This example goes through how to create custom modular resources using Viam's python SDK, and how to connect it to a Robot.
This is a limited document. For a more in-depth understanding of modules, see the documentation.
Modular resources allows you to define custom components and services, and add them to your robot. Viam ships with many component types, but you're not limited to only using those types -- you can create your own using modules.
For more information, see the documentation.
The definition of the new resource is in the src directory. Within this directory are the proto and gizmo subdirectories.
The proto directory contains the gizmo.proto definition of all the message types and calls that can be made to the Gizmo component. It also has the compiled python output of the protobuf definition.
The gizmo directory contains all the necessary definitions for creating a custom Gizmo component type. The api.py file defines what a Gizmo can do (mirroring the proto definition), implements the gRPC GizmoService for receiving calls, and the gRPC GizmoClient for making calls. See the API docs for more info. The my_gizmo.py file in contains the unique implementation of a Gizmo. This is defined as a specific Model. See the Model docs for more info. This implementation uses the validate_config function to specify an implicit dependency on a arg1 parameter by default and throw an error if there is an invalid attribute.
There is also a main.py file, which creates a module, adds the desired resources, and starts the module. This file is called by the run.sh script, which is the entrypoint for this module. Read further to learn how to connect this module to your robot.
Outside the src directory, there is the client.py file. This can be used to test the module once it's connected to the robot. You will have to update the credentials and robot address in that file.
These steps assume that you have a robot available at app.viam.com.
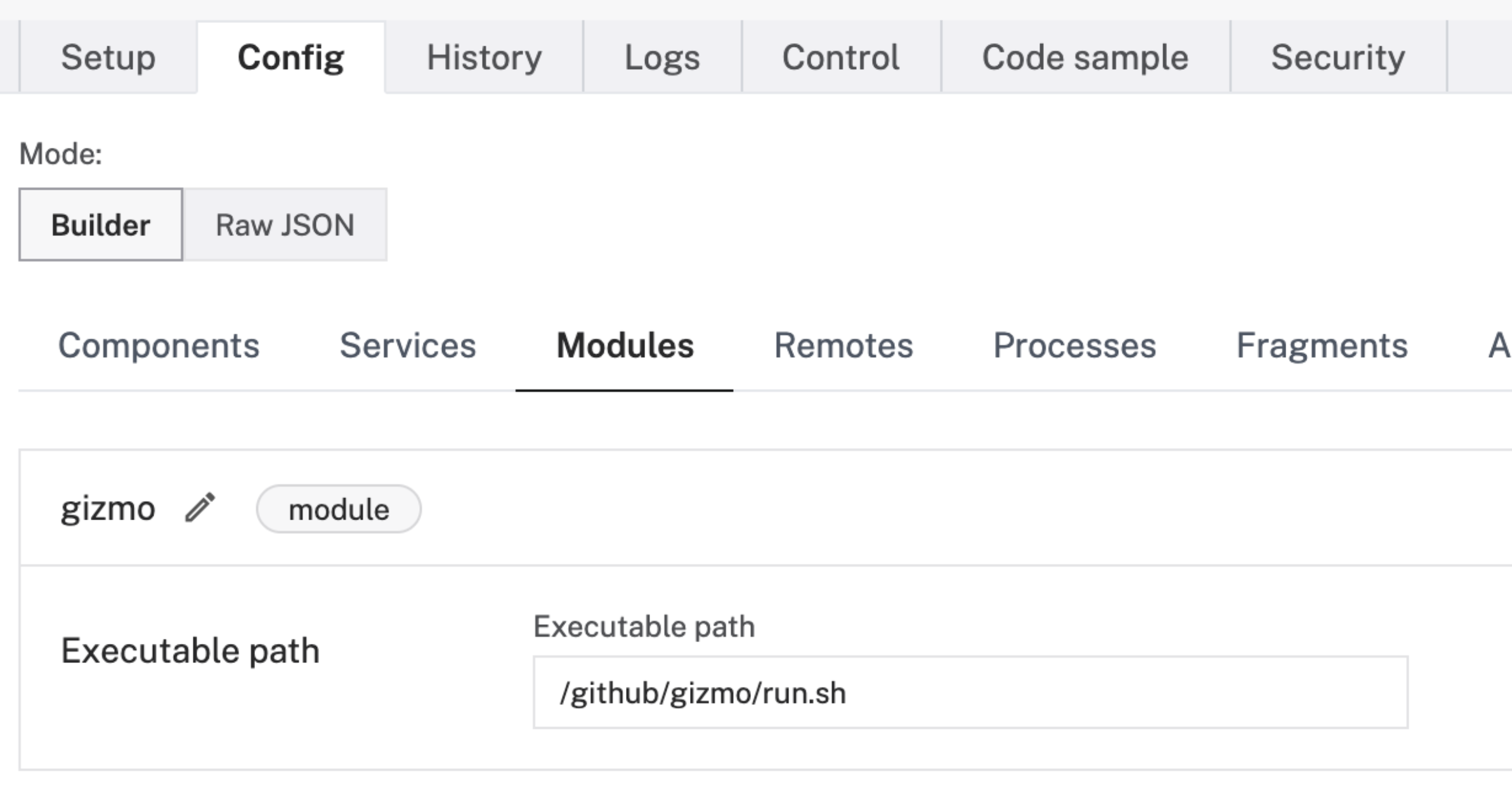
The run.sh script is the entrypoint for this module. To connect this module with your robot, you must add this module's entrypoint to the robot's config. For example, this could be /home/viam-python-sdk/examples/module/run.sh. See the documentation for more details.
