Netpoll is a high-performance non-blocking I/O networking framework, which focused on RPC scenarios, developed by ByteDance.
RPC is usually heavy on processing logic and therefore cannot handle I/O serially. But Go's standard library net designed blocking I/O API, so that the RPC framework can only follow the One Conn One Goroutine design. It will waste a lot of cost for context switching, due to a large number of goroutines under high concurrency. Besides, net.Conn has no API to check Alive, so it is difficult to make an efficient connection pool for RPC framework, because there may be a large number of failed connections in the pool.
On the other hand, the open source community currently lacks Go network libraries that focus on RPC scenarios. Similar repositories such as: evio, gnet, etc., are all focus on scenarios like Redis, Haproxy.
But now, Netpoll was born and solved the above problems. It draws inspiration from the design of evio and netty, has excellent Performance, and is more suitable for microservice architecture. Also Netpoll provides a number of Features, and it is recommended to replace net in some RPC scenarios.
We developed the RPC framework KiteX and HTTP framework Hertz (to be open sourced) based on Netpoll, both with industry-leading performance.
Examples show how to build RPC client and server using Netpoll.
For more information, please refer to Document.
-
Already
- LinkBuffer provides nocopy API for streaming reading and writing
- gopool provides high-performance goroutine pool
- mcache provides efficient memory reuse
- multisyscall supports batch system calls
IsActivesupports checking whether the connection is aliveDialersupports building clientsEventLoopsupports building a server- TCP, Unix Domain Socket
- Linux, Mac OS (operating system)
-
Future
- io_uring
- Shared Memory IPC
- Serial scheduling I/O, suitable for pure computing
- TLS
- UDP
-
Unsupported
- Windows (operating system)
Benchmark is not a digital game, it should meet the requirements of industrial use first. In the RPC scenario, concurrent calls and waiting timeout are necessary support items.
Therefore, we set that the benchmark should meet the following conditions:
- Support concurrent calls, support timeout(1s)
- Use protocol: header(4 bytes) indicates the total length of payload
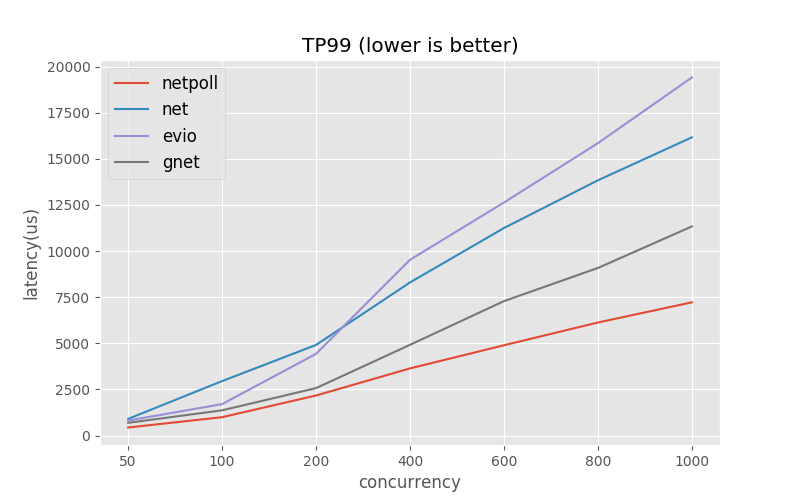
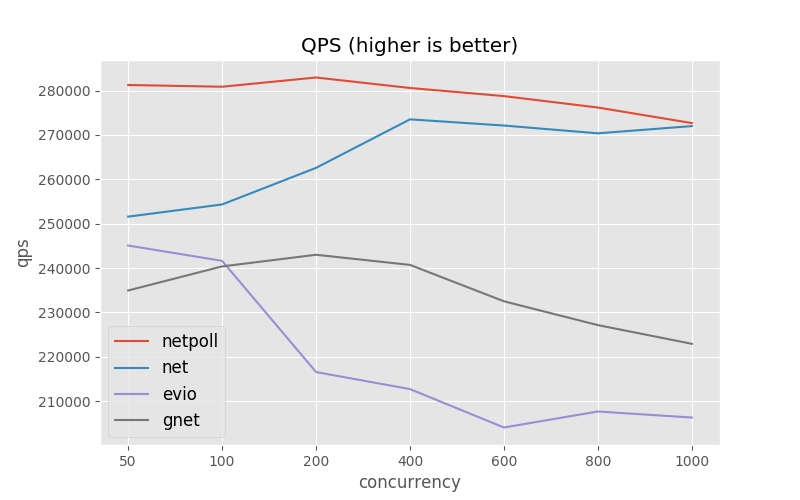
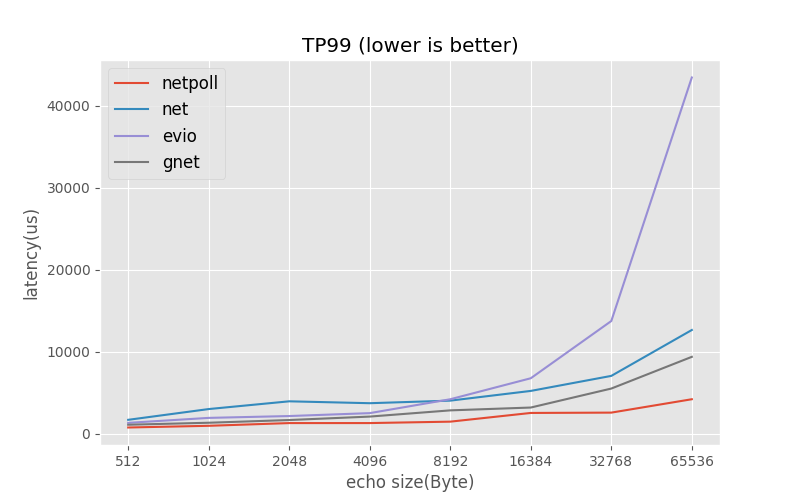
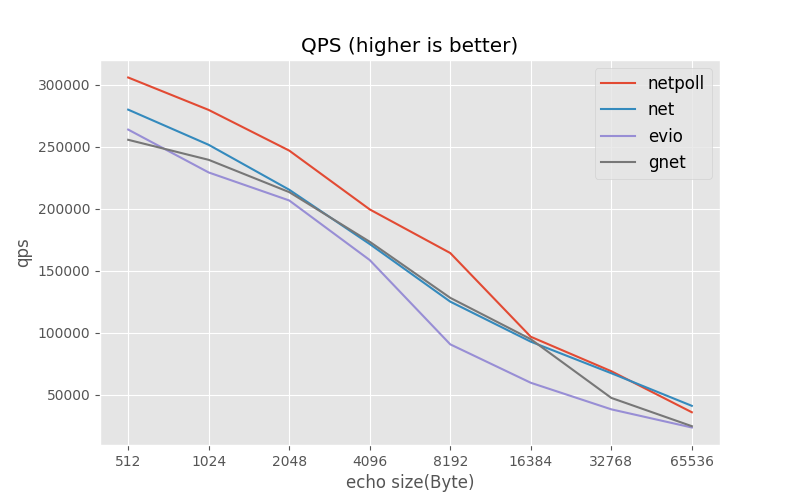
Similar repositories such as net , evio, gnet. We compared their performance through Benchmarks, as shown below.
For more benchmark reference Netpoll-Benchmark , KiteX-Benchmark and Hertz-Benchmark .
- CPU: Intel(R) Xeon(R) Gold 5118 CPU @ 2.30GHz, 4 cores
- Memory: 8GB
- OS: Debian 5.4.56.bsk.1-amd64 x86_64 GNU/Linux
- Go: 1.15.4
Compared with net , Netpoll latency about 34% and qps about 110% (continue to pressurize, net latency is too high to reference)