This repository contains our solution to the Kaggle challenge for astronomical sources classification [1]. We need to classify different sources into thirteen different unknown classes, with the information that we expect to obtain from the future LSST survey.
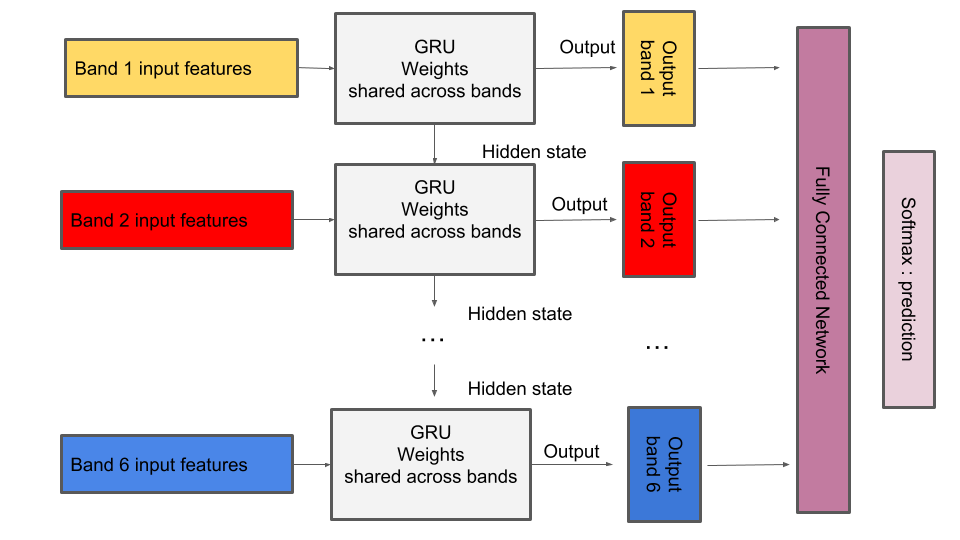
The main difficulty of the challenge is dealing with different bands that have recorded information from the same source at different times. The time series are unevenly sampled and we need a way to combine their information. We have implemented a recurrent neural network to process the given sequential data, sharing its weights accross bands to look for the same features on every band. Later on, we combine what they've learned in a fully connected layer to produce the final classificiation. In this way, we do not need any sort of padding and sharing weights makes our solution computationally efficient. The architecture of the RNN is shown at figure 1.
The sequential features we have used are flux, flux error, time difference between measurements (mjd) and whether the source would have been detected, together with some extra features computed using unevenly sampled fourier transforms as implemented here [2]. These Fourier features are: the magniuted of the dfft, the unwrapped phase, the periodogram and the true alarm probability of agiven period to be produced by an actual signal.
The tensorflow code can be found at classifier/rnn.py. To train the model execute the file train.sh with one of the following command line arguments:
fourier, to use only the fourier space features. time, to use only the time domain features. joint, to use both as separate RNNs that are later on joint by a dense fully connected layer.