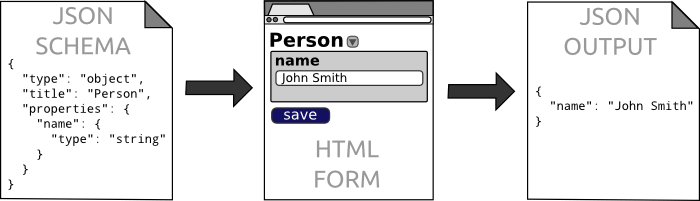
JSON Editor
JSON Editor takes a JSON Schema and uses it to generate an HTML form.
It has full support for JSON Schema version 3 and 4 and can integrate with several popular CSS frameworks (bootstrap, foundation, and jQueryUI).
Check out an interactive demo (demo.html): http://jeremydorn.com/json-editor/
Download the production version (22K when gzipped) or the development version.
Requirements
JSON Editor has no required dependencies. It only needs a modern browser (tested in Chrome and Firefox).
Optional Requirements
The following are not required, but can improve the style and usability of JSON Editor when present.
- A compatible JS template engine (Mustache, Underscore, Hogan, Handlebars, Swig, Markup, or EJS)
- A compatible CSS framework for styling (bootstrap 2/3, foundation 3/4/5, or jqueryui)
- A compatible icon library (bootstrap 2/3 glyphicons, foundation icons 2/3, jqueryui, or font awesome 3/4)
- SCEditor for WYSIWYG editing of HTML or BBCode content
- EpicEditor for editing of Markdown content
- Ace Editor for editing code
- Select2 for nicer Select boxes
Usage
If you learn best by example, check these out:
- Basic Usage Example - http://rawgithub.com/jdorn/json-editor/master/examples/basic.html
- Advanced Usage Example - http://rawgithub.com/jdorn/json-editor/master/examples/advanced.html
- CSS Integration Example - http://rawgithub.com/jdorn/json-editor/master/examples/css_integration.html
The rest of this README contains detailed documentation about every aspect of JSON Editor. For more under-the-hood documentation, check the wiki.
Initialize
var element = document.getElementById('editor_holder');
var editor = new JSONEditor(element, options);Options
Options can be set globally or on a per-instance basis during instantiation.
// Set an option globally
JSONEditor.defaults.options.theme = 'bootstrap2';
// Set an option during instantiation
var editor = new JSONEditor(element, {
//...
theme: 'bootstrap2'
});Here are all the available options:
| Option | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
| ajax | If true, JSON Editor will load external URLs in $ref via ajax. |
false |
| disable_array_add | If true, remove all "add row" buttons from arrays. |
false |
| disable_array_delete | If true, remove all "delete row" buttons from arrays. |
false |
| disable_array_reorder | If true, remove all "move up" and "move down" buttons from arrays. |
false |
| disable_collapse | If true, remove all collapse buttons from objects and arrays. |
false |
| disable_edit_json | If true, remove all Edit JSON buttons from objects. |
false |
| disable_properties | If true, remove all Edit Properties buttons from objects. |
false |
| form_name_root | The first part of the `name` attribute of form inputs in the editor. An full example name is `root[person][name]` where "root" is the form_name_root. | root |
| iconlib | The icon library to use for the editor. See the CSS Integration section below for more info. | null |
| no_additional_properties | If true, objects can only contain properties defined with the properties keyword. |
false |
| refs | An object containing schema definitions for URLs. Allows you to pre-define external schemas. | {} |
| required_by_default | If true, all schemas that don't explicitly set the required property will be required. |
false |
| keep_oneof_values | If true, makes oneOf copy properties over when switching. |
true |
| schema | A valid JSON Schema to use for the editor. Version 3 and Version 4 of the draft specification are supported. | {} |
| show_errors | When to show validation errors in the UI. Valid values are interaction, change, always, and never. |
"interaction" |
| startval | Seed the editor with an initial value. This should be valid against the editor's schema. | null |
| template | The JS template engine to use. See the Templates and Variables section below for more info. | default |
| theme | The CSS theme to use. See the CSS Integration section below for more info. | html |
*Note If the ajax property is true and JSON Editor needs to fetch an external url, the api methods won't be available immediately.
