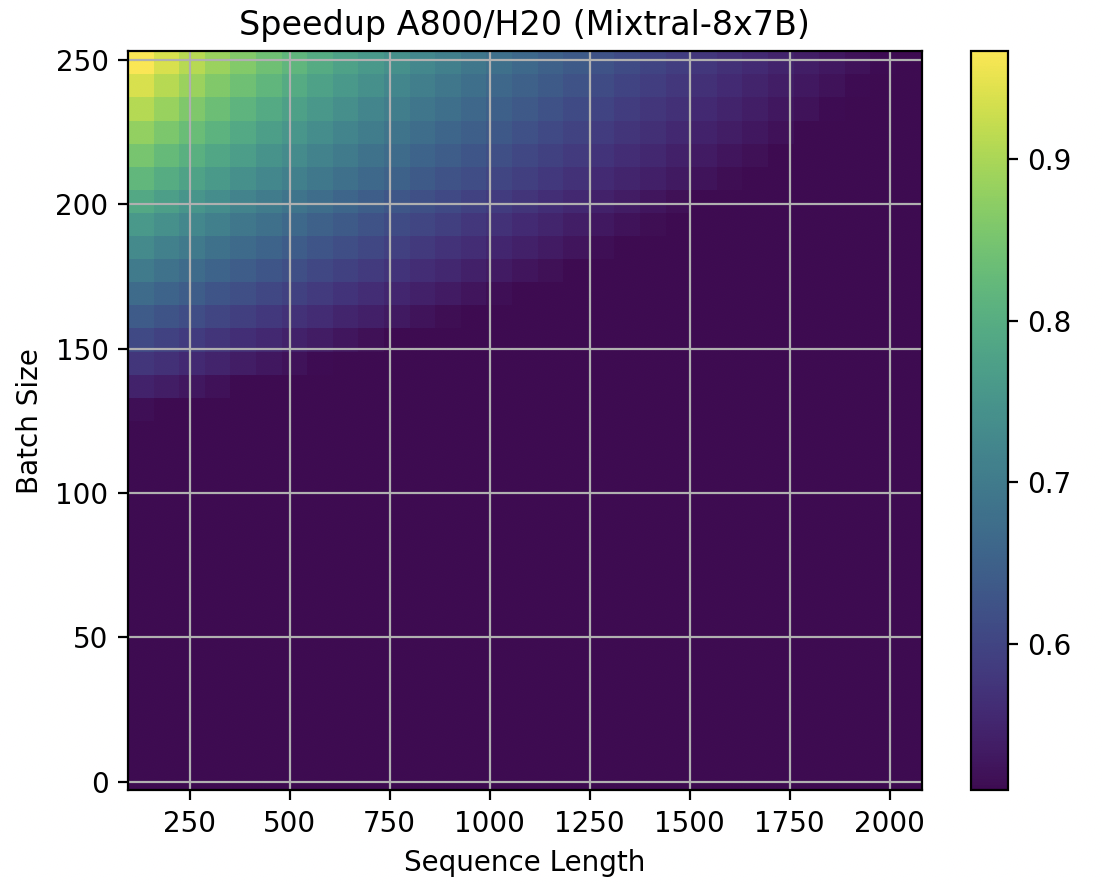
For Mixtral-8X7B MoE, A800 is always worse than H20.
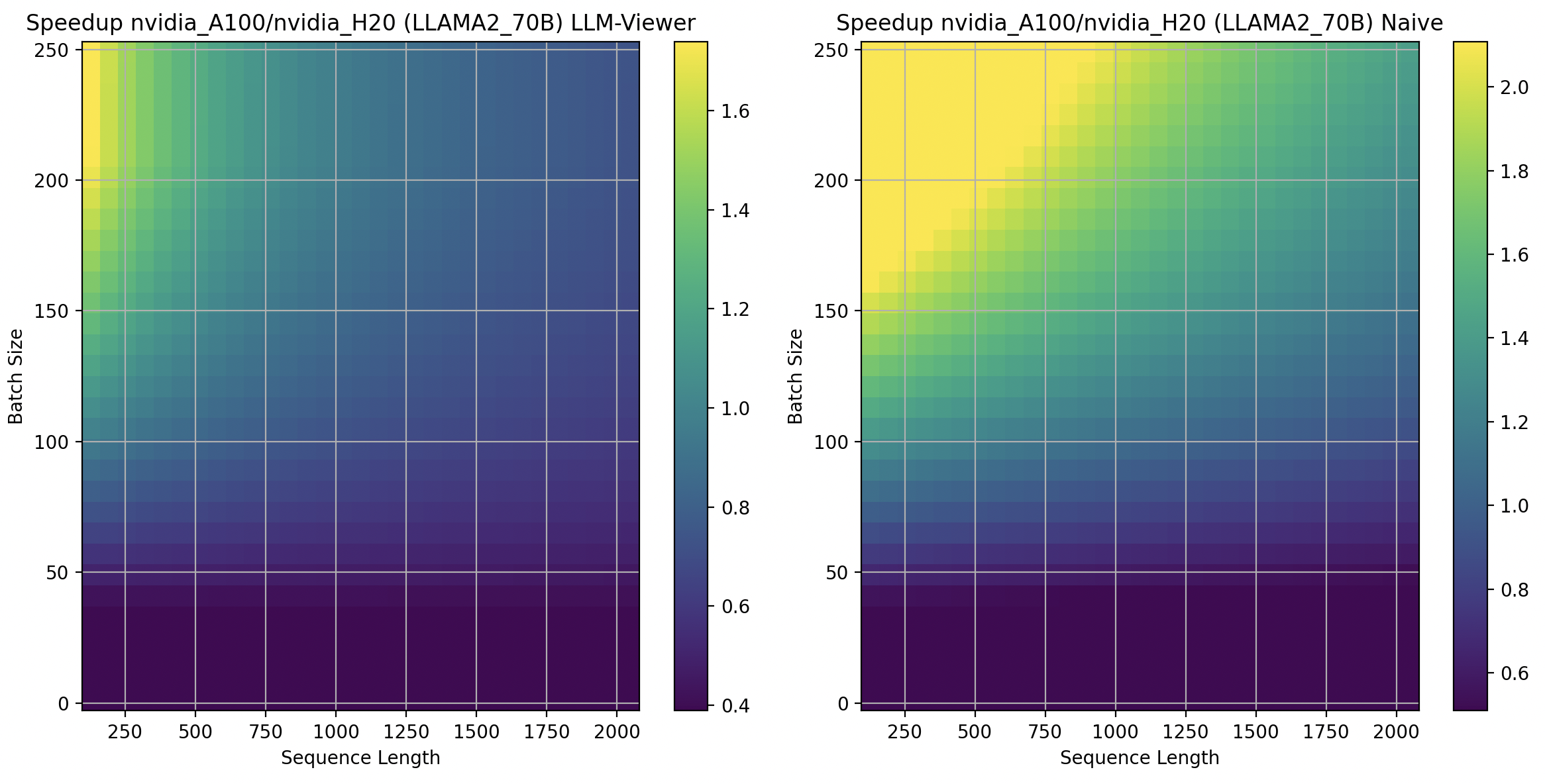
We present the speedup between two hardware platforms in a mesh and compare our naive roofline model with a more complex one from LLM-Viewer. Although the two models are not exactly the same, they exhibit similar distribution patterns. For instance:
For LLAMA2 70B, in some scenerios, A800 is better than H20 on, especially for large batch sizes.