CombineFeedback
Unidirectional Reactive Architecture. This is a Combine implemetation of ReactiveFeedbback and RxFeedback
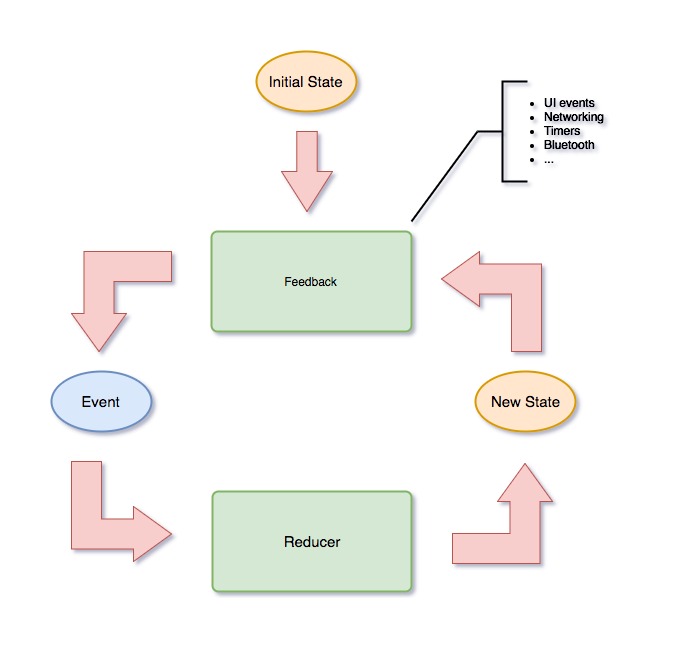
Diagram
Motivation
Requirements for iOS apps have become huge. Our code has to manage a lot of state e.g. server responses, cached data, UI state, routing etc. Some may say that Reactive Programming can help us a lot but, in the wrong hands, it can do even more harm to your code base.
The goal of this library is to provide a simple and intuitive approach to designing reactive state machines.
Core Concepts
State
State is the single source of truth. It represents a state of your system and is usually a plain Swift type. Your state is immutable. The only way to transition from one State to another is to emit an Event.
Event
Represents all possible events that can happen in your system which can cause a transition to a new State.
Reducer
A Reducer is a pure function with a signature of (State, Event) -> State. While Event represents an action that results in a State change, it's actually not what causes the change. An Event is just that, a representation of the intention to transition from one state to another. What actually causes the State to change, the embodiment of the corresponding Event, is a Reducer. A Reducer is the only place where a State can be changed.
Feedback
While State represents where the system is at a given time, Event represents a state change, and a Reducer is the pure function that enacts the event causing the state to change, there is not as of yet any type to decide which event should take place given a particular current state. That's the job of the Feedback. It's essentially a "processing engine", listening to changes in the current State and emitting the corresponding next events to take place. Feedbacks don't directly mutate states. Instead, they only emit events which then cause states to change in reducers.
To some extent it's like reactive Middleware in Redux having a signature of (AnyPublisher<State, Never>) -> AnyPublisher<Event, Never> allows us to observe State changes and perform some side effects based on its changes e.g if a system is in loading state we can start fetching data from network.
CombineFeedbackUI
CombineFeedbackUI provides several convenience API to deal with state management and SwiftUI.
ViewModel
ViewModel - is a base class responsible for initializing a UI state machine. It provides two ways to interact with it.
- We can start a state machine by observing
var state: AnyPublisher<S, Never>. - We can send input events into it via
public final func send(event: E).