Once the module has been added to your robot, you will then need to add a component that uses the MyGizmo model. See the documentation for more details. You can add a service in a similar manner.
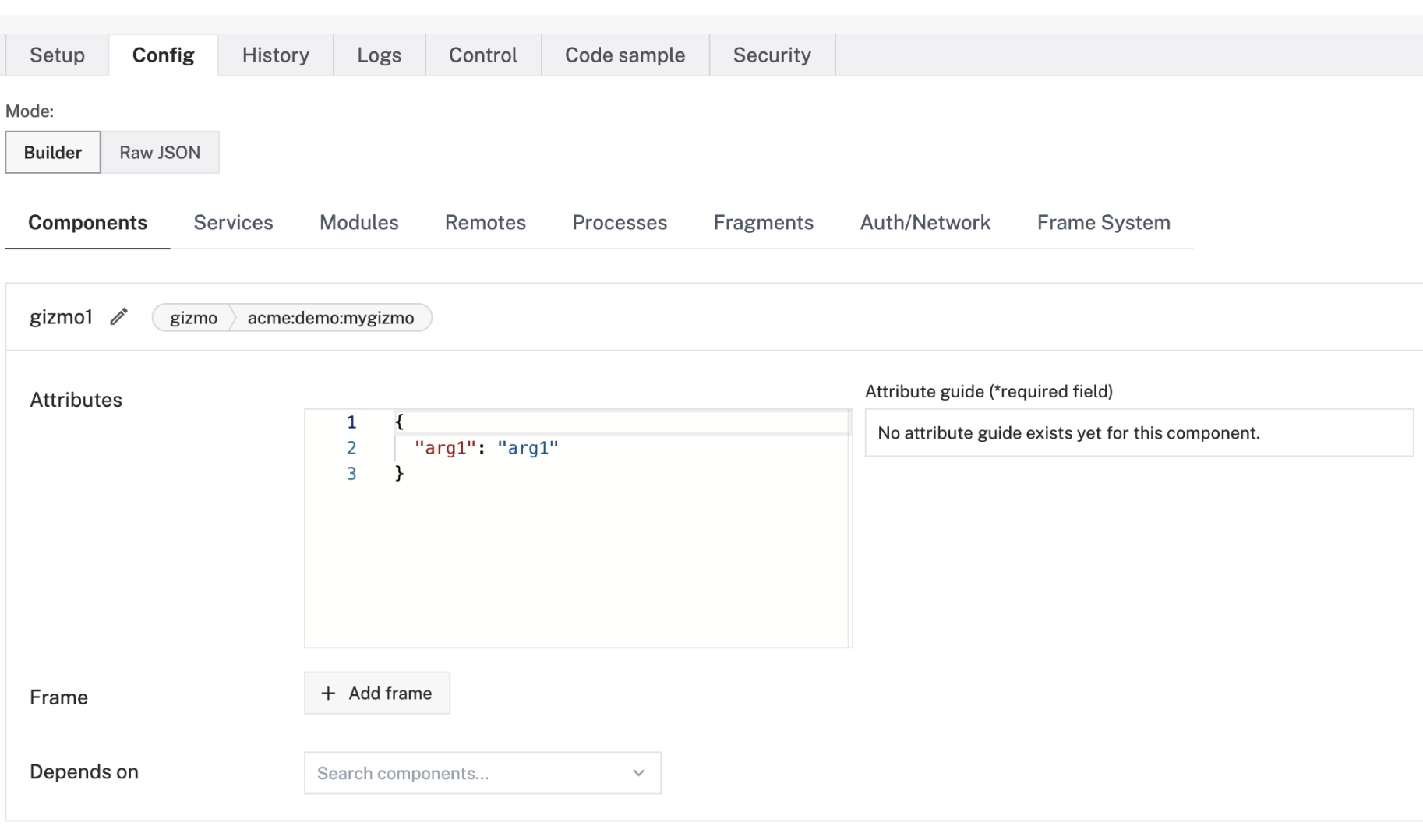
An example configuration for a Gizmo component could look like this:
{
"components": [
{
"name": "gizmo1",
"type": "gizmo",
"namespace": "acme",
"model": "acme:demo:mygizmo",
"attributes": {
"arg1": "arg1",
},
"depends_on": []
}
],
"modules": [
{
"name": "gizmo",
"executable_path": "/github/gizmo/run.sh"
}
]
}After the robot has started and connected to the module, you can use the provided client.py to connect to your robot and make calls to your custom, modular resources.