Coder Gateway connects your JetBrains IDE to Coder workspaces so that you can develop from anywhere.
Manage less
- Ensure your entire team is using the same tools and resources
- Rollout critical updates to your developers with one command
- Automatically shut down expensive cloud resources
- Keep your source code and data behind your firewall
Code more
- Build and test faster
- Leveraging cloud CPUs, RAM, network speeds, etc.
- Access your environment from any place on any client (even an iPad)
- Onboard instantly then stay up to date continuously
Install this plugin from the JetBrains Marketplace
To manually install a local build:
- Install Jetbrains Gateway
- run
./gradlew clean buildPluginto generate a zip distribution - locate the zip file in the
build/distributionsfolder and follow these instructions on how to install a plugin from disk.
Alternatively, ./gradlew clean runIde will deploy a Gateway distribution (the one specified in gradle.properties - platformVersion) with the latest plugin changes deployed.
To simulate opening a workspace from the dashboard pass the Gateway link via --args. For example:
./gradlew clean runIDE --args="jetbrains-gateway://connect#type=coder&workspace=dev&agent=coder&folder=/home/coder&url=https://dev.coder.com&token=<redacted>&ide_product_code=IU&ide_build_number=223.8836.41&ide_download_link=https://download.jetbrains.com/idea/ideaIU-2022.3.3.tar.gz"
Alternatively, if you have separately built the plugin and already installed it
in a Gateway distribution you can launch that distribution with the URL as the
first argument (no --args in this case).
├── .github/ GitHub Actions workflows and Dependabot configuration files
├── gradle
│ └── wrapper/ Gradle Wrapper
├── build/ Output build directory
├── src Plugin sources
│ └── main
│ ├── kotlin/ Kotlin production sources
│ └── resources/ Resources - plugin.xml, icons, i8n
│ └── test
│ ├── kotlin/ Kotlin test sources
├── .gitignore Git ignoring rules
├── build.gradle.kts Gradle configuration
├── CHANGELOG.md Full change history
├── gradle.properties Gradle configuration properties
├── gradlew *nix Gradle Wrapper script
├── gradlew.bat Windows Gradle Wrapper script
├── qodana.yml Qodana profile configuration file
├── README.md README
└── settings.gradle.kts Gradle project settings
src directory is the most important part of the project, the Coder Gateway implementation and the manifest for the plugin – plugin.xml.
The project-specific configuration file gradle.properties contains:
| Property name | Description |
|---|---|
pluginGroup |
Package name, set to com.coder.gateway. |
pluginName |
Zip filename. |
pluginVersion |
The current version of the plugin in SemVer format. |
pluginSinceBuild |
The since-build attribute of the <idea-version> tag. The minimum Gateway build supported by the plugin |
pluginUntilBuild |
The until-build attribute of the <idea-version> tag. Supported Gateway builds, until & not inclusive |
platformType |
The type of IDE distribution, in this GW. |
platformVersion |
The version of the Gateway used to build&run the plugin. |
platformDownloadSources |
Gateway sources downloaded while initializing the Gradle build. Note: Gateway does not have open sources |
platformPlugins |
Comma-separated list of dependencies to the bundled Gateway plugins and plugins from the Plugin Repositories. |
javaVersion |
Java language level used to compile sources and generate the files for - Java 11 is required since 2020.3. |
gradleVersion |
Version of Gradle used for plugin development. |
The properties listed define the plugin itself or configure the gradle-intellij-plugin – check its documentation for more details.
Run tests with ./gradlew test. By default this will test against
https://dev.coder.com but you can set CODER_GATEWAY_TEST_DEPLOYMENT to a URL
of your choice or to mock to use mocks only.
Code quality is monitored with the help of Qodana
Qodana inspections are accessible within the project on two levels:
- using the Qodana IntelliJ GitHub Action, run automatically within the Build workflow,
- with the Gradle Qodana Plugin, so you can use it on the local environment or any CI other than GitHub Actions.
Qodana inspection is configured with the qodana { ... } section in the Gradle build file and qodana.yml YAML configuration file.
NOTE: Qodana requires Docker to be installed and available in your environment.
To run inspections, you can use a predefined Run Qodana configuration, which will provide a full report on http://localhost:8080, or invoke the Gradle task directly with the ./gradlew runInspections command.
A final report is available in the ./build/reports/inspections/ directory.
./gradlew runPluginVerifier can check the plugin compatibility against the specified Gateway. The integration with Github Actions is commented until this gradle intellij plugin issue is fixed.
In the .github/workflows directory, you can find definitions for the following GitHub Actions workflows:
- Build
- Triggered on
pushandpull_requestevents. - Runs the Gradle Wrapper Validation Action to verify the wrapper's checksum.
