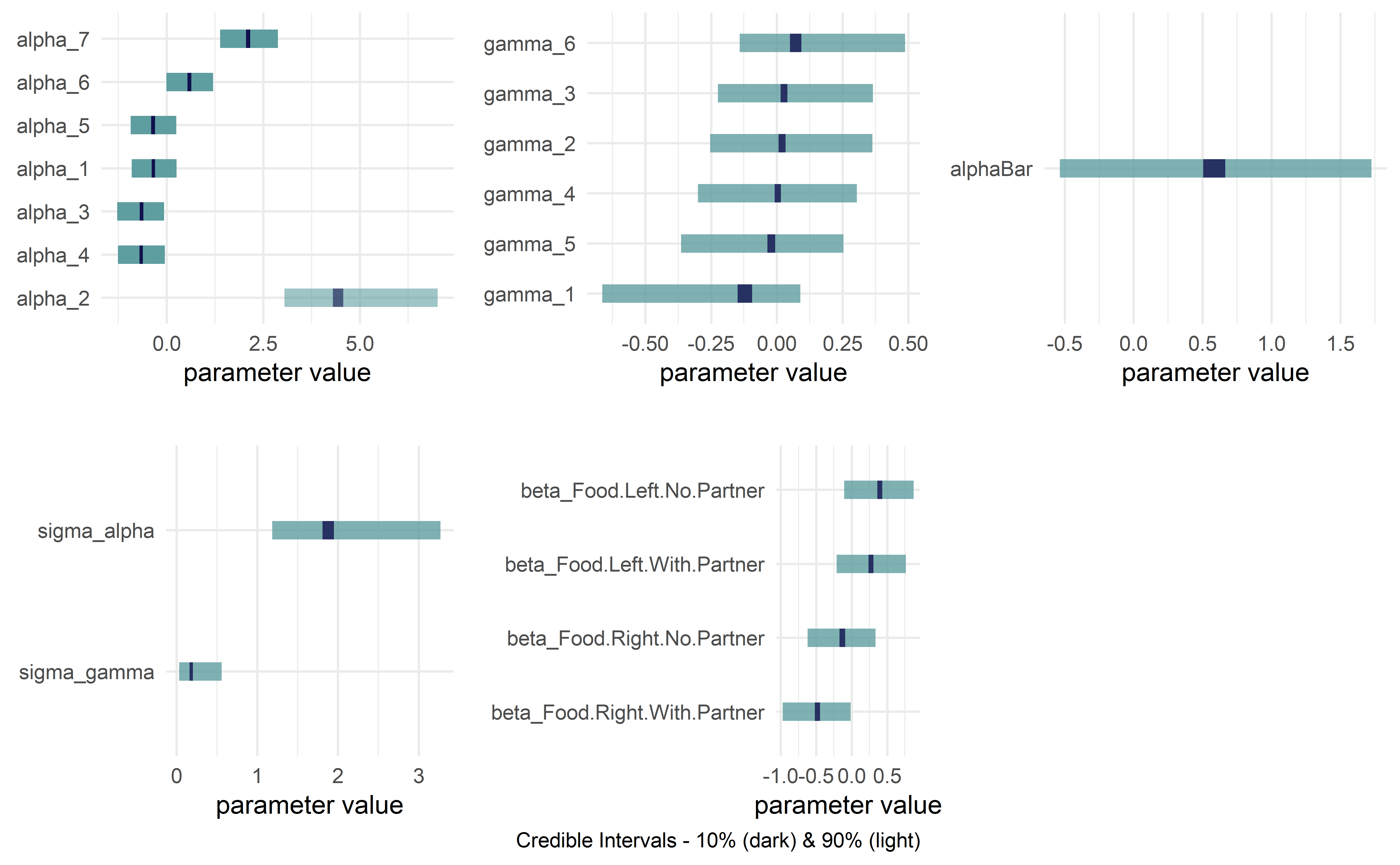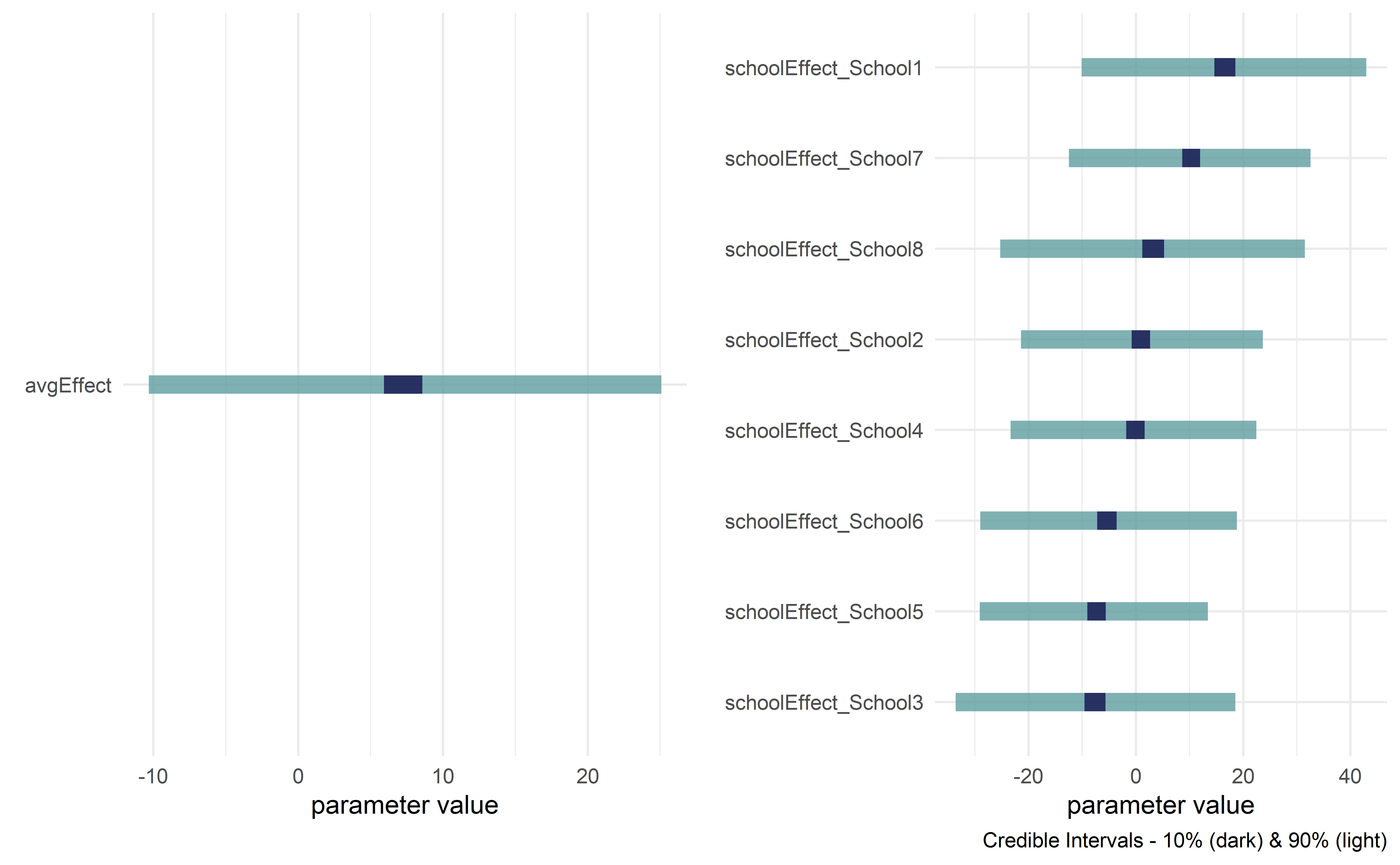Accelerate computational Bayesian inference workflows in R through
interactive modelling, visualization, and inference. The package
leverages directed acyclic graphs (DAGs) to create a unified language
language for business stakeholders, statisticians, and programmers. Due
to its visual nature and simple model construction, causact serves as
a great entry-point for newcomers to computational Bayesian inference.
The
causactpackage offers robust support for both foundational and advanced Bayesian models. While introductory models are well-covered, the utilization of multi-variate distributions such as multi-variate normal, multi-nomial, or dirichlet distributions, may not work as expected. There are ongoing enhancements in the pipeline to facilitate construction of these more intricate models.
While proficiency in R is the only requirement for users of this
package, it also functions as a introductory probabilistic programming
language, seamlessly incorporating the numpyro Python package to
facilitate Bayesian inference without the need to learn any syntax
outside of the package or R. Furthermore, the package streamlines the
process of indexing categorical variables, which often presents a
complex syntax hurdle for those new to computational Bayesian methods.
For enhanced learning, the causact package for Bayesian inference is
featured in A Business Analyst's Introduction to Business Analytics
available at https://www.causact.com/.
Feedback and encouragement is appreciated via github issues.
To install the causact package, follow the steps outlined below:
For the current stable release, which is tailored to integrate with
Python’s numpyro package, employ the following command:
install.packages("causact")Then, see Essential Dependencies if you want
to be able to automate sampling using the numpyro package.
If you want the most recent development version (not recommended), execute the following:
install.packages("remotes")
remotes::install_github("flyaflya/causact")To harness the full potential of causact for DAG visualization and
Bayesian posterior analysis, it’s vital to ensure proper integration
with the numpyro package. Given the Python-based nature of numpyro,
a few essential dependencies must be in place. Execute the following
commands after installing causact:
library(causact)
install_causact_deps()If prompted, respond with Y to any inquiries related to installing
miniconda.
Note: If opting for installation on Posit Cloud, temporarily adjust your project’s RAM to 4GB during the installation process (remember to APPLY CHANGES). This preemptive measure helps avoid encountering an
Error: Error creating conda environment [exit code 137]. After installation, feel free to revert the settings to 1GB of RAM.
