Google Cloud Apigee API Platform notes from the Coursera certification
1. API Design and Fundamentals of Google Cloud's Apigee API Platform
API Fundamentals
New challenges (Connected digital experiences)
- Secure
- Scale
- Manage
- Analyze
- Connect
Apigee API Management platform
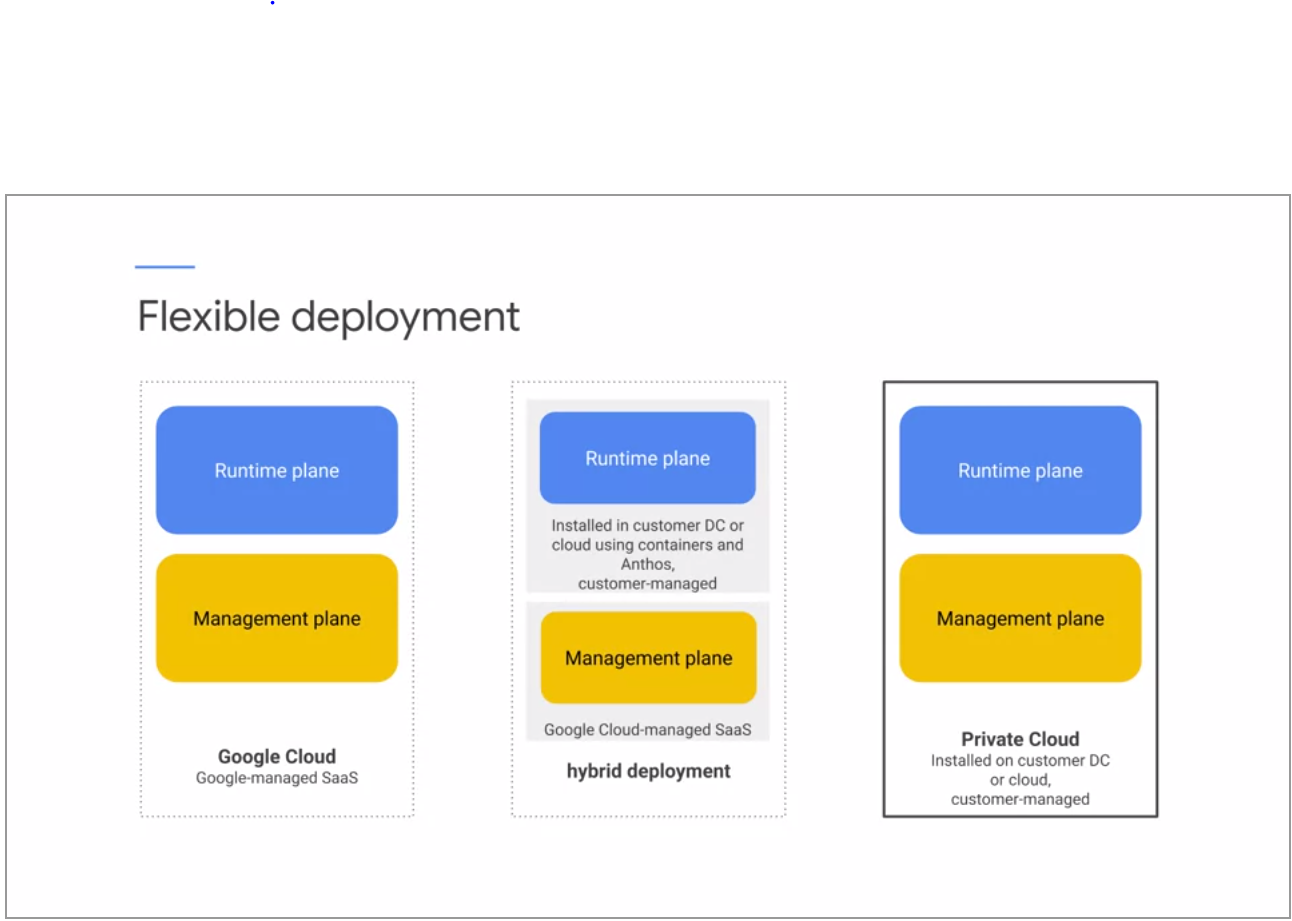
Flex deployment
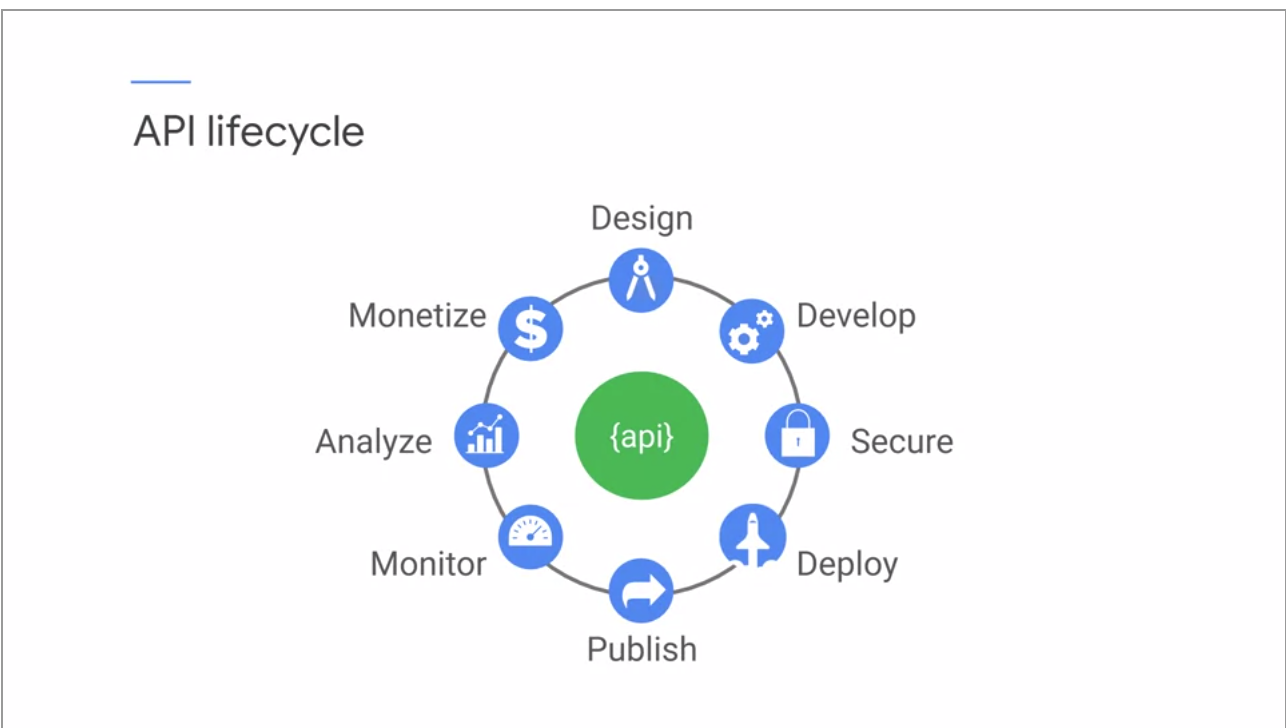
API lifecycle
Open API 3.0 (yaml)
API Proxy
- Proxy Endpoint
- Target Endpoint
Multi-tenancy
-
Virtual hosts:
- name
- alias(es)
- protocol (http/https)
- port
- certificate (if https)
-
ProxyEndpoint
- HttpProxyConnection
- BasePath
- VirtualHost (1 or more)
- HttpProxyConnection
-
Condition
-
RouteRule
-
HTTPTargetConnection
- LoadBalancer
- Algorithmn (RoundRobin, LeastConnection ...)
