This repository provides a Dockerfile to allow you to build (and tweak) a Fedora Linux Docker container for cross-platform development of CS3203's Static Program Analyzer.
The target environment for builds is Fedora 32.
This Docker container is also set up for remote toolchain integration with CLion.
-
Ensure that you have Docker installed on your system.
-
Build the Docker image using the Dockerfile with:
docker build -t cs3203/fedora-dev-env -f Dockerfile.cs3203-fedora . -
Create and run the container (for the first time) using the built image with:
- If you intend to simply use it as a target build environment (or you're developing in Visual Studio or others)
docker run -d --cap-add sys_ptrace --mount type=bind,source=<PathToCodeDirectory>,target=/home/user/cs3203 --name fedora-dev-env cs3203/fedora-dev-env- Note that for Linux or MacOS systems, the
<PathToCodeDirectory>can use the$(pwd)subcommand for the current working directory as in:but for Windows systems, the...,source="$(pwd)"/CS3203/Team06/Code06,...<PathToCodeDirectory>should be an absolute path as in:...,source=c:\CS3203\Team06\Code06,...
- Note that for Linux or MacOS systems, the
- If you intend to develop in CLion using the Full Remote Mode
docker run -d --cap-add sys_ptrace -p127.0.0.1:2222:22 --name fedora-dev-env cs3203/fedora-dev-env
Note: It's also a good idea to remove [localhosts]:2222 if it exists in your system's SSH known_hosts file. The following command tries to find an entry and removes it if it exists:
ssh-keygen -f "$HOME/.ssh/known_hosts" -R "[localhost]:2222" - If you intend to simply use it as a target build environment (or you're developing in Visual Studio or others)
-
After you're done, stop the container with:
docker stop fedora-dev-env -
Subsequently after the first run, start the stopped container with:
docker start fedora-dev-env
To attach a terminal session to the container, you can do so with:
docker exec -it fedora-dev-env /bin/bashThis can also be done in the Docker Desktop application.
- Ensure that the
fedora-dev-envcontainer is running. - Open the CLI for the container in the Docker Desktop application or start a new terminal session and run
docker exec -it fedora-dev-env /bin/bashto attach to the container's CLI. - Navigate to the target folder specified during
docker run, i.e.cd /home/user/cs3203and ensure that the source folder has been properly bind-mounted. - Carry on build instructions as per the CS3203 Wiki guide here
-
Ensure that the
fedora-dev-envcontainer is running. -
In CLion, navigate to your project folder and open the top-level CMakeLists.txt using
Open as Project -
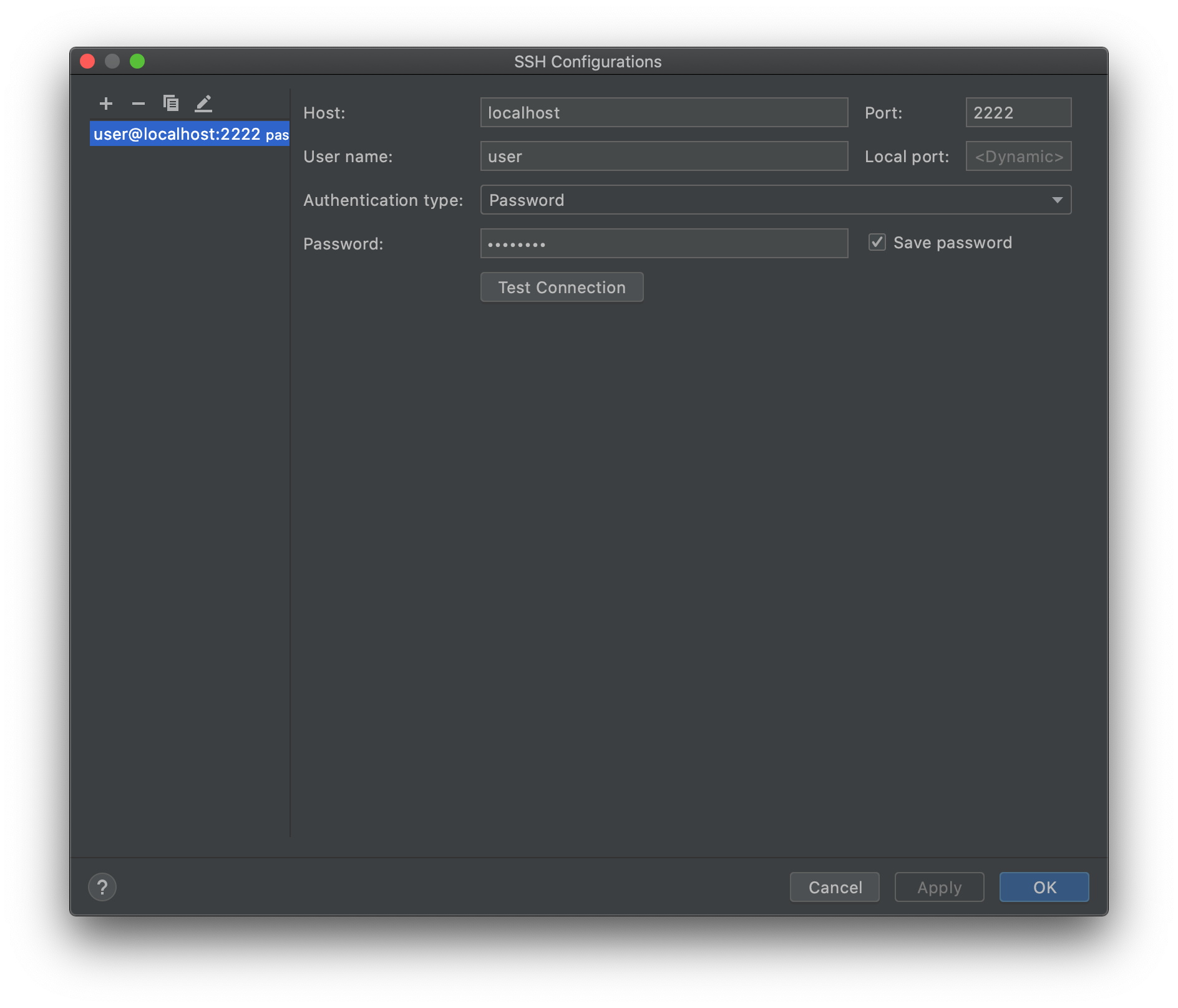
In
Preferences > Build, Execution, Deployment > Toolchain, add a newRemote Hostand set the credentials to- Host:
localhost - Port:
2222 - User name:
user - Authentication type:
Password - Password:
password
and click
Test Connectionto ensure that the connection to the Docker container works. Once done correctly, CLion should be able to detect the tools' versions and path on the Fedora container.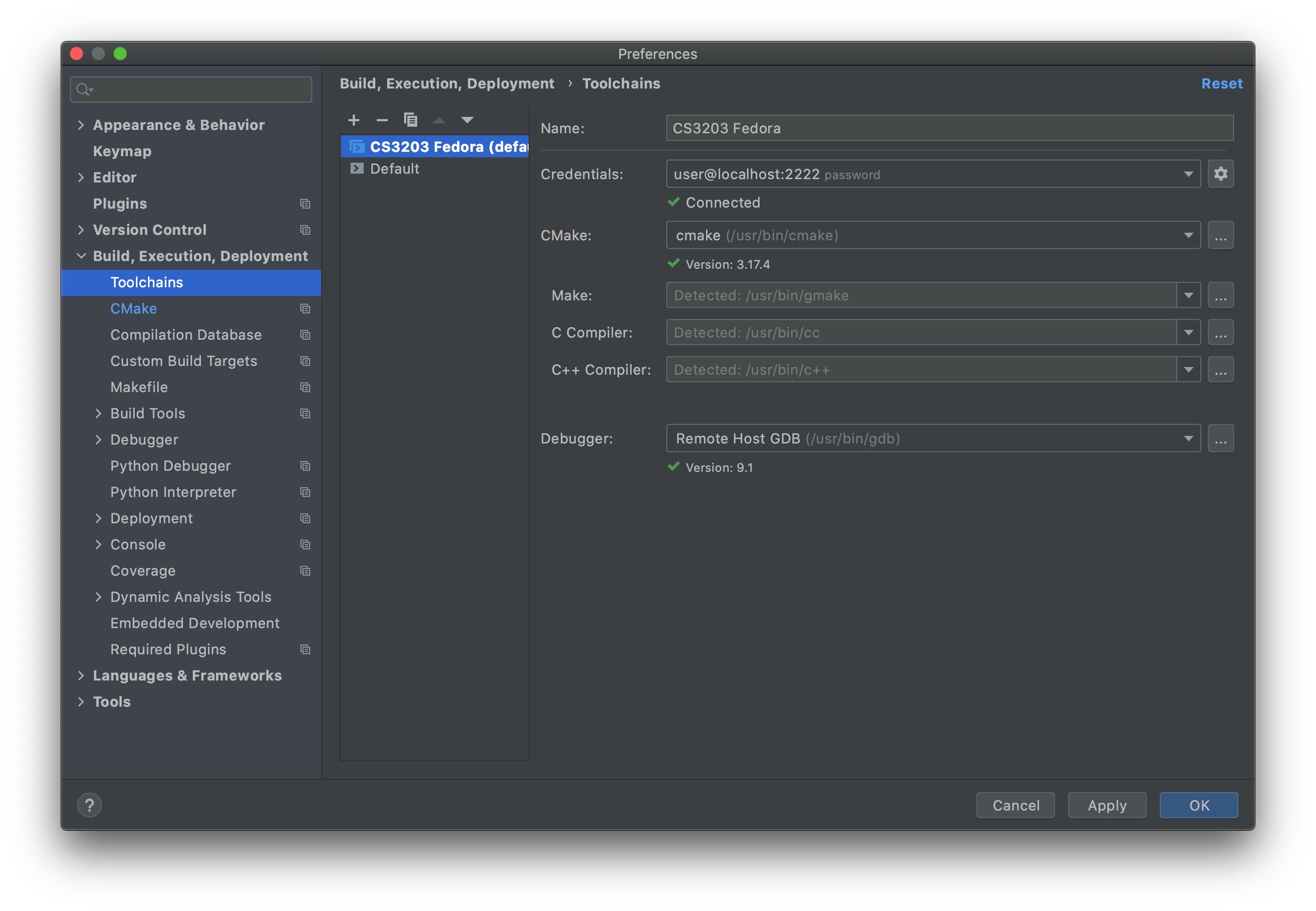
- Host:
-
In
Preferences > Build, Execution, Deployment > CMake, ensure that in the profile,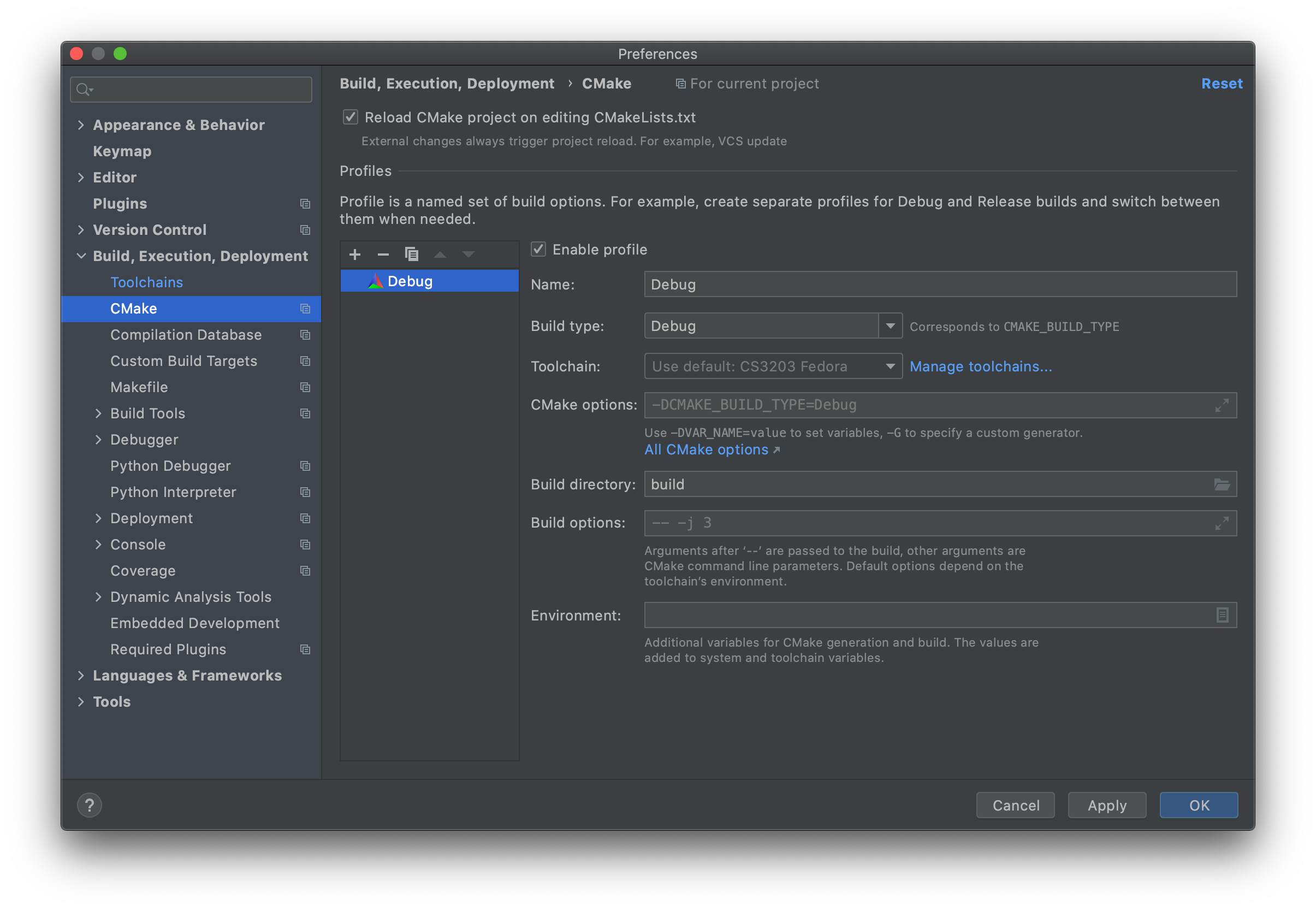
- Toolchain: Fedora toolchain made in step 3 (especially if the toolchain was not set to the default one)
- Build directory:
build(as per CS3203 SPA build instructions, but can be changed to your own preference)
-
In
Preferences > Build, Execution, Deployment > Deployment, ensure the following settings for the deployment server (create a new SFTP server if it doesn't exist)- Under