Note: The September 11, 2023 release of
reticulate(v1.32) has caused an issue which gives aTypeError: the first argument must be callableerror when usingdag_numpyro()on windows. If you experience this, install the dev version ofreticulateby following the below steps:
Install RTOOLS by using installer at: https://cran.r-project.org/bin/windows/Rtools/
Run this to get the dev version of
reticulate:
# install DEV version of reticulate
# install.packages("pak") #uncomment as needed
pak::pak("rstudio/reticulate")
In cases where legacy compatibility is paramount and you still rely on
the operationality of the dag_greta() function, consider installing
v0.4.2 of the causact package. However, it’s essential to emphasize
that this approach is not recommended for general usage:
### EXERCISE CAUTION BEFORE EXECUTING THESE LINES
### Only proceed if dag_greta() is integral to your existing codebase
install.packages("remotes")
remotes::install_github("flyaflya/causact@v0.4.2")Your judicious choice of installation method will ensure a seamless and
effective integration of the causact package into your computational
toolkit.
Example taken from
https://www.causact.com/graphical-models-tell-joint-distribution-stories.html#graphical-models-tell-joint-distribution-stories
with the packages dag_foo() functions further described here:
#> Initializing python, numpyro, and other dependencies. This may take up to 15 seconds...
#> Initializing python, numpyro, and other dependencies. This may take up to 15 seconds...COMPLETED!
#>
#> Attaching package: 'causact'
#> The following objects are masked from 'package:stats':
#>
#> binomial, poisson
#> The following objects are masked from 'package:base':
#>
#> beta, gamma
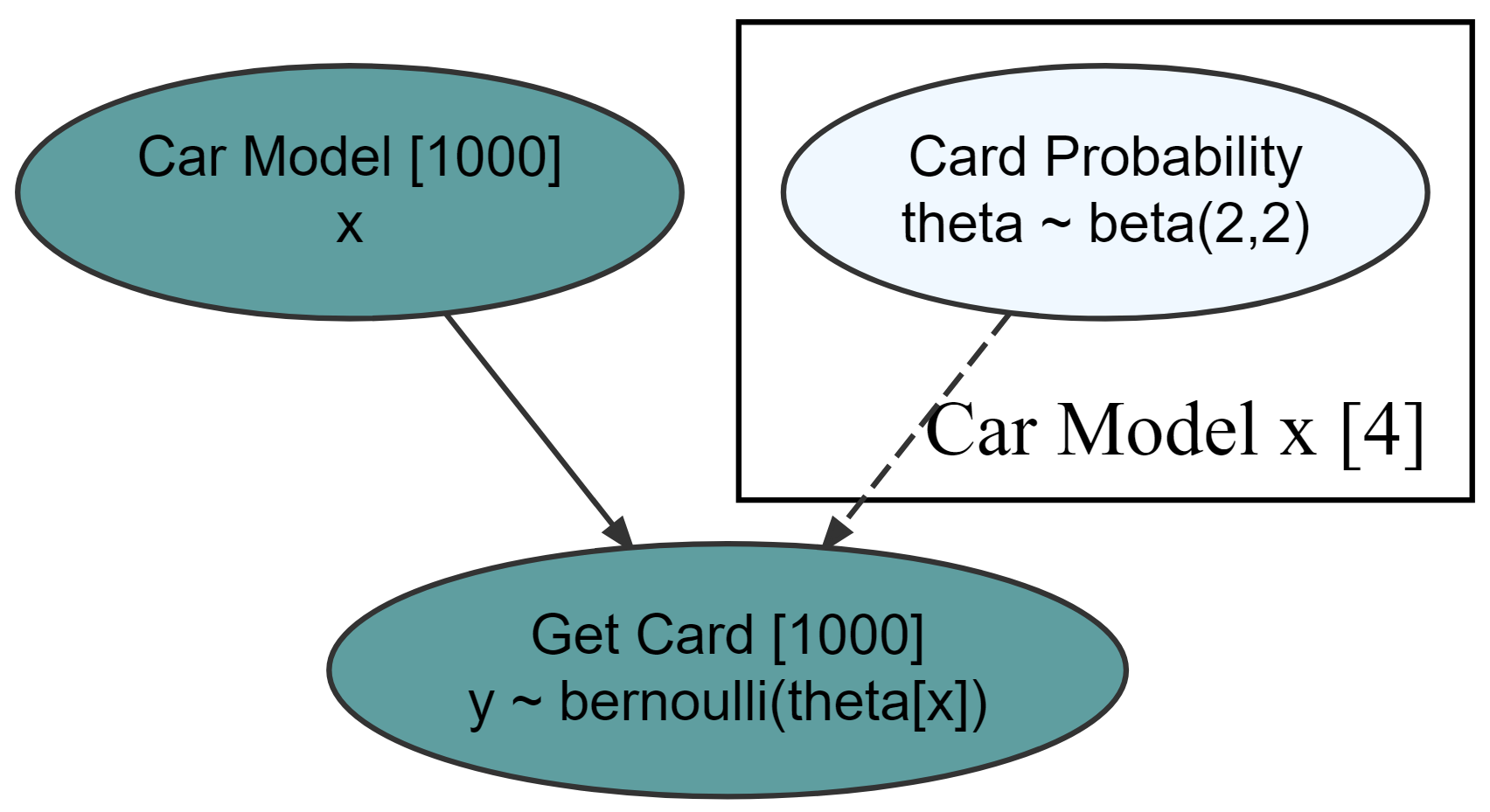
library(causact)
graph = dag_create() %>%
dag_node(descr = "Get Card", label = "y",
rhs = bernoulli(theta),
data = carModelDF$getCard) %>%
dag_node(descr = "Card Probability", label = "theta",
rhs = beta(2,2),
child = "y") %>%
dag_plate(descr = "Car Model", label = "x",
data = carModelDF$carModel,
nodeLabels = "theta",
addDataNode = TRUE)
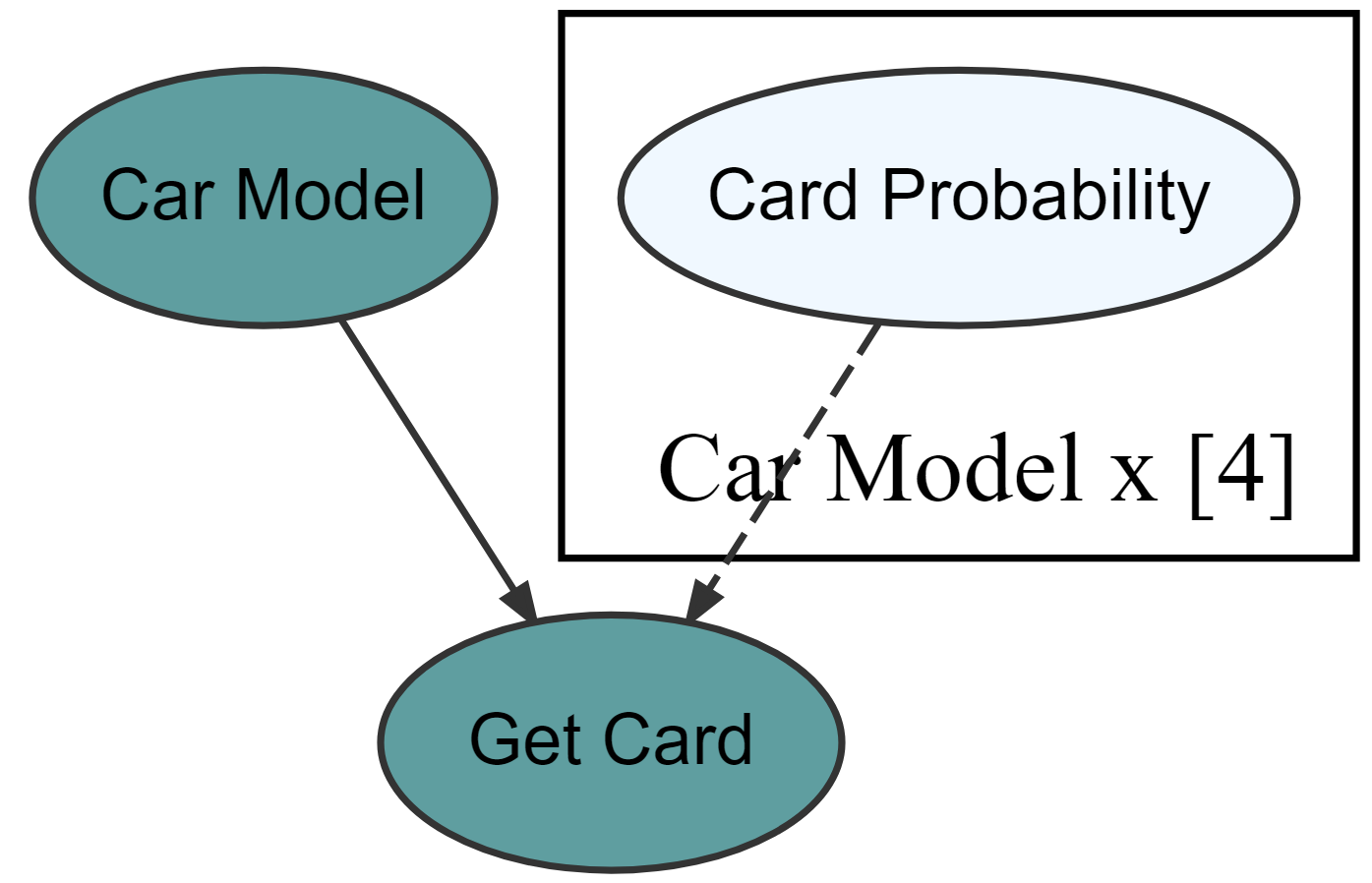
graph %>% dag_render()Hide model complexity, as appropriate, from domain experts and other less statistically minded stakeholders.