- Server (1 or more)
- MaxFailures
-
HealthMonitor (if using MaxFailures)
- LoadBalancer
Dev
- Developers
- Apps
- Products
- API keys
API Product
- API Product: bundle of APIs
- Control access to APIs
- Use for access or service levels
Status codes
- 200: 0K
- 400: Bad Request
- 401: Unauthorized
- 403: Forbidden
- 404: Not found
- 429: Too Many Requests
- 500: Internal Server Error
Other status codes
- 201: Created
- 204: No Content
- 304: Not Modified
- 405: Method Not Allowed
- 406: Not Acceptable
- 409: Conflict
- 503: Service Unavaiable
Status code ranges
- 1xx: Informational
- 2xx: Success
- 3xx: Redirection
- 4xx: Client error
- 5xx: Server error
2. API Security on Google Cloud's Apigee API Platform
API Security
Security concerns
- Public APIs
- Private APIs
Concerns
- Rate limiting
- Spike arrest policy
- Quota policy
- Traffic management: Source IP
- Access control policy (allows or denies by IP address or IP range)
- Applicataion identity
- Create or revoke API keys
- Verify API Key policy
- User authentification and authorization
- Basic Authentification
- OAuth 2.0
- Json Web Tokens and signatures (JWT/JWS)
- Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML)
- Can integrate with other security providers
- Data in transit
- Transport Layer Security (TLS) for all API traffic
- Injection and data-based attacks
- Regular Expression Protection policy
- Application-level denial of service
- JSON Threat Protection
- XML Threat Protection
- Data confidentiality
- Role-based access control
- Data masking and private variables
- API security compliance
- Audit logs
- API Security Reporting
- Traffic management: Bot detection
- Apigee Sense
Identity, Authentification and Authorization
- Identity tracking
- Tracking usage/access
- => API Key
- Authentification
- Validating credentials
- => App credentials: consumer key & secret
- => User credentials: username & password
- => Machine credentials: TLS certificate
- Credentials must be protected with TLS
- Standards:
- AD/LDAP
- OpenID Connect
- Authorization
- What is allowed
- Proof of authentification often via token
- Standards:
- OAuth 2.0
- SAML 2.0
OAuth
-
OAuth: An authorization framework that allows users or clients to grant access to server resources to another entity without sharing credentials
-
Access Tokens: are issued to allow limited access to specific resources for a specified period of time and may be revoked byt the user that granted the permission or by the server that issued the token
-
Grant types: Authentification scenarios supported by OAuth 2.0
-
Client Credentials
- Service to Service (No user data involved)
- For confidential clients
- POST /token -> Apigee Proxy
- Headers:
{ "Authorization": "Basic {Base64(client_id:client_secret)}", "Content-Type": "x-www-form-urlencoded" } - Payload (Form parameters):
{ "grant_type": "client_credentials", "scope": "{scope}" }
- Headers:
- Response from POST /token
- Returns:
{ "access_token": "{access_token}", "scope": "{scope}", "expiry": "{expiry}" } - No refresh token
- Returns:
- GET /resource -> Backend
- Headers:
{ "Authorization": "Bearer {access_token}" }
- Headers:
-
Resource Owner Password:
-
User data involved
-
For confidential && trusted client
-
Authorization server involved (for validating user credentials)
-
POST /token -> Apigee Proxy
- Headers:
{ "Authorization": "Basic {Base64(username:password)}", "Content-Type": "x-www-form-urlencoded" } - Payload (Form parameters):
{ "grant_type": "password", "scope": "{scope}" } - POST /auth -> Authorization Server
- Payload:
{ "username": "{username}", "password": "{password}" } - Response of POST /auth:
Returns:
{ "auth_success": "{auth_success}", "user_details": "{user_details}" }
- Payload:
- Response of POST /token
- Returns:
{ "access_token": "{access_token}", "refresh_token": "{refresh_token}", "scope": "{scope}", "expiry": "{expiry}" }
- Returns:
- Headers:
-
GET /resource -> Backend
- Headers:
{ "Authorization": "Bearer {access_token}" }
- Headers:
-
-
Authorization Code:
-
User data involved
-
For trusted || untrusted apps
-
When app developer doesn't want to maintain credentials for users
-
Authorization server involved (for validating user credentials)
-
User Agent (browser) involved (for communicating with the Authorization server)
-
GET /oauth/authorize -> Apigee Proxy
-
Payload:
{ "response_type": "code", "redirect_uri": "{redirect_uri}", "scope": "{scope}", "state": "{state}" } -
Response of GET /oauth/authorize Returns