Listen for the ready event before calling them.
editor.on('ready',function() {
// Now the api methods will be available
editor.validate();
});Get/Set Value
editor.setValue({name: "John Smith"});
var value = editor.getValue();
console.log(value.name) // Will log "John Smith"Instead of getting/setting the value of the entire editor, you can also work on individual parts of the schema:
// Get a reference to a node within the editor
var name = editor.getEditor('root.name');
// `getEditor` will return null if the path is invalid
if(name) {
name.setValue("John Smith");
console.log(name.getValue());
}Validate
When feasible, JSON Editor won't let users enter invalid data. This is done by using input masks and intelligently enabling/disabling controls.
However, in some cases it is still possible to enter data that doesn't validate against the schema.
You can use the validate method to check if the data is valid or not.
// Validate the editor's current value against the schema
var errors = editor.validate();
if(errors.length) {
// errors is an array of objects, each with a `path`, `property`, and `message` parameter
// `property` is the schema keyword that triggered the validation error (e.g. "minLength")
// `path` is a dot separated path into the JSON object (e.g. "root.path.to.field")
console.log(errors);
}
else {
// It's valid!
}By default, this will do the validation with the editor's current value. If you want to use a different value, you can pass it in as a parameter.
// Validate an arbitrary value against the editor's schema
var errors = editor.validate({
value: {
to: "test"
}
});Listen for Changes
The change event is fired whenever the editor's value changes.
editor.on('change',function() {
// Do something
});
editor.off('change',function_reference);You can also watch a specific field for changes:
editor.watch('path.to.field',function() {
// Do something
});
editor.unwatch('path.to.field',function_reference);Enable and Disable the Editor
This lets you disable editing for the entire form or part of the form.
// Disable entire form
editor.disable();
// Disable part of the form
editor.getEditor('root.location').disable();
// Enable entire form
editor.enable();
// Enable part of the form
editor.getEditor('root.location').enable();
// Check if form is currently enabled
if(editor.isEnabled()) alert("It's editable!");Destroy
This removes the editor HTML from the DOM and frees up resources.
editor.destroy();CSS Integration
JSON Editor can integrate with several popular CSS frameworks out of the box.
The currently supported themes are:
- html (the default)
- bootstrap2
- bootstrap3
- foundation3
- foundation4
- foundation5
- jqueryui
The default theme is html, which doesn't use any special class names or styling.
This default can be changed by setting the JSONEditor.defaults.options.theme variable.
JSONEditor.defaults.options.theme = 'foundation5';You can override this default on a per-instance basis by passing a theme parameter in when initializing:
var editor = new JSONEditor(element,{
schema: schema,
theme: 'jqueryui'
});Icon Libraries
JSON Editor also supports several popular icon libraries. The icon library must be set independently of the theme, even though there is some overlap.
The supported icon libs are:
- bootstrap2 (glyphicons)
- bootstrap3 (glyphicons)
- foundation2
- foundation3
- jqueryui
- fontawesome3
- fontawesome4
By default, no icons are used. Just like the CSS theme, you can set the icon lib globally or when initializing:
// Set the global default
JSONEditor.defaults.options.iconlib = "bootstrap2";
// Set the icon lib during initialization
var editor = new JSONEditor(element,{
schema: schema,
iconlib: "fontawesome4"
});It's possible to create your own custom themes and/or icon libs as well. Look at any of the existing classes for examples.
JSON Schema Support
JSON Editor fully supports version 3 and 4 of the JSON Schema core and validation specifications.
Some of The hyper-schema specification is supported as well.
$ref and definitions
JSON Editor supports schema references to external URLs and local definitions. Here's an example showing both:
{
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"name": {
"title": "Full Name",
"$ref": "#/definitions/name"
},
"location": {
"$ref": "http://mydomain.com/geo.json"
}
},
"definitions": {
"name": {
"type": "string",
"minLength": 5
}
}
}Local references must point to the definitions object of the root node of the schema.
So, #/customkey/name will throw an exception.
