Use evolutionary algorithms instead of gridsearch in scikit-learn. This allows you to exponentially reduce the time required to find the best parameters for your estimator. Instead of trying out every possible combination of parameters, evolve only the combinations that give the best results.
Here is an ipython notebook comparing EvolutionaryAlgorithmSearchCV against GridSearchCV and RandomizedSearchCV.
It's implemented using deap library: https://github.com/deap/deap
To install the library use pip:
pip install sklearn-deap
or clone the repo and just type the following on your shell:
python setup.py install
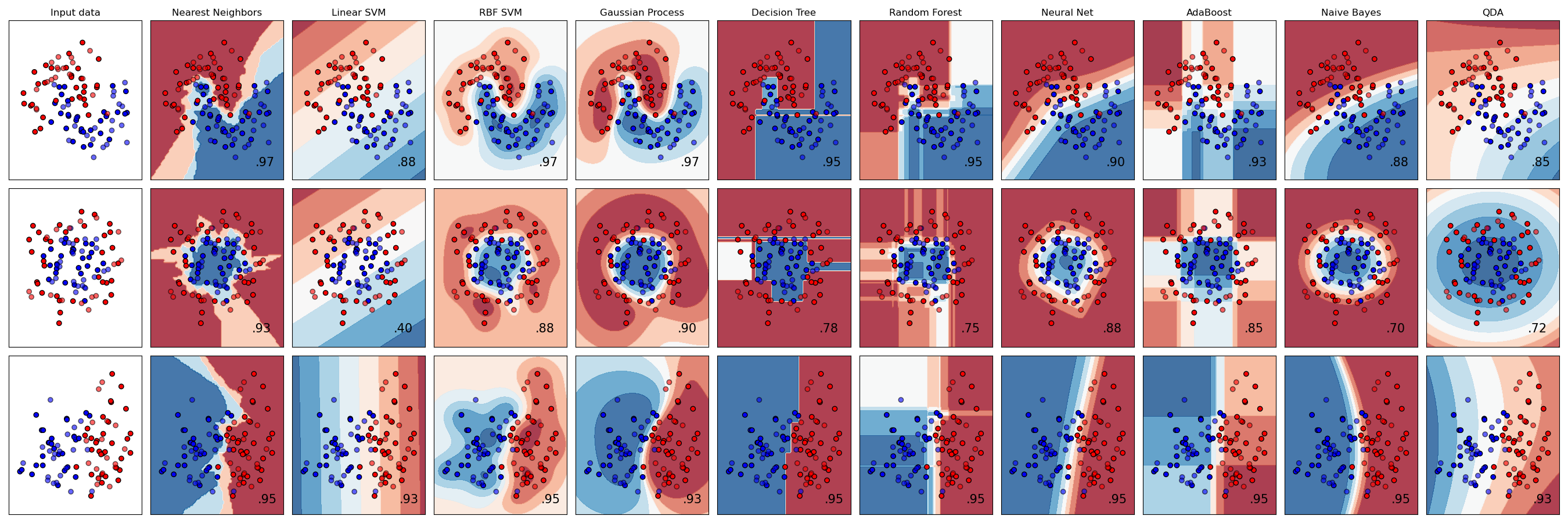
Recreating the sklearn classifier comparison plot with no prior hyper-parameter knowledge. The average fitness of the GA is shown below each plot for 50 generations in orange. The best fitness of the GA is shown in blue.
This example code can be found in /example and demonstrates tuned hyper-parameters can easily be found for a variety of algorithms.
We can compare to the original classifier comparison and see that there is generally an improvement in accuracy
Example of usage:
import sklearn.datasets
import numpy as np
import random
data = sklearn.datasets.load_digits()
X = data["data"]
y = data["target"]
from sklearn.svm import SVC
from sklearn.model_selection import StratifiedKFold
paramgrid = {"kernel": ["rbf"],
"C" : np.logspace(-9, 9, num=25, base=10),
"gamma" : np.logspace(-9, 9, num=25, base=10)}
random.seed(1)
from evolutionary_search import EvolutionaryAlgorithmSearchCV
cv = EvolutionaryAlgorithmSearchCV(estimator=SVC(),
params=paramgrid,
scoring="accuracy",
cv=StratifiedKFold(n_splits=4),
verbose=1,
population_size=50,
gene_mutation_prob=0.10,
gene_crossover_prob=0.5,
tournament_size=3,
generations_number=5,
n_jobs=4)
cv.fit(X, y)Output:
Types [1, 2, 2] and maxint [0, 24, 24] detected
--- Evolve in 625 possible combinations ---
gen nevals avg min max
0 50 0.202404 0.10128 0.962716
1 26 0.383083 0.10128 0.962716
2 31 0.575214 0.155259 0.962716
3 29 0.758308 0.105732 0.976071
4 22 0.938086 0.158041 0.976071
5 26 0.934201 0.155259 0.976071
Best individual is: {'kernel': 'rbf', 'C': 31622.776601683792, 'gamma': 0.001}
with fitness: 0.976071229827
Example for maximizing just some function:
from evolutionary_search import maximize
def func(x, y, m=1., z=False):
return m * (np.exp(-(x**2 + y**2)) + float(z))
param_grid = {'x': [-1., 0., 1.], 'y': [-1., 0., 1.], 'z': [True, False]}
args = {'m': 1.}
best_params, best_score, score_results, _, _ = maximize(func, param_grid, args, verbose=False)Output:
best_params = {'x': 0.0, 'y': 0.0, 'z': True}
best_score = 2.0
score_results = (({'x': 1.0, 'y': -1.0, 'z': True}, 1.1353352832366128),
({'x': -1.0, 'y': 1.0, 'z': True}, 1.3678794411714423),
({'x': 0.0, 'y': 1.0, 'z': True}, 1.3678794411714423),
({'x': -1.0, 'y': 0.0, 'z': True}, 1.3678794411714423),
({'x': 1.0, 'y': 1.0, 'z': True}, 1.1353352832366128),
({'x': 0.0, 'y': 0.0, 'z': False}, 2.0),
({'x': -1.0, 'y': -1.0, 'z': False}, 0.36787944117144233),
({'x': 1.0, 'y': 0.0, 'z': True}, 1.3678794411714423),
({'x': -1.0, 'y': -1.0, 'z': True}, 1.3678794411714423),
({'x': 0.0, 'y': -1.0, 'z': False}, 1.3678794411714423),
({'x': 1.0, 'y': -1.0, 'z': False}, 1.1353352832366128),
({'x': 0.0, 'y': 0.0, 'z': True}, 2.0),
({'x': 0.0, 'y': -1.0, 'z': True}, 2.0))