graph %>% dag_render(shortLabel = TRUE)drawsDF = graph %>% dag_numpyro()
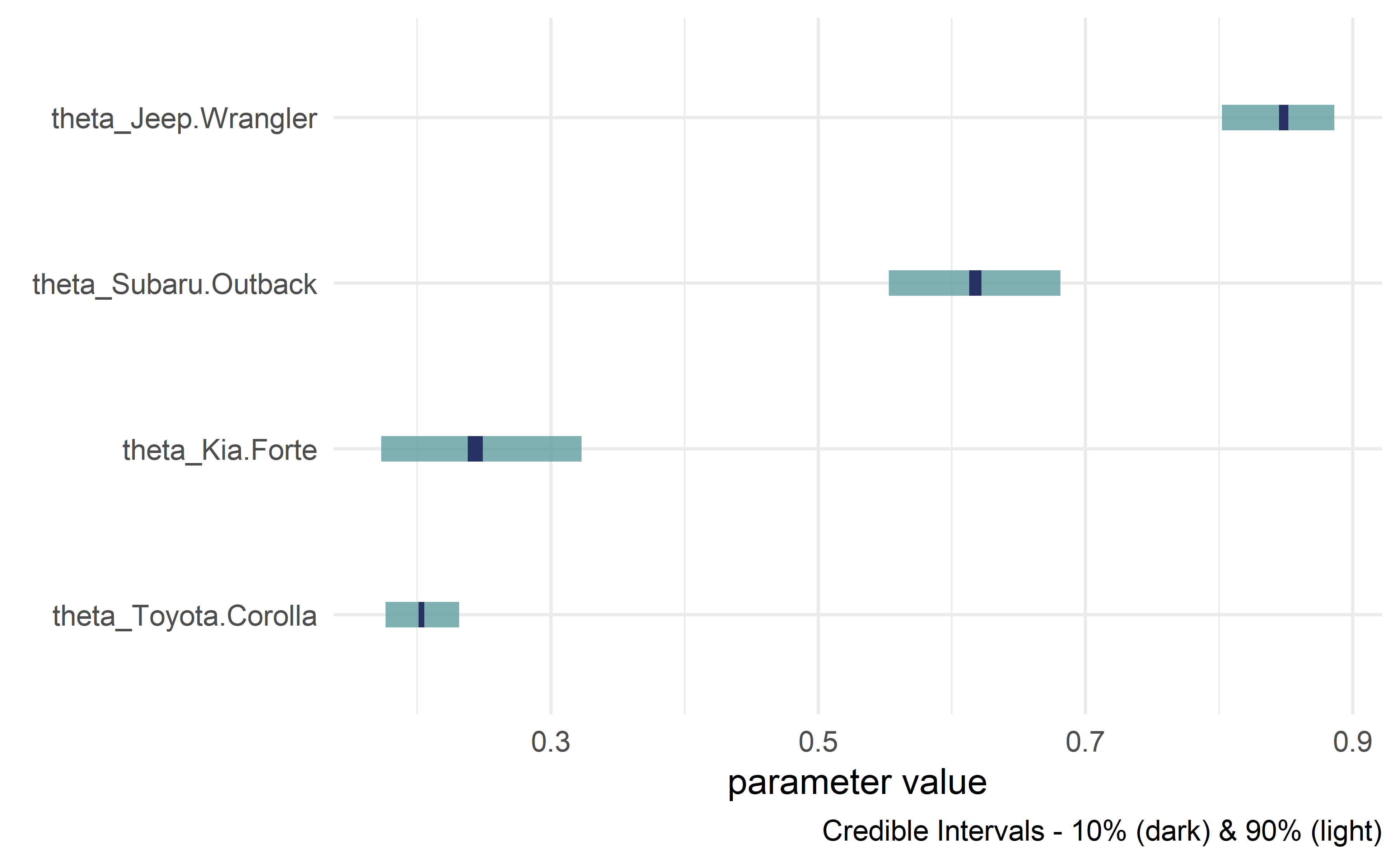
drawsDF ### see top of data frame
#> # A tibble: 4,000 × 4
#> theta_Toyota.Corolla theta_Subaru.Outback theta_Kia.Forte theta_Jeep.Wrangler
#> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 0.210 0.609 0.192 0.844
#> 2 0.227 0.563 0.239 0.818
#> 3 0.215 0.612 0.256 0.849
#> 4 0.204 0.646 0.253 0.874
#> 5 0.192 0.642 0.303 0.847
#> 6 0.166 0.607 0.255 0.843
#> 7 0.218 0.621 0.220 0.843
#> 8 0.196 0.646 0.251 0.841
#> 9 0.218 0.606 0.223 0.863
#> 10 0.203 0.583 0.241 0.863
#> # ℹ 3,990 more rowsNote: if you have used older versions of causact, please know that dag_numpyro() is a drop-in replacement for dag_greta().
drawsDF %>% dagp_plot()numpyroCode = graph %>% dag_numpyro(mcmc = FALSE)
#>
#> ## The below code will return a posterior distribution
#> ## for the given DAG. Use dag_numpyro(mcmc=TRUE) to return a
#> ## data frame of the posterior distribution:
#> reticulate::py_run_string("
#> import numpy as np
#> import numpyro as npo
#> import numpyro.distributions as dist
#> import pandas as pd
#> import arviz as az
#> from jax import random
#> from numpyro.infer import MCMC, NUTS
#> from jax.numpy import transpose as t
#> from jax.numpy import (exp, log, log1p, expm1, abs, mean,
#> sqrt, sign, round, concatenate, atleast_1d,
#> cos, sin, tan, cosh, sinh, tanh,
#> sum, prod, min, max, cumsum, cumprod )
#> ## note that above is from JAX numpy package, not numpy.