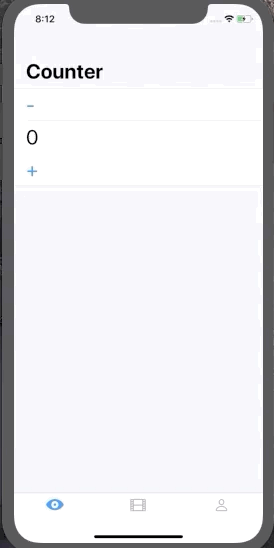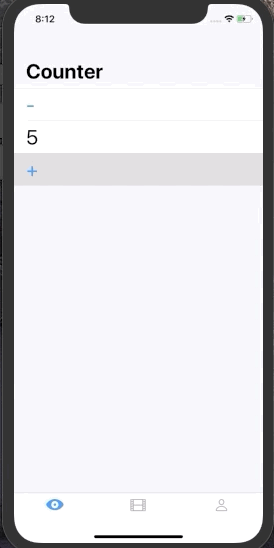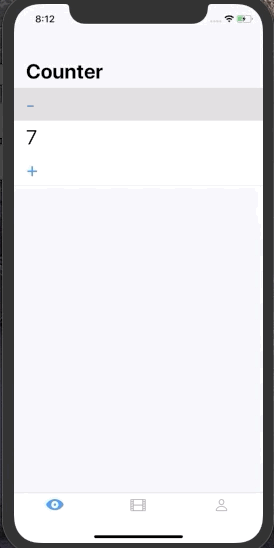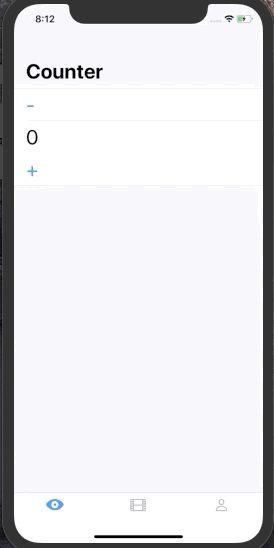
This is useful if we want to mutate our state in response to user input. Let's consider a Counter example
struct State {
var count = 0
}
enum Event {
case increment
case decrement
}When we press + button we want the State of the system to be incremented by 1. To do that somewhere in our UI we can do:
Button(action: {
viewModel.send(event: .increment)
}) {
return Text("+").font(.largeTitle)
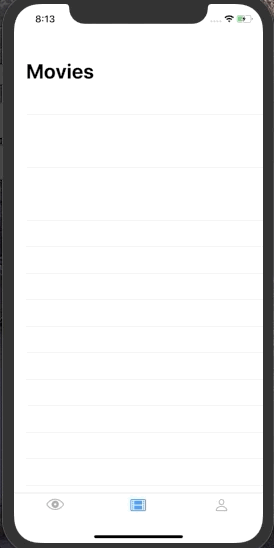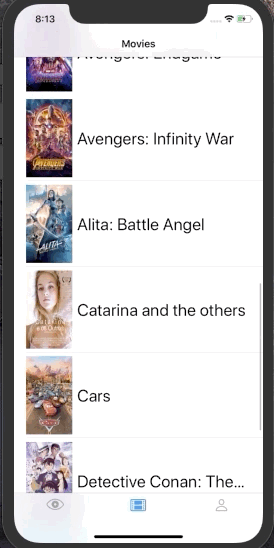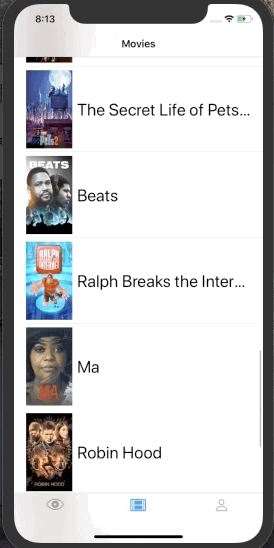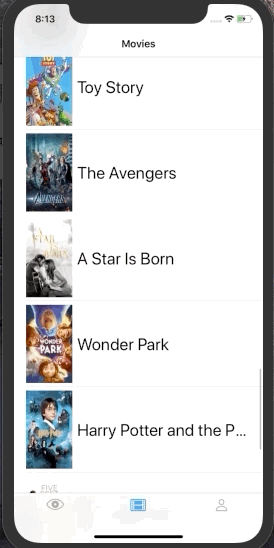
}Also, we can use the send(event:) method to initiate side effects. For example, imagine that we are building an infinite list, and we want to trigger the next batch load when a user reaches the end of the list.
enum Event {
case didLoad(Results)
case didFail(Error)
case fetchNext
}
struct State: Builder {
var batch: Results
var movies: [Movie]
var status: Status
}
enum Status {
case idle
case loading
case failed(Error)
}
struct MoviesView: View {
typealias State = MoviesViewModel.State
typealias Event = MoviesViewModel.Event
let context: Context<State, Event>
var body: some View {
List {
ForEach(context.movies.identified(by: \.id)) { movie in
MovieCell(movie: movie).onAppear {
// When we reach the end of the list
// we send `fetchNext` event
if self.context.movies.last == movie {
self.context.send(event: .fetchNext)
}
}
}
}
}
}When we send .fetchNext event, it goes to the reducer where we put our system into .loading state, which in response triggers effect in the whenLoading feedback, which is reacting to particular state changes
private static func reducer(state: State, event: Event) -> State {
switch event {
case .didLoad(let batch):
return state.set(\.batch, batch)
.set(\.movies, state.movies + batch.results)
.set(\.status, .idle)
case .didFail(let error):
return state.set(\.status, .failed(error))
case .fetchNext:
return state
.set(\.status, .loading)
}
}
private static func whenLoading() -> Feedback<State, Event> {
return Feedback(effects: { state -> AnyPublisher<Event, Never> in
guard case .loading = state.status else {
return Publishers.Empty().eraseToAnyPublisher()
}
return URLSession.shared
.fetchMovies(page: state.batch + 1)
.map(Event.didLoad)
.replaceError(replace: Event.didFail)
})
}Sometimes tho we are only interested in the particular value of State property to be changed. E.g if we are building a signup form and we just want to change email property on the state. We can do something like this
struct State {
var email = ""
var password = ""
}
viewModel.mutate(keyPath: \.email, "example@example.com")
Widget
Widget<State, Event> - is a convenience View that takes a ViewModel and render closure which renders new content every time the State changes.