login_page?scope={scope}&state={state}&client_id={auth_client_id}
-
-
User authentification in browser: -> Authorization server
- User enters credentials in displayed login_page
- User provides consent in consent_page
-
POST /oauth/authcode -> Apigee proxy (from Authorization server)
- Payload:
{ "client_id": "{apigee_client_id}", "redirect_uri": "{redirect_uri}", "scope": "{scope}", "state": "{state}", "user_infos": "{user_infos}" } - Response of POST /oauth/authcode:
Returns:
302 redirect(redirect_uri?code={code}&state={state}
- Payload:
-
POST /token -> Apigee Proxy
-
Headers:
{ "Authorization": "Basic {Base64(client_id:client_secret)}", "Content-Type": "x-www-form-urlencoded" } -
Payload (Form parameters):
{ "grant_type": "authorization_code", "code": "{code}", "redirect_uri": "{redirect_uri}" } -
Response of POST /token
- Returns:
{ "access_token": "{access_token}", "refresh_token": "{refresh_token}", "scope": "{scope}", "expiry": "{expiry}" }
- Returns:
-
-
GET /resource -> Backend
- Headers:
{ "Authorization": "Bearer {access_token}" }
- Headers:
-
-
Authorization Code with PKCE (Proof Key for Code Exchange):
-
User data involved
-
For trusted || untrusted apps
-
When app developer doesn't want to maintain credentials for users
-
Authorization server involved (for validating user credentials)
-
User Agent (browser) involved (for communicating with the Authorization server)
-
App generates PKCE
code_verifier(cryptographically random number)code_challenge(base64 urlencoded string of SHA56 hash of code_verifier)- code_verifier is stored in session
-
GET /oauth/authorize -> Apigee Proxy
-
Payload:
{ "response_type": "code", "client_id": "{client_id}", "redirect_uri": "{redirect_uri}", "scope": "{scope}", "state": "{state}", "code_challenge": "{code_challenge}", "code_challenge_method": "S256" } -
Response of GET /oauth/authorize Returns
login_page?scope={scope}&state={state}&client_id={auth_client_id}
-
-
User authentification in browser: -> Authorization server
- User enters credentials in displayed login_page
- User provides consent in consent_page
-
POST /oauth/authcode -> Apigee proxy (from Authorization server)
- Payload:
{ "client_id": "{apigee_client_id}", "redirect_uri": "{redirect_uri}", "scope": "{scope}", "state": "{state}", "user_infos": "{user_infos}" } - Response of POST /oauth/authcode:
Returns:
302 redirect(redirect_uri?code={code}&state={state}
- Payload:
-
POST /token -> Apigee Proxy
-
Headers: (No client_secret with PKCE so no auth header, add client_id as a form parameter)
{ "Content-Type": "x-www-form-urlencoded" } -
Payload (Form parameters):
{ "grant_type": "authorization_code", "code": "{code}", "redirect_uri": "{redirect_uri}", "client_id": "{client_id}", "code_verifier": "{code_verifier}" } -
Response of POST /token
- Returns:
{ "access_token": "{access_token}", "refresh_token": "{refresh_token}", "scope": "{scope}", "expiry": "{expiry}" }
- Returns:
-
-
GET /resource -> Backend
- Headers:
{ "Authorization": "Bearer {access_token}" }
- Headers:
-
-
Implicit:
- Designed for public web & mobile apps
- Not recommended, use Authorization Code with PKCE instead
-
-
Refresh token:
-
Scope remains the same as for previous access_token
-
POST /token -> Apigee Proxy
-
Headers: (no auth header with PKCE)
{ "Authorization": "Basic {Base64(client_id:client_secret)}", "Content-Type": "x-www-form-urlencoded" } -
Payload (Form parameters): add client_id with PKCE
{ "grant_type": "refresh_token", "refresh_token": "{refresh_token}" } -
Response of POST /token
- Returns:
{ "access_token": "{access_token}", "refresh_token": "{refresh_token}", "scope": "{scope}", "expiry": "{expiry}" }
- Returns:
-
-
GET /resource -> Backend
- Headers:
{ "Authorization": "Bearer {access_token}" }
- Headers:
-
-
Client ids and client secrets: used to identify and authenticate apps
-
Generate Basic auth base64 string
echo -n "username:password" | base64
-
Scopes: limit access for a given token
-
TLS: All OAuth 2.0 traffic must be sent encrypted via TLS (successor of SSL)
-
Types of Apps:
- Confidential or Public
- Trusted or Untrusted
JWT, JWS, SAML, OpenID Connect
-
JWT (JSON Web Token)
-
Digitally signed
-
Decoded locally (doesn't need network trip) so valuable for microservices
-
Thus can not be revoked => Keep TTL (Time To Live) fairly short
-
Has 3 sections:
header.payload.signature- Header: algorithm for signing
- unencoded header:
{ "alg": "HS256", "typ": "JWT" }
- unencoded header:
- Payload: claims about the user
- unencoded payload:
