Kubernetes Copilot powered by OpenAI.
Features:
- Automate Kubernetes cluster operations using ChatGPT (GPT-4 or GPT-3.5).
- Diagnose and analyze the potential issues for Kubernetes workloads.
- Generate the Kubernetes manifests based on the provided prompt instructions.
- Utilize native kubectl and trivy commands for Kubernetes cluster access and security vulnerability scanning.
Install the copilot with pip command below. It is highly recommended to use pipx or venv to install the copilot to avoid conflicts with other Python packages.
# Option 1: use pipx to install the copilot
pipx install kube-copilot
# Option 2: use venv to install the copilot
python3 -m venv copilotenv
source copilotenv/bin/activate
pip install kube-copilot
# Option 3: Use pip to install the copilot (not recommended)
pip install kube-copilotSetup:
- Ensure
kubectlis installed on the local machine and the kubeconfig file is configured for Kubernetes cluster access. - Install
trivyto assess container image security issues (for theauditcommand). - Set the OpenAI API key as the
OPENAI_API_KEYenvironment variable to enable ChatGPT functionality.- For Azure OpenAI service, please set
AZURE_OPENAI_API_KEY=<your-key>andAZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT=https://<replace-this>.openai.azure.com/.
- For Azure OpenAI service, please set
Option 1: Web UI with Helm (recommended)
# Option 1: OpenAI
export OPENAI_API_KEY="<replace-this>"
helm install kube-copilot kube-copilot \
--repo https://feisky.xyz/kube-copilot \
--set openai.apiModel=gpt-4 \
--set openai.apiKey=$OPENAI_API_KEY
# Option 2: Azure OpenAI Service
export AZURE_OPENAI_API_KEY="<replace-this>"
export AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT="<replace-this>"
helm install kube-copilot kube-copilot \
--repo https://feisky.xyz/kube-copilot \
--set openai.apiModel=gpt-4 \
--set openai.apiKey=$AZURE_OPENAI_API_KEY \
--set openai.apiBase=$AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT
# Forwarding requests to the service
kubectl port-forward service/kube-copilot 8080:80
echo "Visit http://127.0.0.1:8080 to use the copilot"Option 2: CLI with kubectl
kubectl run -it --rm copilot \
--env="OPENAI_API_KEY=$OPENAI_API_KEY" \
--restart=Never \
--image=ghcr.io/feiskyer/kube-copilot \
-- execute --verbose 'What Pods are using max memory in the cluster'
kubectl run -it --rm copilot \
--env="AZURE_OPENAI_API_KEY=$AZURE_OPENAI_API_KEY" \
--env="AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT=$AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT" \
--restart=Never \
--image=ghcr.io/feiskyer/kube-copilot \
-- execute --verbose 'What Pods are using max memory in the cluster'Refer kubernetes.md for more detailed steps.
Running directly in the terminal:
Usage: kube-copilot [OPTIONS] COMMAND [ARGS]...
Kubernetes Copilot powered by OpenAI
Options:
--version Show the version and exit.
--help Show this message and exit.
Commands:
analyze analyze issues for a given resource
audit audit security issues for a Pod
diagnose diagnose problems for a Pod
execute execute operations based on prompt instructions
generate generate Kubernetes manifestskube-copilot audit POD [NAMESPACE] will audit security issues for a Pod:
Usage: kube-copilot audit [OPTIONS] POD [NAMESPACE]
audit security issues for a Pod
Options:
--verbose Enable verbose information of copilot execution steps
--model MODEL OpenAI model to use for copilot execution, default is gpt-4
--help Show this message and exit.kube-copilot diagnose POD [NAMESPACE] will diagnose problems for a Pod:
Usage: kube-copilot diagnose [OPTIONS] POD [NAMESPACE]
diagnose problems for a Pod
Options:
--verbose Enable verbose information of copilot execution steps
--model MODEL OpenAI model to use for copilot execution, default is gpt-4
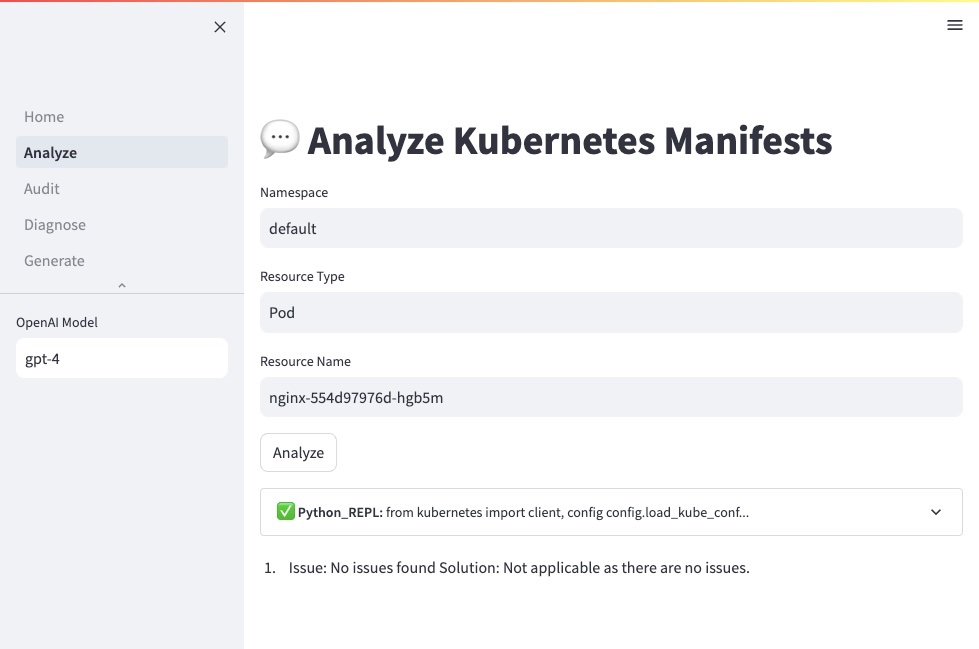
--help Show this message and exit.kube-copilot analyze RESOURCE NAME [NAMESPACE] will analyze potential issues for the given resource object:
Usage: kube-copilot analyze [OPTIONS] RESOURCE NAME [NAMESPACE]
analyze issues for a given resource
Options:
--verbose Enable verbose information of copilot execution steps
--model TEXT OpenAI model to use for copilot execution, default is gpt-4
--help Show this message and exit.kube-copilot execute INSTRUCTIONS will execute operations based on prompt instructions.
It could also be used to ask any questions.
Usage: kube-copilot execute [OPTIONS] INSTRUCTIONS
execute operations based on prompt instructions
Options:
--verbose Enable verbose information of copilot execution steps
--model MODEL OpenAI model to use for copilot execution, default is gpt-4
--help Show this message and exit.Use the kube-copilot generate command to create Kubernetes manifests based on
the provided prompt instructions. After generating the manifests, you will be
prompted to confirm whether you want to apply them.
Usage: kube-copilot generate [OPTIONS] INSTRUCTIONS
generate Kubernetes manifests
Options:
--verbose Enable verbose information of copilot execution steps
--model TEXT OpenAI model to use for copilot execution, default is gpt-4
--help Show this message and exit.The project is opensource at github feiskyer/kube-copilot-python with Apache License. The Go version of this project is maintained at feiskyer/kube-copilot with same license.
If you would like to contribute to the project, please follow these guidelines:
- Fork the repository and clone it to your local machine.
- Create a new branch for your changes.
- Make your changes and commit them with a descriptive commit message.
- Push your changes to your forked repository.
- Open a pull request to the main repository.