Widget(viewModel: SignInViewModel()) { context in
SignInView(context: context)
}
Context
Context<State, Event> - is a rendering context that we can use to interact with UI and render information. Via @dynamicMemberLookup it has all of the properties of the State and several conveniences methods for more seamless integration with SwiftUI. (Credits to @andersio)
struct State {
var email = ""
var password = ""
}
enum Event {
case signIn
}
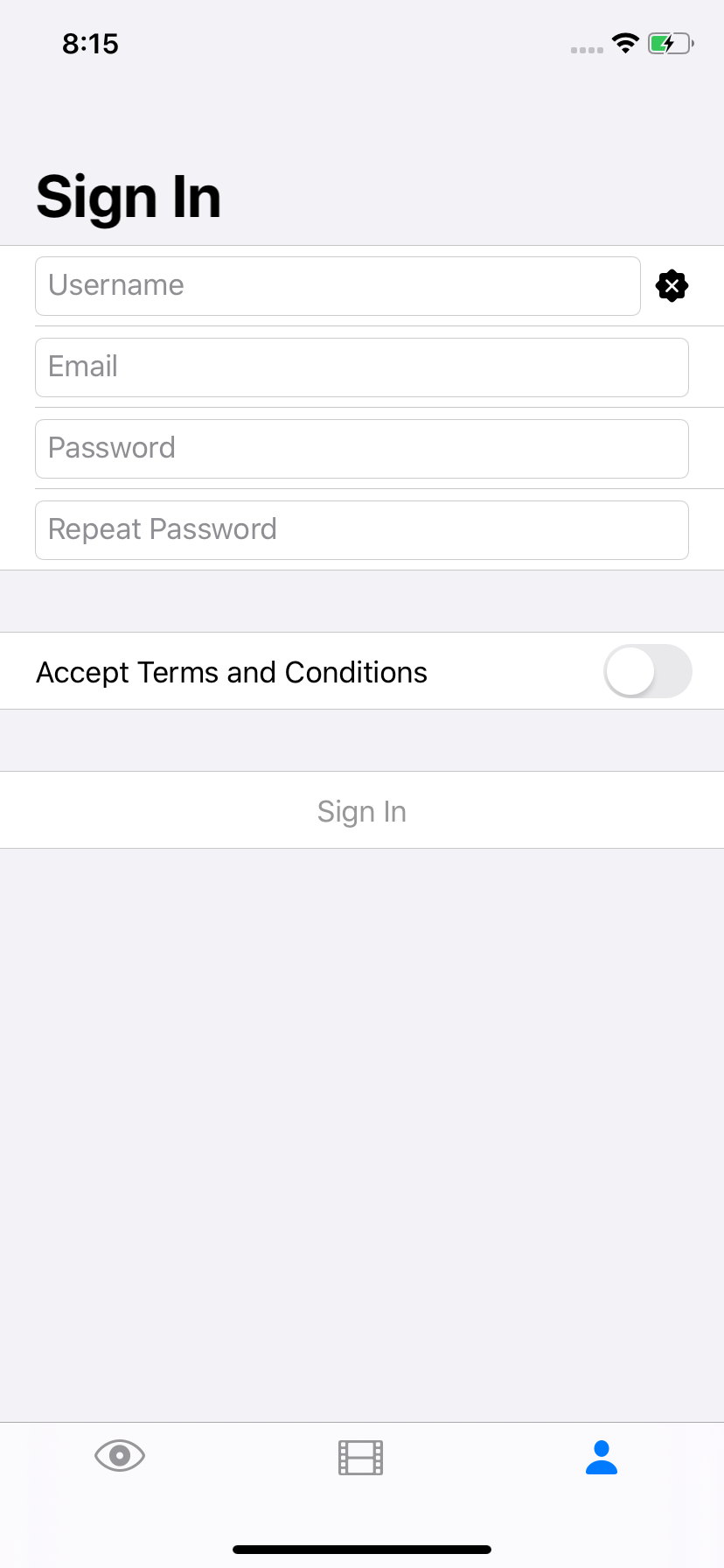
struct SignInView: View {
private let context: Context<State, Event>
init(context: Context<State, Event>) {
self.context = context
}
var body: some View {
return Form {
Section {
TextField(context.binding(for: \.email))
TextField(context.binding(for: \.password))
Button(action: context.action(for: .signIn)) {
Text("Sign In")
}
}
}
}
}
Example
| Counter | Infinite List | SignIn Form | Traffic Light |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |