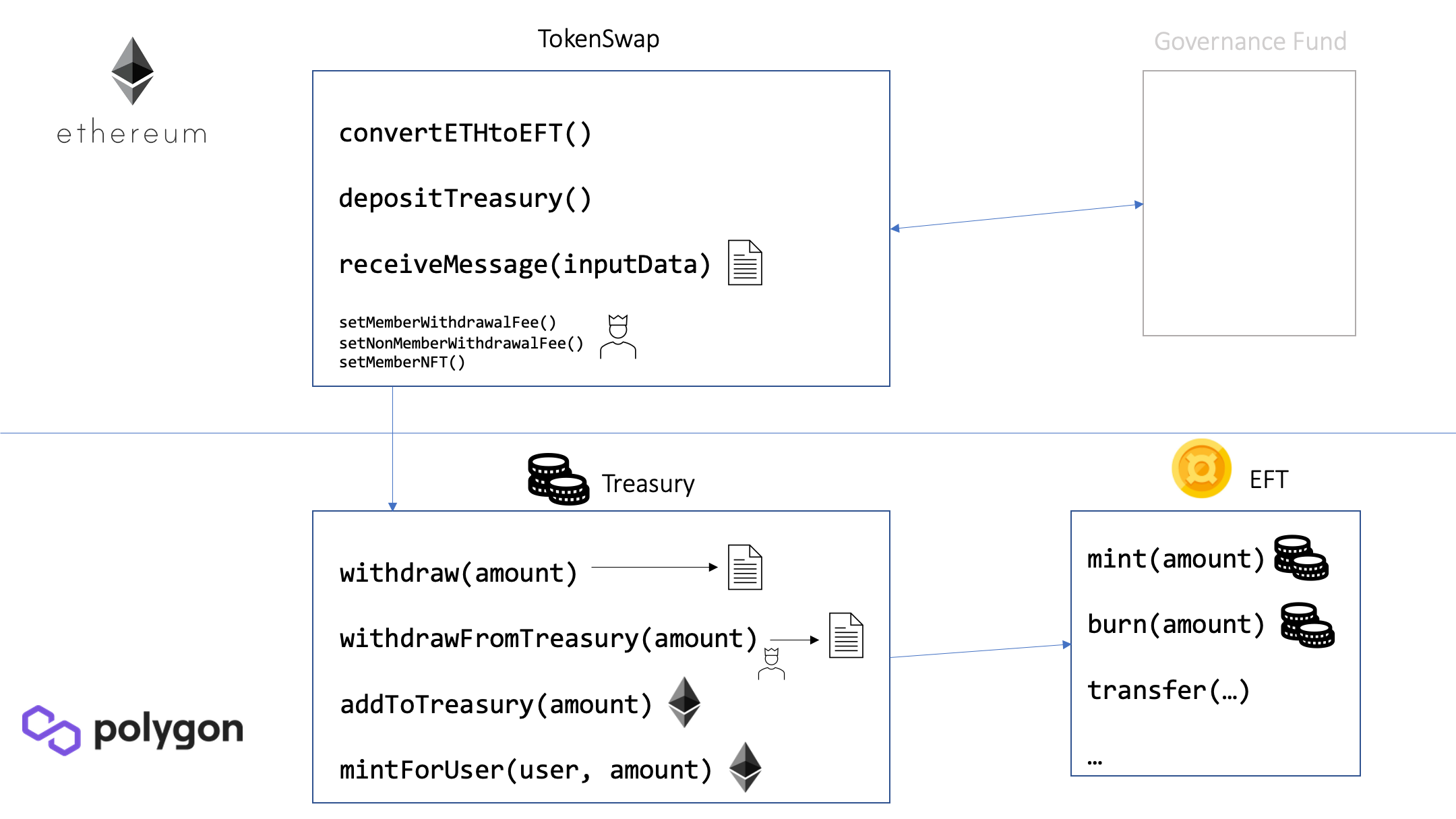
Smart contracts to bridge a custom ERC20 token called EFT (backed by ETH in a customizable proportion) to Polygon and back to Ethereum (for redemption of the ETH). Additionally, there are withdrawal fees that can be reduced when the user holds a certain NFT.
The contracts are used to swap between Ethereum (on the Ethereum blockchain) and the EFT token (on the Polygon blockchain) and vice-versa. For every 1000 EFT tokens (using the default proportion) that are minted on Polygon, there exists 1 ETH on Ethereum that is deposited in the governance fund. On the other hand, whenever a user burns 1000 EFT, 1 ETH can be redeemed from the TokenSwap contract on Ethereum.
For the deployment, the example scripts scripts/deploy_eth.js and scripts/deploy_polygon.js are provided. Note that the Treasury contract expects the address of the Ethereum TokenSwap contract in the constructor (which is passed via the environment variable TOKENSWAP), the Ethereum deployment has therefore to happen first.
After the Treasury contract is deployed, this address also has to be communicated to the TokenSwap contract by calling setFxChildTunnel with the (Polygon) address.
In scripts/deploy_eth.js, the governance fund is currently set to the address of the deployer. This needs to be changed for a real deployment.
Users that want to buy EFT with ETH send ETH to convertETHtoEFT. The ETH is sent to the governance fund and a message is transmitted to Polygon that increases the users's EFT balance (i.e., new EFTs are minted for the user).
To fund the Treasury contract on Polygon with EFTs, the depositTreasury method is used. All of the sent ETH is sent to the governance fund and a message is transmitted to Polygon that increases the EFT balance of the Treasury contract itself. Everyone can fund the treasury, but in practice this will only be done by the governance fund, because the resulting EFTs are not added to a user's balance, i.e. a user has no incentive to fund the treasury.
When a user wants to withdraw EFT tokens from Polygon (and get ETH on Ethereum), he calls withdraw on the Polygon Treasury contract.
The Treasury burns the coins of the user and generates an event that can be relayed to Ethereum. Note that these events are not automatically relayed to Ethereum, this has to be done by the user (or alternatively some relayer bot).
For the relaying, a withdraw proof based on the event has to be generated. This is illustrated in the script scripts/withdraw_proof.mjs.
In this script, txnHash has to be replaced with the transaction hash of the previous transaction (where withdraw was called). Of course, this will be done dynamically in practice (e.g., in the frontend or backend).
The generated proof (a long hex string) can then be used to call receiveMessage on the Ethereum TokenSwap contract, which will pay out the requested amount (in ETH, i.e. divided by 1,000) to the user that initiated the withdrawal on Polygon.
npx hardhat test
Note that some test (because of the checkpoint manager validation) run forked on Goerli, which is configured in hardhat.config.js.