Bromate is an experimental project that explores the capabilities of agent workflows for automating web browser interactions.
Bromate leverages the power of large language models (LLMs), specifically Google's Gemini, to understand user requests expressed in natural language and translate them into a series of actions that automate web browsing tasks.
It utilizes Selenium for browser control and interaction, offering a seamless way to automate complex workflows within a web browser environment.
Before using Bromate, you need to obtain an API key from Google for the Gemini API. You can get a key by following these steps:
- Go to Google AI Studio and click on "Get an API key".
- Set the secret key as an environment variables in your system.
Setting the API Key in .env during development:
You can set the API key in a .env file in the project repository:
GOOGLE_API_KEY=YOUR_API_KEYYou can check if the key is configured by typing echo $GOOGLE_API_KEY in your shell.
Bromate is available on PyPI and can be easily installed using pip:
pip install bromateTo use Bromate, you can provide a natural language query describing the task you want to automate. Bromate will then interact with the agent (Gemini) to interpret the query and generate a sequence of actions to be executed by the Selenium WebDriver.
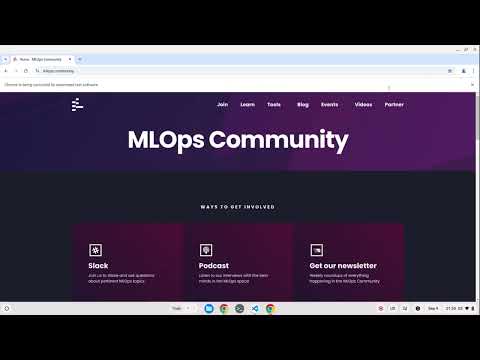
Example 1: Subscribe to the MLOps Community Newsletter:
bromate "Open the https://MLOps.Community website. Click on the 'Join' link. Write the address 'hello@mlops'"
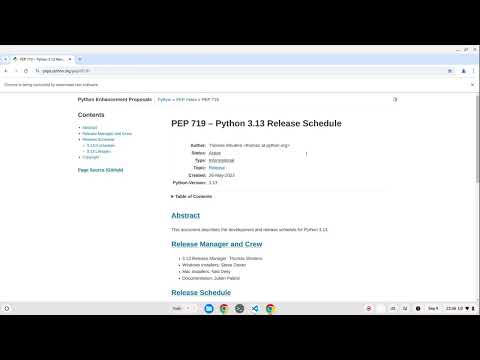
Example 2: Find the latest version of the Python language:
bromate --interaction.stay_open=False --agent.name "gemini-1.5-pro-latest" "Go to Python.org. Click on the downloads page. Click on the PEP link for the future Python release. Summarize the release schedule dates."
bromate -h
usage: bromate [-h] [--agent JSON] [--agent.api_key {SecretStr,null}] [--agent.name str] [--agent.temperature float] [--agent.candidate_count int]
[--agent.max_output_tokens int] [--agent.system_instructions str] [--action JSON] [--action.sleep_time float] [--driver JSON]
[--driver.name {Chrome,Firefox}] [--driver.keep_alive bool] [--driver.maximize_window bool] [--execution JSON] [--execution.stop_actions list[str]]
[--execution.default_message str] [--interaction JSON] [--interaction.stay_open bool] [--interaction.interactive bool] [--interaction.max_interactions int]
QUERY
Execute actions on web browser from a user query in natural language.
positional arguments:
QUERY User query in natural language
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
agent options:
Configuration of the agent
--agent JSON set agent from JSON string
--agent.api_key {SecretStr,null}
API key of the agent platform (Google) (default: **********)
--agent.name str Name of the agent to use (default: gemini-1.5-flash-latest)
--agent.temperature float
Temperature of the agent (default: 0.0)
--agent.candidate_count int
Number of candidates to generate (default: 1)
--agent.max_output_tokens int
Maximum output tokens to generate (default: 1000)
--agent.system_instructions str
System instructions for the agent (default: You are a browser automation system. Your goal is to understand the user request and execute actions
on its browser using the tools at your disposal. After each step, you will receive a screenshot and the page source of the current browser
window.)
action options:
Configuration for all actions
--action JSON set action from JSON string
--action.sleep_time float
Time to sleep after loading a page (default: 0.5)
driver options:
Configuration of the web driver
--driver JSON set driver from JSON string
--driver.name {Chrome,Firefox}
Name of the driver to use (default: Chrome)
--driver.keep_alive bool
Keep the browser open at the end of the execution (default: True)
--driver.maximize_window bool
Maximize the browser window at the start of the execution (default: True)
execution options:
Configuration of the execution
--execution JSON set execution from JSON string
--execution.stop_actions list[str]
Name of actions that can stop the execution (default: ['done'])
--execution.default_message str
Default message to send to the agent when no input is provided by the user (default: Continue the execution if necessary or call the done tool if
you are done)
interaction options:
Configuration of the interaction
--interaction JSON set interaction from JSON string
--interaction.stay_open bool
Keep the browser open before exiting (default: True)
--interaction.interactive bool
Ask for user input after every action (default: False)
--interaction.max_interactions int
Maximum number of interactions for the agent (default: 5)Bromate operates in a loop, continuously interacting with the Gemini agent and the Selenium WebDriver to automate browser tasks. Here's a breakdown of the core behavior:
1. Initialization:
- A Selenium WebDriver is initialized based on your configuration (e.g., Chrome or Firefox). This provides the interface for controlling the browser.
- The Gemini LLM is initialized, and its "tools" are defined. These tools correspond to the actions that the model can instruct the WebDriver to perform. The available actions are defined in the
src/bromate/actions.pyfile. Examples include:get: Open a specific URL in the browser.click: Click on an element identified by a CSS selector.write: Enter text into an element.back: Navigate back to the previous page.done: Signal the end of the automation task.
2. Action Selection and Execution:
- You provide an initial query in natural language describing the task you want to automate.
- At each step, the Gemini model analyzes the current state of the browser (HTML code and screenshot), considers your query and previous interactions, and decides on the most relevant action to take.
- The chosen action is then executed by the Selenium WebDriver, modifying the browser state.
3. Feedback Loop:
- After each action is performed, the updated HTML code of the page and a screenshot of the browser window are sent back to the Gemini model. This provides the model with feedback about the effects of its actions.
- The loop continues until the model either decides to execute the
doneaction, indicating the task is complete, or a maximum number of interactions is reached.
This iterative process allows Bromate to dynamically adapt to changes in the browser environment and perform complex automation tasks based on natural language instructions.
Bromate's development workflow is managed using Pyinvoke. The tasks/ folder contains various tasks for managing the project:
- checks.py: Tasks for code quality checks (linting, type checking, testing, security).
- cleans.py: Tasks for cleaning up build artifacts and caches.
- containers.py: Tasks for building and running Docker containers.
- docs.py: Tasks for generating and serving API documentation.
- formats.py: Tasks for code formatting.
- installs.py: Tasks for installing dependencies and pre-commit hooks.
- packages.py: Tasks for building and publishing Python packages.
- publishes.py: Tasks for publishing artifacts on software repositories.
Bromate is licensed under the MIT License. See the LICENSE file for more details.