{ "sub": "18373426", "iss": "example.com", "aud": "idsvc", "iat": 1570819380, "exp": 1570819680, "name": "John Doe", "loacle": "en", "email": "john.doe@example.com" }
- unencoded payload:
- Signature: guaranties integrity of the token
- signature calculation:
HMACSHA256( base64UrlEncoded(header) + "." base64UrlEncoded(payload), secret )
- signature calculation:
- Policies
- GenerateJWT
- VerifyJWT
- DecodeJWT
- Header: algorithm for signing
-
-
JWS (JSON Web Signature)
- Can be used to digitally sign any payload
- A JWS payload can have any format and does not require the payload to be attached to the JWS
- Signed JWT is a JWS with attached payload containing set of claims in a JSON object
- Policies
- GenerateJWS
- VerifyJWS
- DecodeJWS
-
Federated Identity (IdP)
- Identity provider
- stores user profiles
- responsible for authenticating users
- Service provider
- can delegate identity management to trusted IdPs
- Benefits for user
- fewer accounts and password to manage
- SSO (Single sign-on) to multiple apps and services
- Standards:
- SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language) (v2 2005)
- SOAP and XML based protocol
- uses security tokens called security assertions
- complex protocol, typically entreprise-oriented
- Policies
- GenerateSAMLAssertion
- ValidateSAMLAssertion
- OpenID Connect
- Lightweight RESTful redesign of SAML (2014)
- Layers user authentification and identiy on OAuth 2.0
- Adds ID token to OAuth 2.0
- ID token is secure JWT containing user claims
- ID tokens can be used to verify the authentification of users and get user details without contacting the issuer
- Apigee's JWT and OAuthV2 policies can be used to create OIDC providers and consumers
- SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language) (v2 2005)
- Identity provider
Content based attacks
-
Input validation:
- Extract fields from payloads using JSONPath/XPath in the ExtractVariables policy
- Validate required fields, field interactions and regular expression pattern by using proxy conditions or Javascript policies
- Rewrite validation error messages from the backend
-
Malicious input
- Ex: SQL injection code
- RegularExpressionProtection policy
-
Policies
- JSONThreatProtection and XMLThreatProtection policies use string-based evaluation of the payload instead of parsing the payload
- These policies should be run before doing any JSON/XML parsing
-
Transport Security
-
TLS (Transport Layer Security)
- Successor of SSL (Secure Sockets Layer)
- Establishes encrypted http link between client and server (https)
- Certificates prove identity
- TLS handshake: Client encrypt some data with server's public key and sends it to Server. Server must be able de decrypt it using its secret key
- One-way TLS (server validation)
- Standard web https
- Server presents certificate to prove identity, client does not (Server Keystore)
- Client can validate server certificate (Server Certificate Truststore)
- Two-way TLS (mutual authentification)
- Best practice for creating secure link from Apigee to backend services
- Both client and server present certificates (Server Keystore and Client Keystore)
- Client and Server each validate each other's certificate (Server Certificate Truststore and Client Certificate Truststore )
- KeyStore and TrustStore may be specified by using a name or a reference
- References must be prefered
- allows Keystore and Truststore modification without redeployment of proxy/target server and reboot of virtual host
- also allows key and certificate rotation without downtime
-
Acces Control
- Allows/Deny list for IPs addresses or ranges
- AccessControl policy
-
Apigee Management Security
-
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
- Permissions: create/read/update/delete access to resources
- Roles: group of permissions that can be assigned to a person
- Predefined roles
- Organization administrator (superuser access, including adding users and roles)
- Read-Only Organization administrator (full readonly access)
- Operations Administrator (responsible for production)
- Business User
- User (API developer)
- Custom roles can be created for fine grained Access Control
-
Data masking and private Variables
- blocks field being viewed in live trace or trace files
- Data masking can be configured only by using the Management API (not the Management UI)
- Can be configured to the Organization level or for a specific proxy
- Organisation: POST /v1/o/{org}/maskconfigs
- Single Proxy POST /v1/o{org}/apis/{proxy}/maskconfigs