Connectiontab: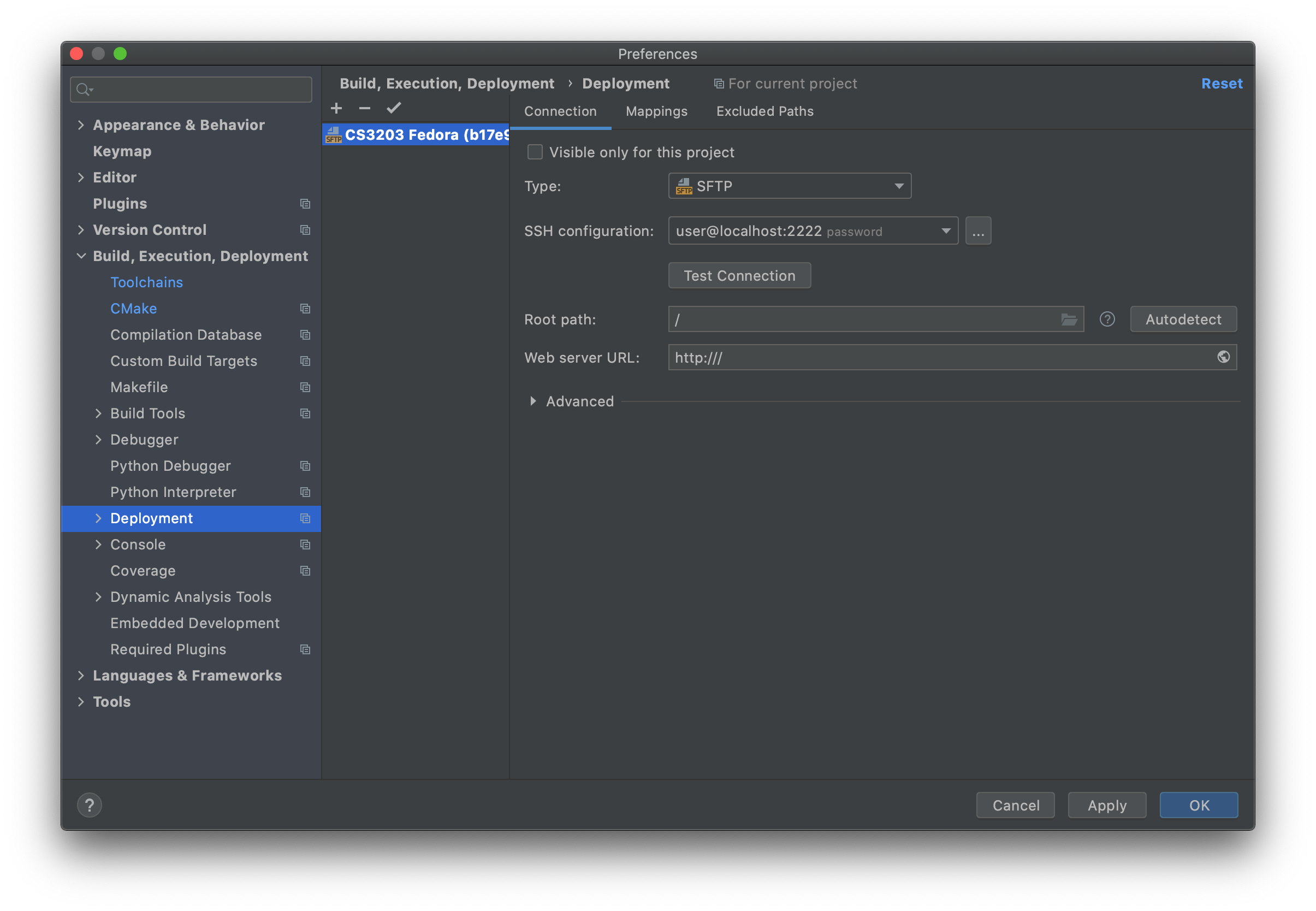
- Type:
SFTP - SSH configuration: (same as toolchain)
- Root path: preferably
\but can be set to your own preference
- Type:
- Under
Mappingstab: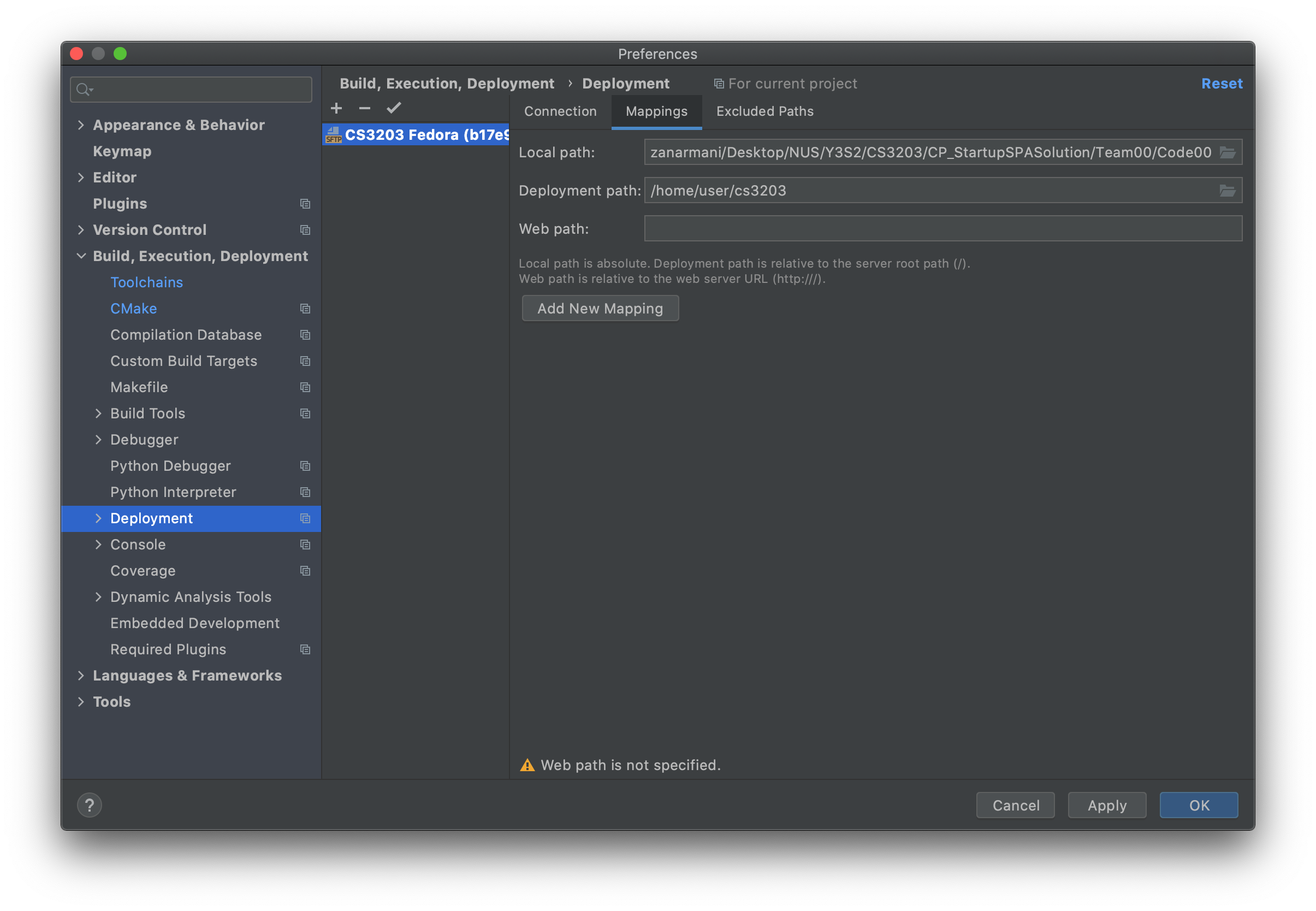
- Local path: (current project path)
- Deployment path: (specify a path for your project preferably somewhere in
/home/user)
- Under
Excluded Pathstab: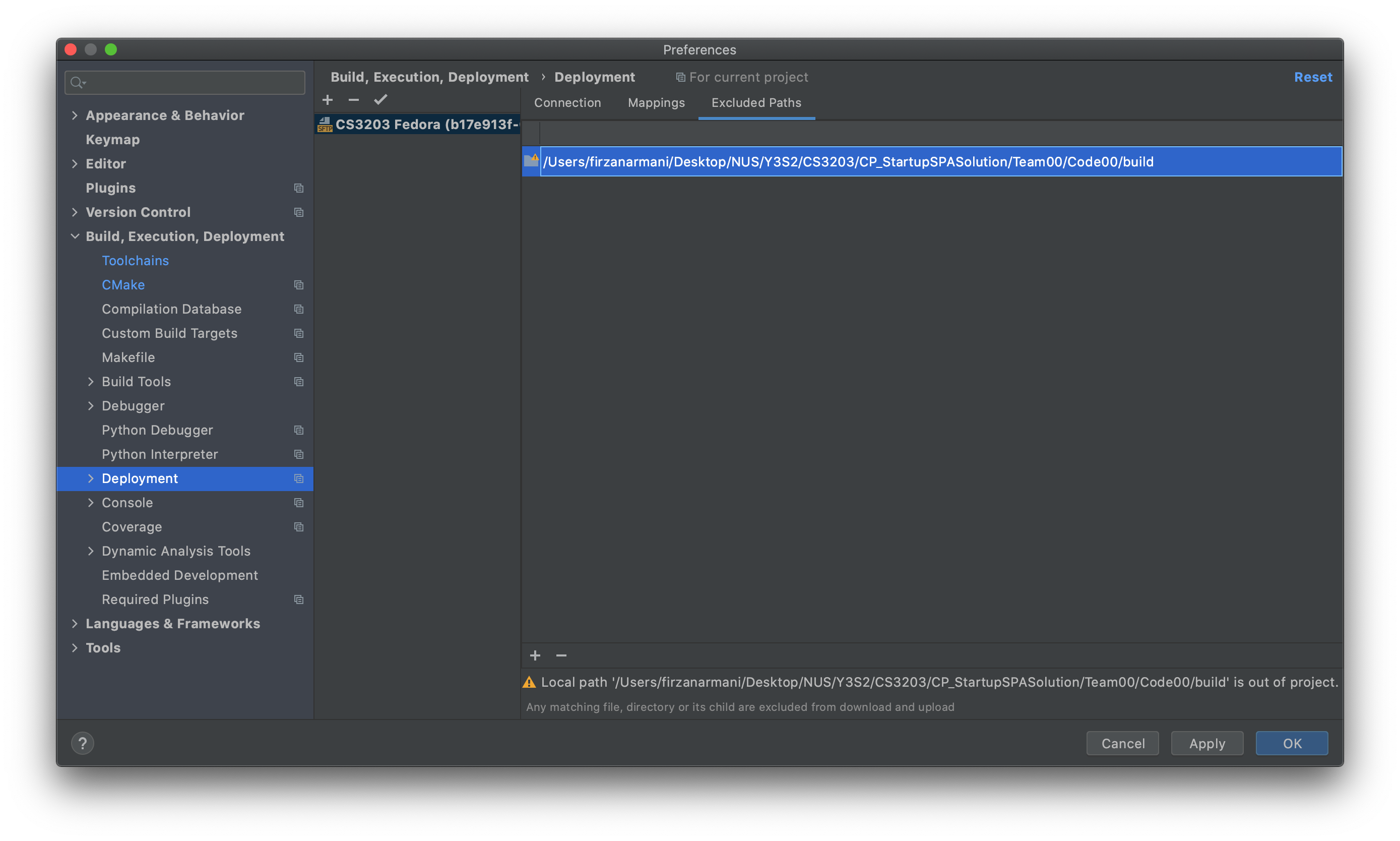
Local pathpointing to thebuild directoryspecified in step 4- Note that this will show a
...<path>... is out of projectwarning. You can ignore this warning.
- Note that this will show a
- Under
-
Close the Preferences window by click on the
OKbutton. CMake should automatically reload the project using these new settings. If it does not, go toFile > Reload CMake Project.
You may encounter the following error in reloading the CMake project:
Cannot resolve path: <build directory>
This is a bug that has been raised to the CLion developers as seen here. To work around this:
- Go to
Help > Find Actionsand enterRegistry- In the
Registrywindow, uncheck the registryclion.remote.sync.text.filesand close the window- Go to
File > Invalidate Caches / Restartand selectInvalidate and Restart- Once CLion restarts, CMake build should run automatically and the bug should be fixed
- Build configurations are now automatically added as seen in the top right of the window.