If loading an external url via Ajax, the url must either be on the same domain or return the correct HTTP cross domain headers. If your URLs don't meet this requirement, you can pass in the references to JSON Editor during initialization (see Usage section above).
Self-referential $refs are supported. Check out examples/recursive.html for usage examples.
hyper-schema links
The links keyword from the hyper-schema specification can be used to add links to related documents.
JSON Editor will use the mediaType property of the links to determine how best to display them.
Image, audio, and video links will display the media inline as well as providing a text link.
Here are a couple examples:
Simple text link
{
"title": "Blog Post Id",
"type": "integer",
"links": [
{
"rel": "comments",
"href": "/posts/{{self}}/comments/"
}
]
}
Show a video preview (using HTML5 video)
{
"title": "Video filename",
"type": "string",
"links": [
{
"href": "/videos/{{self}}.mp4",
"mediaType": "video/mp4"
}
]
}
The href property is a template that gets re-evaluated every time the value changes.
The variable self is always available. Look at the Dependencies section below for how to include other fields or use a custom template engine.
Property Ordering
There is no way to specify property ordering in JSON Schema (although this may change in v5 of the spec).
JSON Editor introduces a new keyword propertyOrder for this purpose. The default property order if unspecified is 1000. Properties with the same order will use normal JSON key ordering.
{
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"prop1": {
"type": "string"
},
"prop2": {
"type": "string",
"propertyOrder": 10
},
"prop3": {
"type": "string",
"propertyOrder": 1001
},
"prop4": {
"type": "string",
"propertyOrder": 1
}
}
}In the above example schema, prop1 does not have an order specified, so it will default to 1000.
So, the final order of properties in the form (and in returned JSON data) will be:
- prop4 (order 1)
- prop2 (order 10)
- prop1 (order 1000)
- prop3 (order 1001)
Default Properties
The default behavior of JSON Editor is to include all object properties defined with the properties keyword.
To override this behaviour, you can use the keyword defaultProperties to set which ones are included:
{
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"name": {"type": "string"},
"age": {"type": "integer"}
},
"defaultProperties": ["name"]
}Now, only the name property above will be included by default. You can use the "Object Properties" button
to add the "age" property back in.
format
JSON Editor supports many different formats for schemas of type string. They will work with schemas of type integer and number as well, but some formats may produce weird results.
If the enum property is specified, format will be ignored.
JSON Editor uses HTML5 input types, so some of these may render as basic text input in older browsers:
- color
- date
- datetime
- datetime-local
- month
- number
- range
- tel
- text
- textarea
- time
- url
- week
Here is an example that will show a color picker in browsers that support it:
{
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"color": {
"type": "string",
"format": "color"
}
}
}Specialized String Editors
In addition to the standard HTML input formats, JSON Editor can also integrate with several 3rd party specialized editors. These libraries are not included in JSON Editor and you must load them on the page yourself.
SCEditor provides WYSIWYG editing of HTML and BBCode. To use it, set the format to html or bbcode and set the wysiwyg option to true:
{
"type": "string",
"format": "html",
"options": {
"wysiwyg": true
}
}You can configure SCEditor by setting configuration options in JSONEditor.plugins.sceditor. Here's an example:
JSONEditor.plugins.sceditor.emoticonsEnabled = false;EpicEditor is a simple Markdown editor with live preview. To use it, set the format to markdown:
{
"type": "string",
"format": "markdown"
}You can configure EpicEditor by setting configuration options in JSONEditor.plugins.epiceditor. Here's an example:
JSONEditor.plugins.epiceditor.basePath = 'epiceditor';Ace Editor is a syntax highlighting source code editor. You can use it by setting the format to any of the following:
- actionscript
- batchfile
- c
- c++
- cpp (alias for c++)
- coffee
- csharp
- css
- dart
- django
- ejs
- erlang
- golang
- handlebars
- haskell
- haxe
- html
- ini
- jade
- java
- javascript
- json
- less
- lisp
- lua
- makefile
- markdown
- matlab
- mysql
- objectivec
- pascal
- perl
- pgsql
- php
- python
- r
- ruby
- sass
- scala
- scss
- smarty
- sql
- stylus
- svg
- twig
- vbscript
- xml
- yaml
{
"type": "string",
"format": "yaml"
}You can use the hyper-schema keyword media instead of format too if you prefer for formats with a mime type:
{
"type": "string",
"media": {
"type": "text/html"
}
}You can override the default Ace theme by setting the JSONEditor.plugins.ace.theme variable.