#>
#> y = np.array(r.carModelDF.getCard) #DATA
#> x = pd.factorize(np.array(r.carModelDF.carModel),use_na_sentinel=True)[0] #DIM
#> x_dim = len(np.unique(x)) #DIM
#> x_crd = pd.factorize(np.array(r.carModelDF.carModel),use_na_sentinel=True)[1] #DIM
#> def graph_model(y,x):
#> ## Define random variables and their relationships
#> with npo.plate('x_dim',x_dim):
#> theta = npo.sample('theta', dist.Beta(2,2))
#>
#> y = npo.sample('y', dist.Bernoulli(theta[x]),obs=y)
#>
#>
#> # computationally get posterior
#> mcmc = MCMC(NUTS(graph_model), num_warmup = 1000, num_samples = 4000)
#> rng_key = random.PRNGKey(seed = 1234567)
#> mcmc.run(rng_key,y,x)
#> drawsDS = az.from_numpyro(mcmc,
#> coords = {'x_dim': x_crd},
#> dims = {'theta': ['x_dim']}
#> ).posterior
#> # prepare xarray dataset for export to R dataframe
#> dimensions_to_keep = ['chain','draw','x_dim']
#> drawsDS = drawsDS.squeeze(drop = True ).drop_dims([dim for dim in drawsDS.dims if dim not in dimensions_to_keep])
#> # unstack plate variables to flatten dataframe as needed
#> for x_da in drawsDS['x_dim']:
#> new_varname = f'theta_{x_da.values}'
#> drawsDS = drawsDS.assign(**{new_varname:drawsDS['theta'].sel(x_dim = x_da)})
#> drawsDS = drawsDS.drop_dims(['x_dim'])
#> drawsDF = drawsDS.squeeze().to_dataframe()"
#> ) ## END PYTHON STRING
#> drawsDF = reticulate::py$drawsDFWhether you encounter a clear bug, have a suggestion for improvement, or just have a question, we are thrilled to help you out. In all cases, please file a GitHub issue. If reporting a bug, please include a minimal reproducible example.
We welcome help turning causact into the most intuitive and fastest
method of converting stakeholder narratives about data-generating
processes into actionable insight from posterior distributions. If you
want to help us achieve this vision, we welcome your contributions after
reading the new contributor
guide.
Please note that this project is released with a Contributor Code of
Conduct.