- Body
{ "logonPassword": "******", "lastName": "John", "firstName" "Doe" }
-
Key Value Maps (KVMs)
- Storage for non-expiring data retrieved at runtime
- Keys and Values must both be strings
- Can be scoped to an Organization, an Environment or a specific Proxy (typically Environment-scoped)
- Read/Update/Delete KVM entries via
- Management API
- Management UI
- KVM Policy
- Mark sensitive data as encrypted at KVM creation
- Encrypted values cannot be retrieved by using Management UI or API
- Can only retrieve values of encrypted KVM by using private variables in a proxy (using KeyValueMapOperations policy)
-
Private variables
- private.{varname} is a private variable
3. API Development on Google Cloud's Apigee API Platform
Topics
- API mediation
- Traffic management
- API publishing
- Analytics
- Apigee offline development
- Apigee deployment options
API mediation
-
Set Content-Type header
-
JSONToXML and XMLToJSON policies (JSON: Javascript Object Notation, XML: eXtensible Markup Language)
- StripLevels
- RecognizeNumber
- RecognizeBoolean
-
XSL Transform policy (eXtensible Stylesheet Language)
-
MessageValidation policy validates (Content-Type must be set, XSD and WSDL files must be stored in the proxy for validation to occur):
- XML against XSD stored in proxy resources (eXtensible Service Description)
- SOAP against WSDL stored in proxy resources (WSDL: Web Service Description Language)
- Confirm that JSON or SOAP is well-formed (SOAP: Simple Object Access Protocol)
-
SOAP to REST Wizard
-
Mediation pattern: Format conversion:
-
ExtractVariables
- Header
- URIPath
- QueryParam
- JSONPath
- XPath
-
AssignMessage
- AssignVariable
- Set
- Remove
-
Templates
-
-
Mediation pattern: Orchestration
-
ServiceCallout policy
- Request
- Response
- Timeout
- HTTPTargetConnection
- URL
-
Proxy chaining (in same org & env), can be used in TargetEndpoints and ServiceCallouts
- LocalTargetConnection
- Path
- or
- APIProxy and ProxyEndpoint
- LocalTargetConnection
-
-
Custom code policies
- Javascript policy
- IncludeURL
- ResourceURL
- JavaCallout policy
- Python policy
- Javascript policy
-
Shared Flow
-
A method for sharing code inside proxies (just like proxy chaining)
-
Single flow of reusable logic containing policies, policy conditions, and resources
-
Cannot be invoked directly (shared flows live in the context of a hosting proxy flow)
-
Hosted in an org and deployed to an env
-
Can only be used by proxy or shared flow deployed to the same org/env
-
FlowCallout policy
- Call shared flow from a proxy or another shared flow
- Shared flow must be deployed to an environment before proxy or shared flow using it can be deployed
- FlowCallout
- SharedFlowBundle
- SharedFlow name
- SharedFlowBundle
-
Flow hooks
- Attach shared flow for all proxies in an environment
- Pre-proxy Flow Hook
- Pre-target Flow Hook
- Post-target Flow Hook
- Post-proxy Flow Hook
- Attach shared flow for all proxies in an environment
-
Fault Handling
-
FaultRules
- FaultRules
- FaultRules are evaluated from bottom to top in ProxyEndpoint (only part of a proxy that is evaluated in reverse order)
- FaultRules are evaluated in normal order in TargetEndpoint
-
DefaultFaultRule
- AlwaysEnforce
- true: always runs after the fault rules
- false: runs after the fault rules only if no matching fault rule was found
- AlwaysEnforce
-
Faults are raised:
-
When continueOnError = false in policy
-
Non success response recieved from backend or service callout (success codes default to 1xx, 2xx, 3xx, can be overriden by success.codes property)
-
Using a RaiseFault policy
- RaiseFault
- FaultResponse
- RaiseFault
-
404 Not Found
- Bsest practice is to allow approved operations
-
-
-
Extensions
- Stores and manages service credentials
- Retrieves tokens and manages token expiration
- Builds and parses the API request and response
-
Apigee components
- Gateway
- Router
- Message Processor
- Runtime Data Store
- Analytics services
- Management service (API)
- Management UI
- Developer Portal
- Gateway
-
Rate Limiting with Spike Arrests and Quotas
-
Traffic spikes
- SpikeArrest policy
- Keeps track of when the last matching request was allowed
- Does not use au counter
- Solves a technical problem
- Rejected traffic returns 429 Too Many Requests status code
- The variable "system.uuid" is unique for each message processor. This value can be specified in a response header if you want to be able to distinguish requests that are handled by different message processors.