JSONEditor.plugins.ace.theme = 'twilight';Booleans
The default boolean editor is a select box with options "true" and "false". To use a checkbox instead, set the format to checkbox.
{
"type": "boolean",
"format": "checkbox"
}Arrays
The default array editor takes up a lot of screen real estate. The table and tabs formats provide more compact UIs for editing arrays.
The table format works great when every array element has the same schema and is not too complex.
The tabs format can handle any array, but only shows one array element at a time. It has tabs on the left for switching between items.
Here's an example of the table format:
{
"type": "array",
"format": "table",
"items": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "string"
}
}
}
}For arrays of enumerated strings, you can also use the select or checkbox format. These formats require a very specific schema to work:
{
"type": "array",
"uniqueItems": true,
"items": {
"type": "string",
"enum": ["value1","value2"]
}
}By default, the checkbox editor (multiple checkboxes) will be used if there are fewer than 8 enum options. Otherwise, the select editor (a multiselect box) will be used.
You can override this default by passing in a format:
{
"type": "array",
"format": "select",
"uniqueItems": true,
"items": {
"type": "string",
"enum": ["value1","value2"]
}
}Objects
The default object layout is one child editor per row. The grid format will instead put multiple child editors per row.
This can make the editor much more compact, but at a cost of not guaranteeing child editor order.
{
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"name": { "type": "string" }
},
"format": "grid"
}Editor Options
Editors can accept options which alter the behavior in some way.
collapsed- If set to true, the editor will start collapsed (works for objects and arrays)disable_array_add- If set to true, the "add row" button will be hidden (works for arrays)disable_array_delete- If set to true, the "delete row" buttons will be hidden (works for arrays)disable_array_reorder- If set to true, the "move up/down" buttons will be hidden (works for arrays)disable_collapse- If set to true, the collapse button will be hidden (works for objects and arrays)disable_edit_json- If set to true, the Edit JSON button will be hidden (works for objects)disable_properties- If set to true, the Edit Properties button will be hidden (works for objects)enum_titles- An array of display values to use for select box options in the same order as defined with theenumkeyword. Works with schema using enum values.expand_height- If set to true, the input will auto expand/contract to fit the content. Works best with textareas.grid_columns- Explicitly set the number of grid columns (1-12) for the editor if it's within an object using a grid layout.hidden- If set to true, the editor will not appear in the UI (works for all types)input_height- Explicitly set the height of the input element. Should be a valid CSS width string (e.g. "100px"). Works best with textareas.input_width- Explicitly set the width of the input element. Should be a valid CSS width string (e.g. "100px"). Works for string, number, and integer data types.remove_empty_properties- If set to true for an object, empty object properties (i.e. those with falsy values) will not be returned by getValue().
{
"type": "object",
"options": {
"collapsed": true
},
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "string"
}
}
}You can globally set the default options too if you want:
JSONEditor.defaults.editors.object.options.collapsed = true;Dependencies
Sometimes, it's necessary to have one field's value depend on another's.
The dependencies keyword from the JSON Schema specification is not nearly flexible enough to handle most use cases,
so JSON Editor introduces a couple custom keywords that help in this regard.
The first step is to have a field "watch" other fields for changes.
{
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"first_name": {
"type": "string"
},
"last_name": {
"type": "string"
},
"full_name": {
"type": "string",
"watch": {
"fname": "first_name",
"lname": "last_name"
}
}
}
}The keyword watch tells JSON Editor which fields to watch for changes.
The keys (fname and lname in this example) are alphanumeric aliases for the fields.
The values (first_name and last_name) are paths to the fields. To access nested properties of objects, use a dot for separation (e.g. "path.to.field").