By participating in this project you agree to abide by its terms.
For more info, see
A Business Analyst's Introduction to Business Analytics available at
https://www.causact.com. You can also check out the package’s
vignette: vignette("narrative-to-insight-with-causact"). Two
additional examples are shown below.
McElreath, Richard. Statistical rethinking: A Bayesian course with examples in R and Stan. Chapman and Hall/CRC, 2018.
library(tidyverse)
library(causact)
# data object used below, chimpanzeesDF, is built-in to causact package
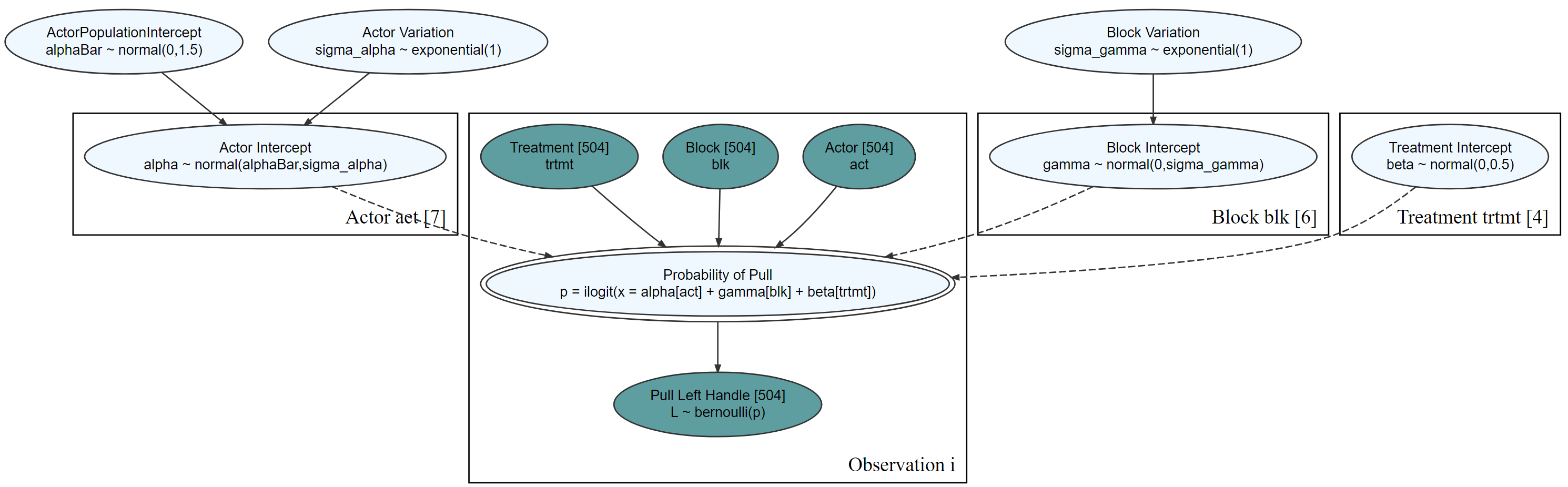
graph = dag_create() %>%
dag_node("Pull Left Handle","L",
rhs = bernoulli(p),
data = causact::chimpanzeesDF$pulled_left) %>%
dag_node("Probability of Pull", "p",
rhs = 1 / (1 + exp(-((alpha + gamma + beta)))),
child = "L") %>%
dag_node("Actor Intercept","alpha",
rhs = normal(alphaBar, sigma_alpha),
child = "p") %>%
dag_node("Block Intercept","gamma",
rhs = normal(0,sigma_gamma),
child = "p") %>%
dag_node("Treatment Intercept","beta",
rhs = normal(0,0.5),
child = "p") %>%
dag_node("Actor Population Intercept","alphaBar",
rhs = normal(0,1.5),
child = "alpha") %>%
dag_node("Actor Variation","sigma_alpha",
rhs = exponential(1),
child = "alpha") %>%
dag_node("Block Variation","sigma_gamma",
rhs = exponential(1),
child = "gamma") %>%
dag_plate("Observation","i",
nodeLabels = c("L","p")) %>%
dag_plate("Actor","act",
nodeLabels = c("alpha"),
data = chimpanzeesDF$actor,
addDataNode = TRUE) %>%
dag_plate("Block","blk",
nodeLabels = c("gamma"),
data = chimpanzeesDF$block,
addDataNode = TRUE) %>%
dag_plate("Treatment","trtmt",
nodeLabels = c("beta"),
data = chimpanzeesDF$treatment,
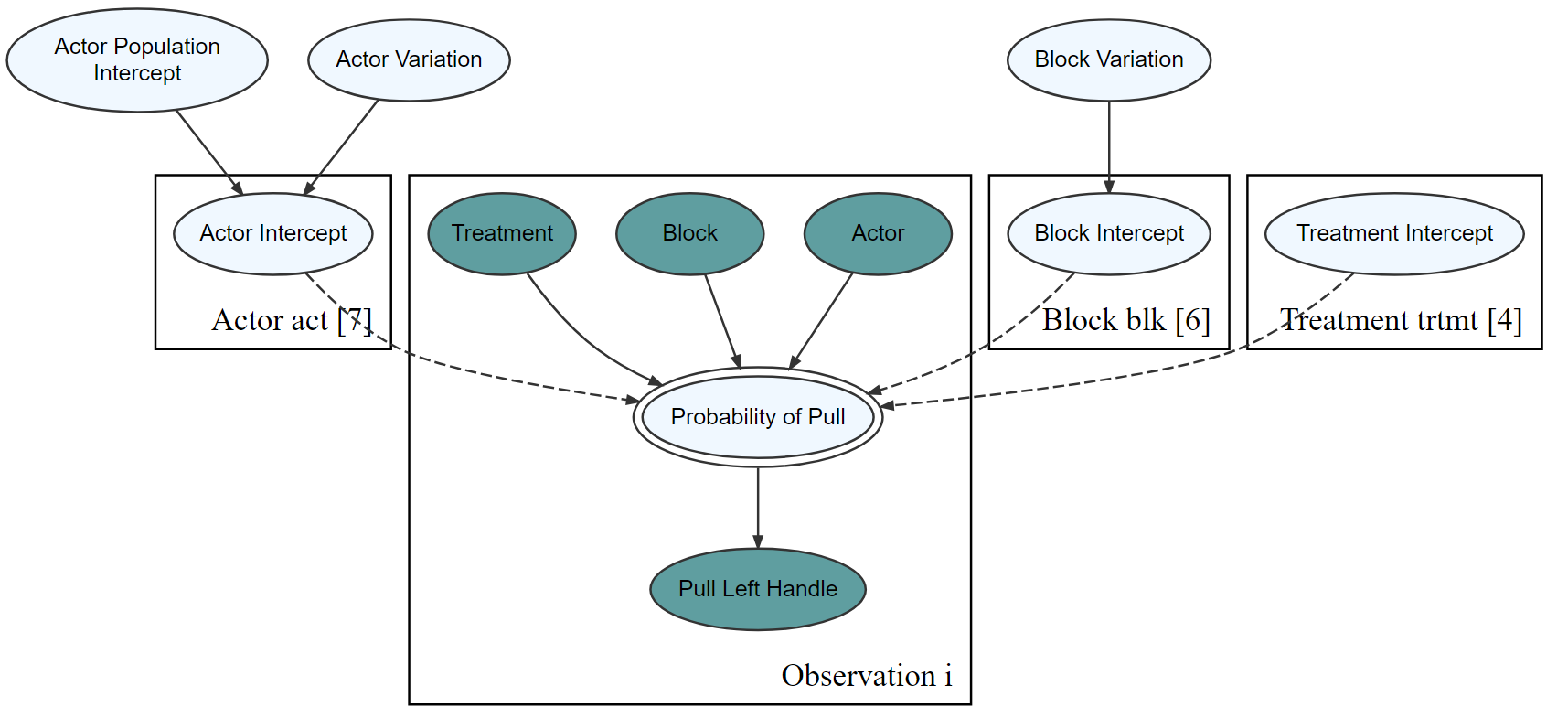
addDataNode = TRUE)graph %>% dag_render(width = 2000, height = 800)graph %>% dag_render(shortLabel = TRUE)drawsDF = graph %>% dag_numpyro()drawsDF %>% dagp_plot()Gelman, Andrew, Hal S. Stern, John B. Carlin, David B. Dunson, Aki Vehtari, and Donald B. Rubin. Bayesian data analysis. Chapman and Hall/CRC, 2013.
