An ARP spoofing program developped in C language at 42 School. Final grade: 125/100.
IMPORTANT: This program has been developped for educationnal purpose, do not use it in a public network.
ARP spoofing is used to sniff network transmitted packets in the Man-in-the-middle attack.
It's a vulnerability exploit of the ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) protocol, that change the intended target of a network communication.
You'll have to make sure that the following dependencies are installed:
- Clang (C Compiler).
- Make
- lolcat & figlet (for pretty output during compilation).
$ makeIn order to run this program in a safe & legal environment, I provided this program with a virtual private network.
In order to use this program safely in a virtual network, you'll have to download & install both VirtualBox and Vagrant.
To see the inbound & outbound network packets, please download Wireshark.
A Vagrantfile is provided with this project to ease the installation & setup of the
virtual network.
Make sure vboxnet1 virtual private network is available in
VirtualBox.
To install the virtual environment, you can type:
$ vagrant upThis virtual network will start the following virtual machines:
| Hostname | IP address | purpose |
|---|---|---|
| blackhat | 192.168.42.2 |
attack targets |
| target1 | 192.168.42.3 |
communicate w/target2 |
| target2 | 192.168.42.4 |
communicate w/target1 |
Then, you'll be able to access to each virtual computer with the command
vagrant ssh <hostname>.
All the inbound & outbound network traffic is written through a
.pcapfifo created during VMs creation. You will be able to sniff the network with wireshark.
To ease this process, you can source the env file, which provides a command to run wireshark with one of these generated files.
$ source ./env
$ sniff blackhat.pcap # sniff network in/out on 192.168.42.2 [if=eth1]To remove the environment, type
vagrant destroyand confirm each computer removal.
Usage:
sudo ./ft_malcom [ -h -v ] [-I ] | [-p [-R] <spoofed IP / hostname> <spoofed MAC addr> <target IP / hostname> <target MAC>] | [-f [-i interval] <spoofed IP / hostname> <target IP / hostname>]
-h Display usage & exit.
-v Enable verbose mode.
-p Perform an ARP Poisoning attack.
-f Perform an ARP Flooding attack.
-I Use the interactive mode (using ARP flooding).
Poisonning arguments:
spoofed host/IP Source IP address / hostname.
spoofed MAC Source MAC address.
dst host/IP Targetted IP address / hostname.
dst MAC Targetted MAC address.
Poisonning options:
-R Send an ARP REQUEST back after a delay to ensure cache poisonning.
Flooding arguments:
spoofed host/IP Source IP address / hostname.
dst host/IP Targetted IP address / hostname.
Flooding options:
-i <interval> Custom flooding interval (default 5 secs).
This mode is based on an ARP flooding attack (see below) with an interval between each ARP request of 5 seconds (default).
$ . ./env
$ sniff ./blackhat.pcap # This will open a Wireshark window$ vagrant ssh target1
Last login: Wed Dec 8 12:47:13 2021 from 10.0.2.2
[vagrant@target1 ~]$ ping 192.168.42.4 # let this command running in a terminal$ vagrant ssh blackhat
Last login: Wed Dec 8 09:24:22 2021 from 10.0.2.2
[vagrant@blackhat ~]$ cd /tmp/ft_malcom/
[vagrant@blackhat ~]$ sudo sysctl -w net.ipv4.ip_forward=1 # ensure packets forwarding
[vagrant@blackhat ft_malcom]$ make # build the program
[...]
[vagrant@blackhat ft_malcom]$ sudo ./ft_malcom -I- Select the network interface to use & wait for the network scanning
- select
eth1
- select
- Select the targetted computer
- either
192.168.42.3(target1) or192.168.42.4(target2)
- either
- Select the spoofed IP address
- The opposite of the previous step
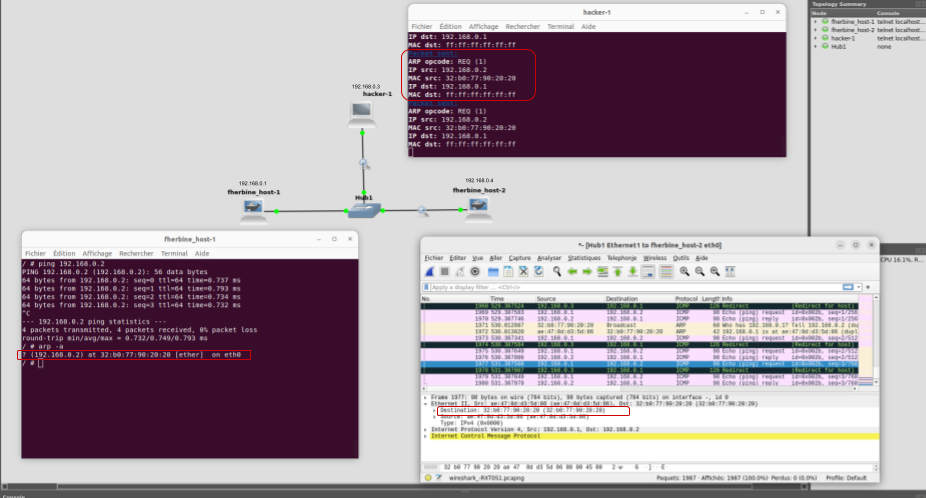
This attack will answer to arp who-has request from a specific target with a custom ARP packet containing a spoofed IP (comming from the who-has request) and the MAC address of the attacker.
Usually who-has requests are sent to the Link layer broadcast (ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff) to initiate connections.
The first step for you, will be to get your (blackhat VM) mac address (ip a command).
Then type:
[vagrant@blackhat ~]$ cd /tmp/ft_malcom
[vagrant@blackhat ft_malcom]$ make
[...]
[vagrant@blackhat ft_malcom]$ sudo ./ft_malcom -p <spoofed IP> <spoofed MAC address> <target IP> ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff This attack method will flood the network with ARP is-at packets to a specific target to force it to update its ARP cache table.
To test it (on black)
[vagrant@blackhat ~]$ cd /tmp/ft_malcom
[vagrant@blackhat ft_malcom]$ make
[...]
[vagrant@blackhat ft_malcom]$ sudo ./ft_malcom -v -f <spoofed IP> <targetted IP>Before openning this project, please make sure that you have built the docker image in this repository, by typing:
$ docker build -t fherbine_host .You can test this project in an isolated environment into GNS3,
thanks to the given topology simulation.gns3project.