Vncdesk was originally developed for scaling up applications on high DPI screens. Applications run in VNC desktops.
Configuration for each desktop goes into a numbered directory below
~/.vncdesk. For example the configuration in ~/.vncdesk/2/ can be run
with:
vncdesk 2 Examples/nikke.fig
Optional arguments, here nikke.fig, are passed to the startup script which
may pass it on to an application:
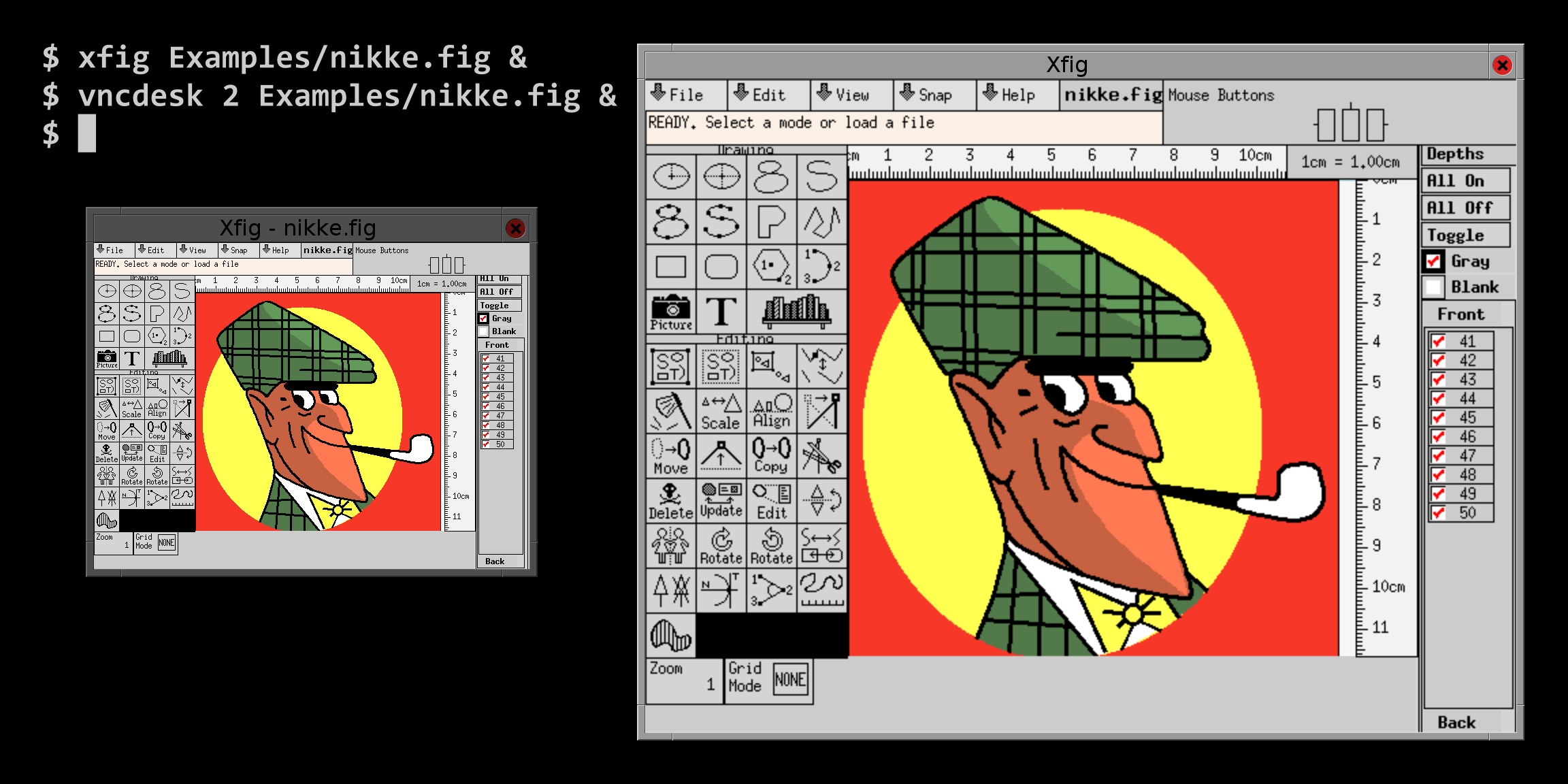
Files:
settings.ini, by example:[desktop] width = 1024 height = 768 depth = 24 [window] title = Xfig name = xfig in vncdesk class = FigInVncdesk scale_factor = 2 smoothing = false
The option
depthis optional, and so is the entire sectionwindow.Consider that GDK 3 will also scale the VNC viewer via the environment variable
GDK_SCALE. You may want to disable GDK scaling in case you run into display errors.Set
smoothingtofalseto get rid of blur when scaling. This option requires gtk-vnc release 0.7.0 or newer.startup: Startup script, executable by the user.Environment variables provided:
WIDTH,HEIGHT: Desktop size.DISPLAY: Display of the VNC server.GUEST_DISPLAY: Display of the VNC client.INVOCATION_DIR: Directory in whichvncdeskwas started.- Arguments passed when calling
vncdesk.
Examples:
Application specific files, for example
Xresources:xfig*image_editor: DISPLAY=$GUEST_DISPLAY xdg-open xfig*pdfviewer: DISPLAY=$GUEST_DISPLAY xdg-open xfig*browser: DISPLAY=$GUEST_DISPLAY xdg-open
.password: Generated every time anew, to password protect the connection also from other users on the same system..Xauthority: Generated every time anew.
Download a release from GitHub.
Install dependencies:
If you want to set up an explicit font path for the VNC server, at the same level as
__init__.pycreatefont_path.py. Example contents:font_path = ','.join(['/usr/share/fonts/misc/', '/usr/share/fonts/75dpi/', '/usr/share/fonts/100dpi/', '/usr/share/fonts/Type1/'])Run with sufficient permissions:
python setup.py install
Or, if you have pip:
pip3 install .
Test, e.g. by:
pip3 install --upgrade --user .; ~/.local/bin/vncdesk 2
Use versioning scheme: major.minor.patch
Set version in:
vncdesk/version.pyTag version in Git.
- Maximum line length: 80 characters
- Comments in reStructuredText.
Except where noted otherwise, files are licensed under the WTFPL.
Copyright © 2015–2017 Felix E. Klee, with contributions by Robin Green, and Giorgio
This work is free. You can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the Do What The Fuck You Want To Public License, Version 2, as published by Sam Hocevar. See the COPYING file for more details.
d3des.py has been taken from Yusuke Shinyama’s vnc2flv version 20100207, then was modified for Python 3 compatibility.