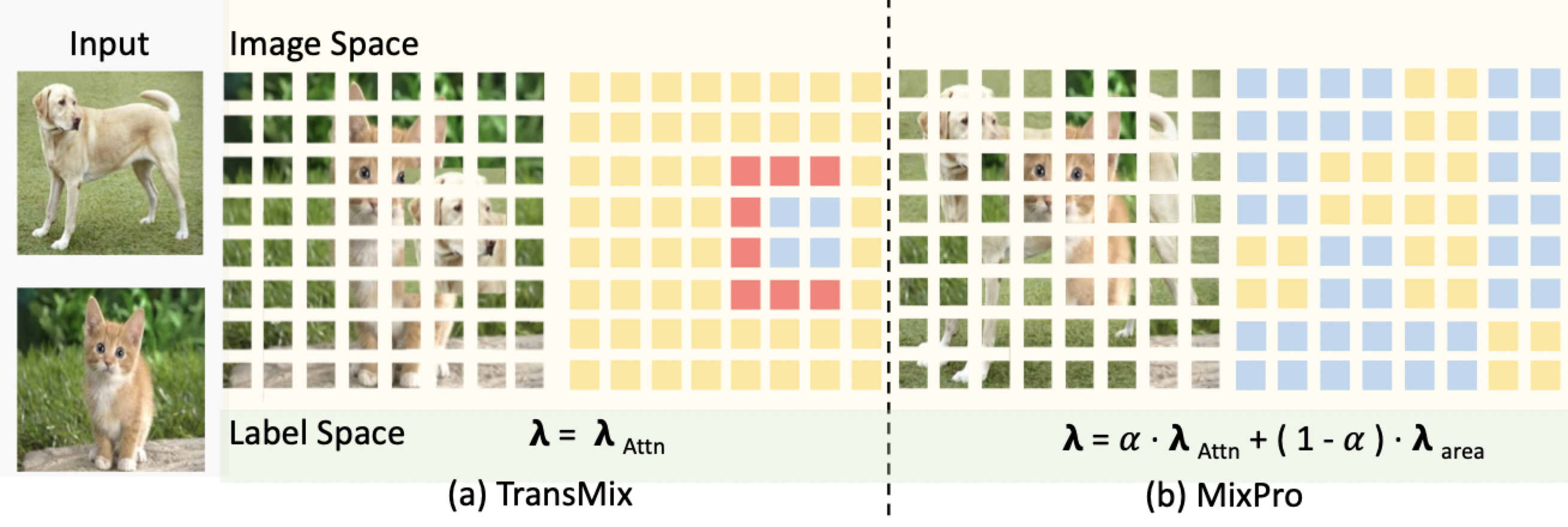
MixPro: Data Augmentation with MaskMix and Progressive Attention Labeling for Vision Transformer [Official, ICLR 2023,paper] 🔥
Qihao Zhao1, Yangyu Huang2, Wei Hu1, Fan Zhang1, Jun Liu3
1 Beijing University of Chemical Technology
2 Microsoft Research Asia
3 Singapore University of Technology and Design
If you find our work inspiring or use our codebase in your research, please consider giving a star ⭐️ and a citation.
@inproceedings{
zhao2023mixpro,
title={MixPro: Data Augmentation with MaskMix and Progressive Attention Labeling for Vision Transformer},
author={Qihao Zhao and Yangyu Huang and Wei Hu and Fan Zhang and Jun Liu},
booktitle={The Eleventh International Conference on Learning Representations },
year={2023},
url={https://openreview.net/forum?id=dRjWsd3gwsm}
}
We recommend using the pytorch docker nvcr>=21.05 by
nvidia: https://catalog.ngc.nvidia.com/orgs/nvidia/containers/pytorch.
- Create a conda virtual environment and activate it:
conda create -n mixpro python=3.7 -y
conda activate mixpro- Install
CUDA>=10.2withcudnn>=7following the official installation instructions - Install
PyTorch>=1.8.0andtorchvision>=0.9.0withCUDA>=10.2:
conda install pytorch==1.8.0 torchvision==0.9.0 cudatoolkit=10.2 -c pytorch- Install
timm==0.4.12:
pip install timm==0.4.12- Install other requirements:
pip install opencv-python==4.4.0.46 termcolor==1.1.0 yacs==0.1.8For ImageNet-1K dataset, you can download it from http://image-net.org/. We provide the following two ways to load data:
-
For standard folder dataset, move validation images to labeled sub-folders. The file structure should look like:
$ tree data imagenet ├── train │ ├── class1 │ │ ├── img1.jpeg │ │ ├── img2.jpeg │ │ └── ... │ ├── class2 │ │ ├── img3.jpeg │ │ └── ... │ └── ... └── val ├── class1 │ ├── img4.jpeg │ ├── img5.jpeg │ └── ... ├── class2 │ ├── img6.jpeg │ └── ... └── ... -
To boost the slow speed when reading images from massive small files, we also support zipped ImageNet, which includes four files:
train.zip,val.zip: which store the zipped folder for train and validate splits.train_map.txt,val_map.txt: which store the relative path in the corresponding zip file and ground truth label. Make sure the data folder looks like this:
$ tree data data └── ImageNet-Zip ├── train_map.txt ├── train.zip ├── val_map.txt └── val.zip $ head -n 5 data/ImageNet-Zip/val_map.txt ILSVRC2012_val_00000001.JPEG 65 ILSVRC2012_val_00000002.JPEG 970 ILSVRC2012_val_00000003.JPEG 230 ILSVRC2012_val_00000004.JPEG 809 ILSVRC2012_val_00000005.JPEG 516 $ head -n 5 data/ImageNet-Zip/train_map.txt n01440764/n01440764_10026.JPEG 0 n01440764/n01440764_10027.JPEG 0 n01440764/n01440764_10029.JPEG 0 n01440764/n01440764_10040.JPEG 0 n01440764/n01440764_10042.JPEG 0
To train a MixPro with Vision Transformer on ImageNet from scratch, run:
python -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node <num-of-gpus-to-use> --master_port 12345 main.py \
--cfg <config-file> --data-path <imagenet-path> [--batch-size <batch-size-per-gpu> --output <output-directory> --tag <job-tag>]Notes:
- To use zipped ImageNet instead of folder dataset, add
--zipto the parameters.- To cache the dataset in the memory instead of reading from files every time, add
--cache-mode part, which will shard the dataset into non-overlapping pieces for different GPUs and only load the corresponding one for each GPU.
- To cache the dataset in the memory instead of reading from files every time, add
- When GPU memory is not enough, you can try the following suggestions:
- Use gradient accumulation by adding
--accumulation-steps <steps>, set appropriate<steps>according to your need. - Use gradient checkpointing by adding
--use-checkpoint, e.g., it saves about 60% memory when trainingDeiT-B. Please refer to this page for more details. - We recommend using multi-node with more GPUs for training very large models, a tutorial can be found in this page.
- Use gradient accumulation by adding
- To change config options in general, you can use
--opts KEY1 VALUE1 KEY2 VALUE2, e.g.,--opts TRAIN.EPOCHS 100 TRAIN.WARMUP_EPOCHS 5will change total epochs to 100 and warm-up epochs to 5. - For additional options, see config and run
python main.py --helpto get detailed message.
For example, to train MixPro DeiT Transformer with 8 GPU on a single node for 300 epochs, run:
MixPro DeiT-T:
python -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node 8 --master_port 12345 main.py \
--cfg configs/deit/deit_tiny_patch14_mask56_224_alpha1.yaml --data-path <imagenet-path> --batch-size 128MixPro DeiT-S:
python -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node 8 --master_port 12345 main.py \
--cfg configs/deit/deit_small_patch14_mask56_224_alpha1.yaml --data-path <imagenet-path> --batch-size 128MixPro DeiT-B:
python -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node 8 --master_port 12345 main.py \
--cfg configs/deit_base_patch14_mask112_224_alpha1_attn_all.yaml --data-path <imagenet-path> --batch-size 64 \
#in config.py
#Probability of switching to mixpro when both mixup and mixpro enabled
_C.AUG.MASKMIX_PROB = 0.5
# MaskMix alpha , maskmix enabled if > 0
_C.AUG.MASKMIX_ALPHA = 1.0
# PAL
_C.AUG.PAL_ATTN = True
The project is based on Swin and Vit(unofficial)
The project is released under the MIT License