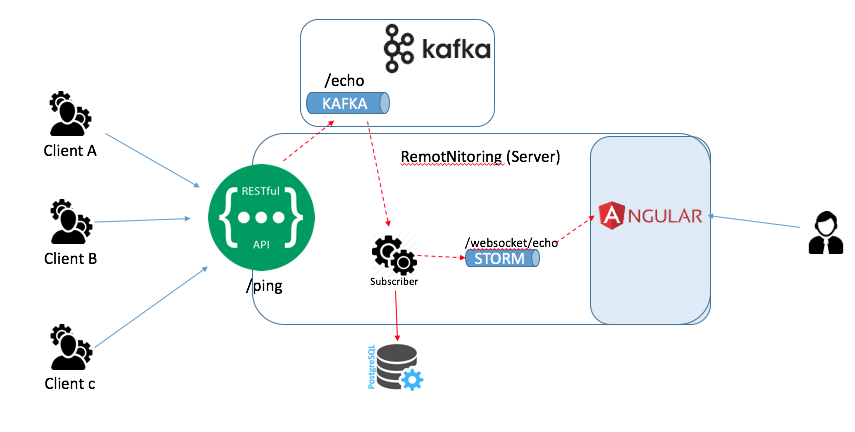
Application created to try to do simple remote monitoring. The idea is simple, clients makes REST call to a SERVER which record the pings/heartbeats.
This application is the SERVER that provide a REST endpoint to can do the ping (and login)
From point of view of architecure, it has been created using JHipster but also like a proof of concept has been included:
-
KAFKA: http://kafka.apache.org/. The endpoint PING publish a message to topic and with a service subscribe to the topic read the message and persist the record. For the communication with KAFKA, it has been used spring-cloud-stream
-
Websocket: spring-websocket using STOMP messaging protocol. Basically, the service subscribe to the topic, a part of persist the record, also generate a message STOMP to inform to web layer.
-
crypto-js: https://github.com/brix/crypto-js. Library JS to can encrypt or decrypt a "secret" field at web layer. The algorith used AES which required that user introduce a pwd to can encrypt or decrypt.
See diagram of how works the ping/heartbeat
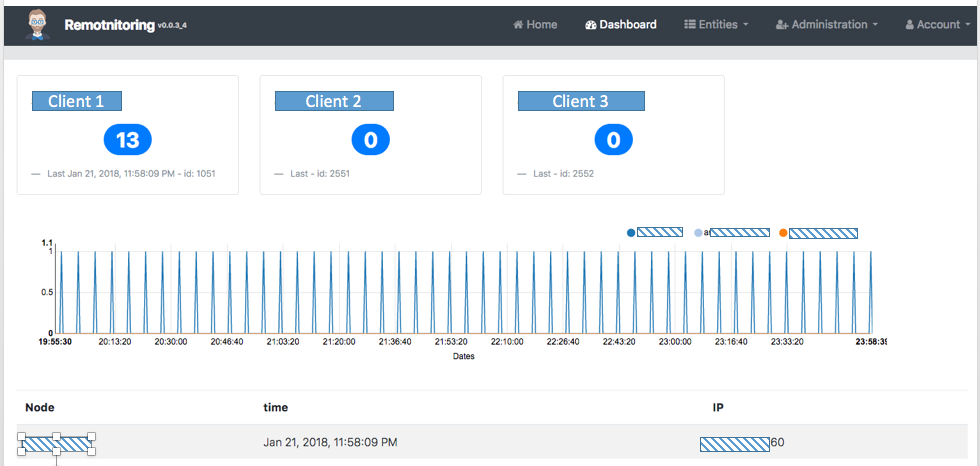
Dashboard
The easy way is using docker-compose. See app.yml
app.yml
version: '2'
services:
remotnitoring-app:
image: fmunozse/remotnitoring
environment:
- SPRING_PROFILES_ACTIVE=prod,swagger
- SPRING_DATASOURCE_URL=jdbc:postgresql://remotnitoring-postgresql:5432/remotnitoring
- SPRING_DATASOURCE_USERNAME=remotnitoring
- SPRING_DATASOURCE_PASSWORD=password
- JHIPSTER_SLEEP=30 # gives time for the database to boot before the application
- SPRING_CLOUD_STREAM_KAFKA_BINDER_BROKERS=kafka
- SPRING_CLOUD_STREAM_KAFKA_BINDER_ZK_NODES=zookeeper
ports:
- 80:8080
zookeeper:
image: wurstmeister/zookeeper:3.4.6
kafka:
image: wurstmeister/kafka:0.10.1.1
environment:
KAFKA_ADVERTISED_HOST_NAME: <IP local host: localhost>
KAFKA_ADVERTISED_PORT: 9092
KAFKA_ZOOKEEPER_CONNECT: zookeeper:2181
KAFKA_CREATE_TOPICS: "echo:1:1"
ports:
- 9092:9092
remotnitoring-postgresql:
image: postgres:9.6.5
volumes:
- /root/remotnitoring/postgresql/data:/var/lib/postgresql/data
environment:
- POSTGRES_USER=remotnitoring
- POSTGRES_PASSWORD=password
remotnitoring-postgresql-backup:
image: fmunozse/pg-cron-backups:9.6.5
volumes:
- /root/remotnitoring/backups/:/data/backups/
environment:
- DB_HOST=remotnitoring-postgresql
- DB_NAME=remotnitoring
- DB_USER=remotnitoring
- DB_PASS=password
- CRON_SCHEDULE=30 23 * * *
- MAIL_GMAIL_USER=remotnitoring.demo.span@gmail.com
- MAIL_GMAIL_PWD=password
- MAIL_TO=info.span@gmail.com
- MAIL_FROM=remotnitoring.demo.span@gmail.com
This application was generated using JHipster 4.11.1, you can find documentation and help at http://www.jhipster.tech/documentation-archive/v4.11.1.