By default paths are from the root of the schema, but you can make the paths relative to any ancestor node with a schema id defined as well. This is especially useful within arrays. Here's an example:
{
"type": "array",
"items": {
"type": "object",
"id": "arr_item",
"properties": {
"first_name": {
"type": "string"
},
"last_name": {
"type": "string"
},
"full_name": {
"type": "string",
"watch": {
"fname": "arr_item.first_name",
"lname": "arr_item.last_name"
}
}
}
}
}Now, the full_name field in each array element will watch the first_name and last_name fields within the same array element.
Templates
Watching fields by itself doesn't do anything. For the example above, you need to tell JSON Editor that full_name should be fname [space] lname.
JSON Editor uses a javascript template engine to accomplish this. A barebones template engine is included by default (simple {{variable}} replacement only), but many of the most popular template engines are also supported:
- ejs
- handlebars
- hogan
- markup
- mustache
- swig
- underscore
You can change the default by setting JSONEditor.defaults.options.template to one of the supported template engines:
JSONEditor.defaults.options.template = 'handlebars';You can set the template engine on a per-instance basis as well:
var editor = new JSONEditor(element,{
schema: schema,
template: 'hogan'
});Here is the completed full_name example using the default barebones template engine:
{
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"first_name": {
"type": "string"
},
"last_name": {
"type": "string"
},
"full_name": {
"type": "string",
"template": "{{fname}} {{lname}}",
"watch": {
"fname": "first_name",
"lname": "last_name"
}
}
}
}
Enum Values
Another common dependency is a drop down menu whose possible values depend on other fields. Here's an example:
{
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"possible_colors": {
"type": "array",
"items": {
"type": "string"
}
},
"primary_color": {
"type": "string"
}
}
}Let's say you want to force primary_color to be one of colors in the possible_colors array. First, we must tell the primary_color field to watch the possible_colors array.
{
"primary_color": {
"type": "string",
"watch": {
"colors": "possible_colors"
}
}
}Then, we use the special keyword enumSource to tell JSON Editor that we want to use this field to populate a drop down.
{
"primary_color": {
"type": "string",
"watch": {
"colors": "possible_colors"
},
"enumSource": "colors"
}
}Now, anytime the possible_colors array changes, the dropdown's values will be changed as well.
This is the most basic usage of enumSource. The more verbose form of this property supports
filtering, pulling from multiple sources, constant values, etc..
Here's a more complex example (this uses the Swig template engine syntax to show some advanced features)
{
// An array of sources
"enumSource": [
// Constant values
["none"],
{
// A watched field source
"source": "colors",
// Use a subset of the array
"slice": [2,5],
// Filter items with a template (if this renders to an empty string, it won't be included)
"filter": "{% if item !== 'black' %}1{% endif %}",
// Specify the display text for the enum option
"title": "{{item|upper}}",
// Specify the value property for the enum option
"value": "{{item|trim}}"
},
// Another constant value at the end of the list
["transparent"]
]
}
You can also specify a list of static items with a slightly different syntax:
{
"enumSource": [{
// A watched field source
"source": [
{
"value": 1,
"title": "One"
},
{
"value": 2,
"title": "Two"
}
],
"title": "{{item.title}}",
"value": "{{item.value}}"
}]
]
}
The colors examples used an array of strings directly. Using the verbose form, you can also make it work with an array of objects. Here's an example:
{
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"possible_colors": {
"type": "array",
"items": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"text": {
"type": "string"
}
}
}
},
"primary_color": {
"type": "string",
"watch": {
"colors": "possible_colors"
},
"enumSource": [{
"source": "colors",
"value": "{{item.text}}"
}]
}
}
}
All of the optional templates in the verbose form have the properties item and i passed into them. item refers to the array element. i is the zero-based index.
Dynamic Headers
The title keyword of a schema is used to add user friendly headers to the editing UI. Sometimes though, dynamic headers, which change based on other fields, are helpful.
Consider the example of an array of children. Without dynamic headers, the UI for the array elements would show Child 1, Child 2, etc..