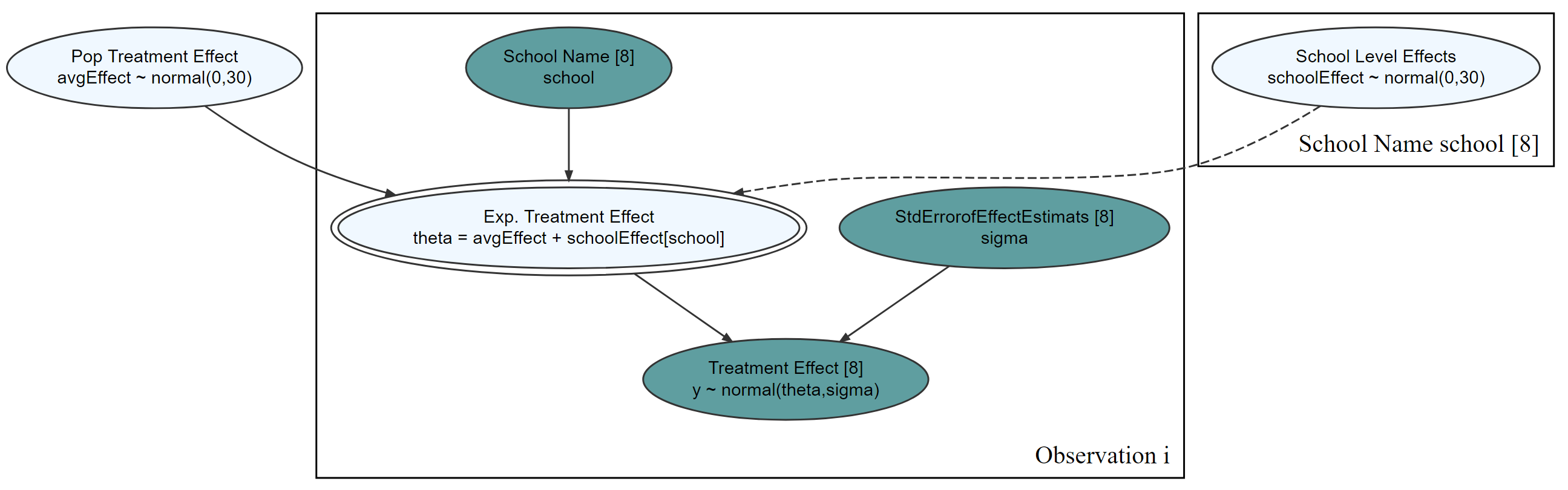
library(tidyverse)
library(causact)
# data object used below, schoolDF, is built-in to causact package
graph = dag_create() %>%
dag_node("Treatment Effect","y",
rhs = normal(theta, sigma),
data = causact::schoolsDF$y) %>%
dag_node("Std Error of Effect Estimates","sigma",
data = causact::schoolsDF$sigma,
child = "y") %>%
dag_node("Exp. Treatment Effect","theta",
child = "y",
rhs = avgEffect + schoolEffect) %>%
dag_node("Pop Treatment Effect","avgEffect",
child = "theta",
rhs = normal(0,30)) %>%
dag_node("School Level Effects","schoolEffect",
rhs = normal(0,30),
child = "theta") %>%
dag_plate("Observation","i",nodeLabels = c("sigma","y","theta")) %>%
dag_plate("School Name","school",
nodeLabels = "schoolEffect",
data = causact::schoolsDF$schoolName,
addDataNode = TRUE)graph %>% dag_render()drawsDF = graph %>% dag_numpyro()drawsDF %>% dagp_plot()