Before you can build this project, you must install and configure the following dependencies on your machine:
- Node.js: We use Node to run a development web server and build the project. Depending on your system, you can install Node either from source or as a pre-packaged bundle.
- Yarn: We use Yarn to manage Node dependencies. Depending on your system, you can install Yarn either from source or as a pre-packaged bundle.
After installing Node, you should be able to run the following command to install development tools. You will only need to run this command when dependencies change in package.json.
yarn install
We use yarn scripts and Webpack as our build system.
Run the following commands in two separate terminals to create a blissful development experience where your browser auto-refreshes when files change on your hard drive.
./mvnw
yarn start
Yarn is also used to manage CSS and JavaScript dependencies used in this application. You can upgrade dependencies by
specifying a newer version in package.json. You can also run yarn update and yarn install to manage dependencies.
Add the help flag on any command to see how you can use it. For example, yarn help update.
The yarn run command will list all of the scripts available to run for this project.
Service workers are commented by default, to enable them please uncomment the following code.
- The service worker registering script in index.html
<script>
if ('serviceWorker' in navigator) {
navigator.serviceWorker
.register('./sw.js')
.then(function() { console.log('Service Worker Registered'); });
}
</script>
- The copy file option in webpack-common.js
{ from: './src/main/webapp/sw.js', to: 'sw.js' },Note: Add the respective scripts/assets in sw.js that is needed to be cached.
For example, to add Leaflet library as a runtime dependency of your application, you would run following command:
yarn add --exact leaflet
To benefit from TypeScript type definitions from DefinitelyTyped repository in development, you would run following command:
yarn add --dev --exact @types/leaflet
Then you would import the JS and CSS files specified in library's installation instructions so that Webpack knows about them: Edit src/main/webapp/app/vendor.ts file:
import 'leaflet/dist/leaflet.js';
Edit src/main/webapp/content/css/vendor.css file:
@import '~leaflet/dist/leaflet.css';
Note: there are still few other things remaining to do for Leaflet that we won't detail here.
For further instructions on how to develop with JHipster, have a look at Using JHipster in development.
You can also use Angular CLI to generate some custom client code.
For example, the following command:
ng generate component my-component
will generate few files:
create src/main/webapp/app/my-component/my-component.component.html
create src/main/webapp/app/my-component/my-component.component.ts
update src/main/webapp/app/app.module.ts
To optimize the remotnitoring application for production, run:
./mvnw -Pprod clean package
This will concatenate and minify the client CSS and JavaScript files. It will also modify index.html so it references these new files.
To ensure everything worked, run:
java -jar target/*.war
Then navigate to http://localhost:8080 in your browser.
Refer to Using JHipster in production for more details.
To launch your application's tests, run:
./mvnw clean test
Unit tests are run by Karma and written with Jasmine. They're located in src/test/javascript/ and can be run with:
yarn test
For more information, refer to the Running tests page.
You can use Docker to improve your JHipster development experience. A number of docker-compose configuration are available in the src/main/docker folder to launch required third party services. For example, to start a postgresql database in a docker container, run:
docker-compose -f src/main/docker/postgresql.yml up -d
To stop it and remove the container, run:
docker-compose -f src/main/docker/postgresql.yml down
You can also fully dockerize your application and all the services that it depends on. To achieve this, first build a docker image of your app by running:
./mvnw verify -Pprod dockerfile:build
Then run:
docker-compose -f src/main/docker/app.yml up -d
For more information refer to Using Docker and Docker-Compose, this page also contains information on the docker-compose sub-generator (jhipster docker-compose), which is able to generate docker configurations for one or several JHipster applications.
To configure CI for your project, run the ci-cd sub-generator (jhipster ci-cd), this will let you generate configuration files for a number of Continuous Integration systems. Consult the Setting up Continuous Integration page for more information.