It would be much nicer if the headers could be dynamic and incorporate information about the children, such as 1 - John (age 9), 2 - Sarah (age 11).
To accomplish this, use the headerTemplate property. All of the watched variables are passed into this template, along with the static title title (e.g. "Child"), the 0-based index i0 (e.g. "0" and "1"), the 1-based index i1, and the field's value self (e.g. {"name": "John", "age": 9}).
{
"type": "array",
"title": "Children",
"items": {
"type": "object",
"title": "Child",
"headerTemplate": "{{ i1 }} - {{ self.name }} (age {{ self.age }})",
"properties": {
"name": { "type": "string" },
"age": { "type": "integer" }
}
}
}
Custom Template Engines
If one of the included template engines isn't sufficient,
you can use any custom template engine with a compile method. For example:
var myengine = {
compile: function(template) {
// Compile should return a render function
return function(vars) {
// A real template engine would render the template here
var result = template;
return result;
}
}
};
// Set globally
JSONEditor.defaults.options.template = myengine;
// Set on a per-instance basis
var editor = new JSONEditor(element,{
schema: schema,
template: myengine
});Language and String Customization
JSON Editor uses a translate function to generate strings in the UI. A default en language mapping is provided.
You can easily override individual translations in the default language or create your own language mapping entirely.
// Override a specific translation
JSONEditor.defaults.languages.en.error_minLength =
"This better be at least {{0}} characters long or else!";
// Create your own language mapping
// Any keys not defined here will fall back to the "en" language
JSONEditor.defaults.languages.es = {
error_notset: "propiedad debe existir"
};
By default, all instances of JSON Editor will use the en language. To override this default, set the JSONEditor.defaults.language property.
JSONEditor.defaults.language = "es";Custom Editor Interfaces
JSON Editor contains editor interfaces for each of the primitive JSON types as well as a few other specialized ones.
You can add custom editors interfaces fairly easily. Look at any of the existing ones for an example.
JSON Editor uses resolver functions to determine which editor interface to use for a particular schema or subschema.
Let's say you make a custom location editor for editing geo data. You can add a resolver function to use this custom editor when appropriate. For example:
// Add a resolver function to the beginning of the resolver list
// This will make it run before any other ones
JSONEditor.defaults.resolvers.unshift(function(schema) {
if(schema.type === "object" && schema.format === "location") {
return "location";
}
// If no valid editor is returned, the next resolver function will be used
});The following schema will now use this custom editor for each of the array elements instead of the default object editor.
{
"type": "array",
"items": {
"type": "object",
"format": "location",
"properties": {
"longitude": {
"type": "number"
},
"latitude": {
"type": "number"
}
}
}
}If you create a custom editor interface that you think could be helpful to others, submit a pull request!
The possibilities are endless. Some ideas:
- A compact way to edit objects
- Radio button version of the
selecteditor - Autosuggest for strings (like enum, but not restricted to those values)
- Better editor for arrays of strings (tag editor)
- Canvas based image editor that produces Base64 data URLs
Custom Validation
JSON Editor provides a hook into the validation engine for adding your own custom validation.
Let's say you want to force all schemas with format set to date to match the pattern YYYY-MM-DD.
// Custom validators must return an array of errors or an empty array if valid
JSONEditor.defaults.custom_validators.push(function(schema, value, path) {
var errors = [];
if(schema.format==="date") {
if(!/^[0-9]{4}-[0-9]{2}-[0-9]{2}$/.test(value)) {
// Errors must be an object with `path`, `property`, and `message`
errors.push({
path: path,
property: 'format',
message: 'Dates must be in the format "YYYY-MM-DD"'
});
}
}
return errors;
});jQuery Integration
*WARNING: This style of usage is deprecated and may not be supported in future versions.
When jQuery (or Zepto) is loaded on the page, you can use JSON Editor like a normal jQuery plugin if you prefer.
$("#editor_holder")
.jsoneditor({
schema: {},
theme: 'bootstrap3'
})
.on('ready', function() {
// Get the value
var value = $(this).jsoneditor('value');
value.name = "John Smith";
// Set the value
$(this).jsoneditor('value',value);
});