react-redux-callbag-example
An example of the use Callbags to generate Redux side effects from a React Component.
- Introduced a new notation or way to define actions for later link between reducer and calls names.
- Callbags-based middleware for Redux.
- Code Splitting with redux-reducer-manager.
- React hooks to inject reducers and actions or Redux side effects.
Yet another intuitive Redux side effect manager. Use of callbags to work with redux in the idea of redux-observable or redux-saga.
You can also have a look at:
- redux-saga An intuitive Redux side effect manager.
- redux-observable RxJS-based middleware for Redux. Compose and cancel async actions to create side effects and more.
Usage
This project uses vitejs as the base. To install run:
# npm
npm install
npm run dev# yarn
yarn
yarn devDoc
Part 1, New notation to define redux actions
Define redux actions
We can have a look to file "/src/pages/App/actions.js" . Go to actions definition
Here, we define methods to access actions types and functions at the same place.
It simplifies the way we work with this elements later thanks to the IDE campabilities like vscode #Go to Definition.
Also we can reuse a function for many action calls like the methods add and minus in the example.
Using redux actions at the reducer
We only import one var for actions. Go to reducer definition
import appActions from './actions';Then we use it at the reducer like:
switch (action.type) {
case appActions.add.type:
draft.total = draft.total + action.amount
break
case appActions.minus.type:
draft.total = draft.total - action.amount
break
default:
}Using redux actions at the react component
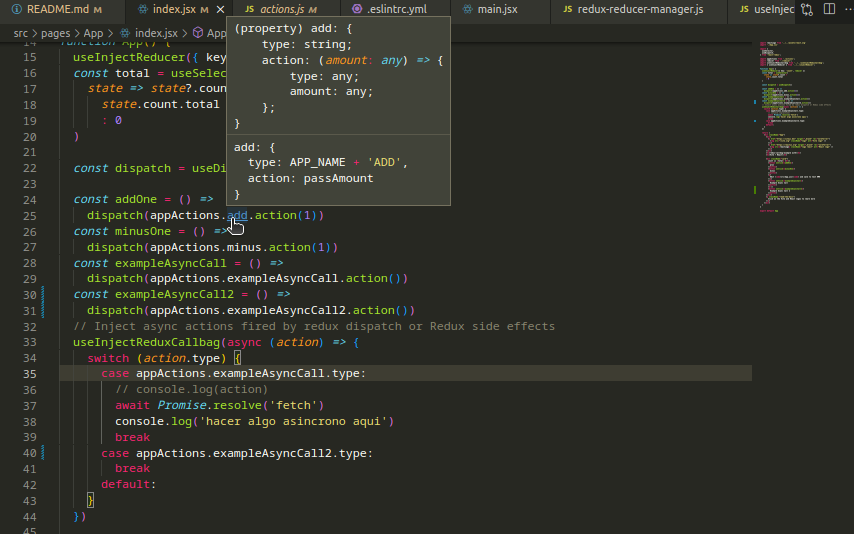
As the reducer definition we only need to import one var.
import appActions from './actions';Later we call actions or types like:
const dispatch = useDispatch()
const addOne = () => dispatch(appActions.add.action(1))switch (action.type) {
case appActions.exampleAsyncCall.type:
// Async/await code, fetch info, etc
await Promise.resolve('fetch')
...
breakIf we use vscode we can see the action type and definition using Ctrl or go to the definition with Ctrl + Click. See vscode #Go to Definition
Part 2, Code splitting
We use a redux-reducer-manager with the idea of code splitting. link to src/redux-reducer-manager.js Use of redux-reducer-manager:
// Create a store where we can manage reducers
import { configureStore } from './redux-reducer-manager'
//... later ...
const store = configureStore({
initialState: {},
initialReducers: {},
middlewares: [
middlewareCallbagReactive
],
})
// Add callbag to the store
// Used to subscribe to store with callbags from components
store.callbagSource = sourceSo we can load our reducers from react components.
For this we use a hook src/injectReducer.js.
Use of injectReducer hook:
import { useInjectReducer } from '../../injectReducer';
import reducer from './reducer';
//... later inside the React Component ...
useInjectReducer({ key: 'count', reducer })Part 3, Redux Callbag
The goal is to easyly call async functions from redux or Redux side effects. For that we use reactive programing using a callbag to subscribe to.
Why we need callbags, by André Staltz
First we add a Middleware to the redux store to pipe redux actions to a callbag.
import fromFunction from 'callbag-from-function';
const {source, emitter} = fromFunction();
// ... later ...
// Middleware where we can subscribe and recibe actions dispatched to store
// function middlewareCallbagReactive({ getState }) {
const middlewareCallbagReactive = ({ getState }) => {
return next => action => {
// Send action to callbag
emitter(action)
// Call the next dispatch method in the middleware chain.
const returnValue = next(action)
// This will likely be the action itself, unless
// a middleware further in chain changed it.
return returnValue
}
}
const store = configureStore({
initialState: {},
initialReducers: {},
middlewares: [
middlewareCallbagReactive
],
})
// Add callbag to the store
// Used to subscribe to store with callbags from components
store.callbagSource = sourceSecond we inject it to our React Component using a hook src/useInjectReduxCallbag.js.
import useInjectReduxCallbag from '../../useInjectReduxCallbag';
//... later inside the React Component ...
// Inject async actions fired by redux dispatch or Redux side effects
useInjectReduxCallbag(async (action) => {
switch (action.type) {
case appActions.exampleAsyncCall.type:
// console.log(action)
await Promise.resolve('fetch')
console.log('async code here')
break
case appActions.exampleAsyncCall2.type:
break
default:
}
})We can move async functions to another file for a clearer code.