- SpikeArrest
- Rate (10ps, 30pm)
- Identifier ref = client_id
- MessageWeight
- UseEffectiveCount = true divides the specified rate accros MPs(Message processors). Default is false
- SpikeArrest policy
-
Quotas
-
Quota policy
- Solves a business problem
- Uses a counter
- Count is typically shared among all message processors
- Quota is scoped to a single proxy and policy. Counters cannot be shared between proxies or policies
- Combination of proxy, policy and identifiers uniquely identifies a quota counter
- Rejected traffic returns 429 Too Many Requests status code
- Quota
- Allow
- Interval
- TimeUnit
- Indentifier
- MessageWeight
- Distributed
- Synchronous
- AsynchronousConfiguration
- SyncIntervalInSeconds
- SyncMessageCount
- Quota can be set at the API Product level and accessed via variables created when an API key or token is verified (verifyapikey.VK-VerifyKey.apiproduct.developer.quota.{limit, interval, timeunit})
- Quota type:
- default
- calendar
- flexi
- rollingwindow
-
Reset Quota policy
- ResetQuota
- Quota
- Identifier
- Allow
- Identifier
- Quota
- ResetQuota
-
-
-
Caching
-
TTL (time-to-live)
-
L1 cache
- in-memory
- is checked first
-
L2 cache
- stored in runtime data store
- slower than L1 but much faster than network calls
- MP populates L1 cache when entry is read from L2
-
L1 automatic caching (180s after access)
- OAuth access tokens
- Developers, Developers apps, API products
- Custom attributes on the aforementioned
-
PopulateCache policy
- adds an entry to the cache
- PopulateCache
- CacheResource
- CacheKey
- Prefix
- KeyFragment
- Scope (must be set if Cache prefix is not set)
- Global: org__env
- Application: orgenvproxy
- Exclusive: orgenvproxy__endpoint
- ExpirySettings
- TimeoutInSec / ExpiryDate / TimeOfDay
- Source
-
LookupCache policy
- looks for an entry in a cache
- cachehit variable is populated (true/false)
- LookupCache
- CacheResource
- CacheKey
- Prefix
- KeyFragment
- Scope (must be set if Cache prefix is not set)
- Global: org__env
- Application: orgenvproxy
- Exclusive: orgenvproxy__endpoint
- CacheLookupTimeoutInSeconds (default: 30s)
- AssignTo
-
InvalidateCache policy
- purge entries from a caches
- InvalidateCache
- CacheResource
- CacheKey
- KeyFragment
- Scope (must be set if Cache prefix is not set)
- Global: org__env
- Application: orgenvproxy
- Exclusive: orgenvproxy__endpoint
- CacheContext
- APIProxyName / ProxyName(endpoint) / TargetName
- PurgeChildEntries
-
Response caching
-
ResponseCache policy
-
streamlines the process of caching HTTP responses
-
handle both the lookup and the population of the cache
-
is attached to exactly 2 places: a request flow (checks the cache) and a response flow (populates the cache)
-
ResponseCache
- CacheResource
- CacheKey
- KeyFragment
- ExpirySettings
- TimeoutInSec / ExpiryDate / TimeOfDay
- UseAcceptHeader
- ExcludeErrorResponse
- SkipCacheLookup
- SkipCachePopulation
- UseResponseCacheHeaders
- If true caching-related headers in the response will be used with this precedence:
- Cache-Control s-max-age
- Cache-Control max-age
- Expires
- If one of those headers is used, its expiration is compared to the ExpirySettings value, and the lower expiration time is used
- If true caching-related headers in the response will be used with this precedence:
-
-
Response cache best practices:
- Only cache GET requests
- Think carefully about cache key fragments
- Use unique user identifier as a key fragment
- Use proxy.pathsuffix and specific query parameters as key fragments instead of entire URL
-
-
-
API Publishing
- API versionning
- Developer Portals
-
Logging
- MessageLogging policy
- continueOnError=true
- in the PostClientFlow
- MessageLogging
- Syslog
- Message
- Host
- Port
- Protocol (TCP/UDP)
- SSLInfo (if TCP)
- Enabled
- Syslog
- MessageLogging policy
-
Analytics
- App analytics
- Developer analytics
- API analytics
- StatisticsCollector policy
- StatisticsCollector
- Statistics
- Statistic (name, ref, type)
- Statistics
- StatisticsCollector
-
CI/CD
- Maven plugins
- apigee-deploy-maven-plugin
- apigee-config-maven-plugin
- CLI tool
- apigeetool
- Management API
- CLI get_token
- CLI acurl
- Maven plugins