- Runs the
verifyPluginandtestGradle tasks. - Builds the plugin with the
buildPluginGradle task and provides the artifact for the next jobs in the workflow. Verifies the plugin using the IntelliJ Plugin Verifier tool.(this is commented until this issue is fixed)- Prepares a draft release of the GitHub Releases page for manual verification.
- Triggered on
- Release
- Triggered on
Publish releaseevent. - Updates
CHANGELOG.mdfile with the content provided with the release note. - Publishes the plugin to JetBrains Marketplace using the provided
PUBLISH_TOKEN. - Sets publish channel depending on the plugin version, i.e.
1.0.0-beta->betachannel. For now, bothmainandeapbranches are published on default release channel. - Patches the Changelog and commits.
- Triggered on
When the main or eap branch receives a new pull request or a direct push, the Build workflow runs builds the plugin and prepares a draft release.
The draft release is a working copy of a release, which you can review before publishing.
It includes a predefined title and git tag, the current plugin version, for example, v2.1.0.
The changelog is provided automatically using the gradle-changelog-plugin.
An artifact file is also built with the plugin attached. Every new Build overrides the previous draft to keep the Releases page clean.
When you edit the draft and use the Publish release button, GitHub will tag the repository with the given version and add a new entry to the Releases tab. Next, it will notify users who are watching the repository, triggering the final Release workflow.
IMPORTANT:
pluginVersionfromgradle.propertiesneeds to be manually increased after a release.
Plugin Signing is a mechanism introduced in the 2021.2 release cycle to increase security in JetBrains Marketplace.
JetBrains Marketplace signing is designed to ensure that plugins are not modified over the course of the publishing and delivery pipeline.
The plugin signing configuration is disabled for coder-gateway. To find out how to generate signing certificates and how to configure the signing task, check the Plugin Signing section in the IntelliJ Platform Plugin SDK documentation.
gradle-intellij-plugin provides the publishPlugin Gradle task to upload the plugin artifacts. The Release workflow
automates this process by running the task when a new release appears in the GitHub Releases section.
Note
Set a suffix to the plugin version to publish it in the custom repository channel, i.e.
v1.0.0-betawill push your plugin to thebetarelease channel.
The authorization process relies on the PUBLISH_TOKEN secret environment variable, specified in the Secrets section of the repository Settings.
You can get that token in your JetBrains Marketplace profile dashboard in the My Tokens tab.
When releasing an update, it is essential to let users know what the new version offers. The best way to do this is to provide release notes.
The changelog is a curated list that contains information about any new features, fixes, and deprecations. When they are provided, these lists are available in a few different places:
- the CHANGELOG.md file,
- the Releases page,
- the What's new section of JetBrains Marketplace Plugin page,
- and inside the Plugin Manager's item details.
Coder Gateway follows the Keep a Changelog approach for handling the project's changelog.
The Gradle Changelog Plugin takes care of propagating information provided within the CHANGELOG.md to the Gradle IntelliJ Plugin.
You only have to take care of writing down the actual changes in proper sections of the [Unreleased] section.
You start with an almost empty changelog:
# YourPlugin Changelog
## [Unreleased]
### Added
- Initial scaffold created from [IntelliJ Platform Plugin Template](https://github.com/JetBrains/intellij-platform-plugin-template)
Now proceed with providing more entries to the Added group, or any other one that suits your change the most (see How do I make a good changelog? for more details).
When releasing a plugin update, you don't have to care about bumping the [Unreleased] header to the upcoming version – it will be handled automatically on the Continuous Integration (CI) after you publish your plugin.
GitHub Actions will swap it and provide you an empty section for the next release so that you can proceed with the development:
# YourPlugin Changelog
## [Unreleased]
## [0.0.1]
### Added
- An awesome feature
### Fixed
- One annoying bug
Gateway API has not reached maturity. More often than not, there are API incompatibilities between the latest stable version of Gateway and EAP ones (Early Access Program). To provide support for both versions of Gateway we've decided:
- to have two branches for releases:
mainandeap mainbranch will provide support for the latest stable Gateway release, whileeapwill provide support for releases in the EAP program.- both versions of the plugin will keep the MAJOR.MINOR.PATCH numbers in sync. When there is a fix
in the plugin's business code, these versions will change and the changes on the
mainbranch will have to be merged on theeapbranch as well. - releases from
eapbranch are suffixed with-eap.x.xwill allow releases for the same plugin functionality but with support for a different Gateway EAP version. In other words, version2.1.2of the plugin supports Gateway 2022.2 while version2.1.2-eap.0supports some builds in the Gateway 2022.3 EAP.2.1.2-eap.1might have to support a newer version of EAP. - when Gateway 2022.3 EAP is released in the stable channel then
eapbranch will have to be merged back in themainbranch, and it will start supporting the next EAP builds. - releases from both branches are published in the stable release channel. Jetbrains provides support for
different release channels (ex:
eaporbeta), but all of them except the stable channel have to be manually configured by users in Gateway - which is super inconvenient.
Coder Gateway includes checks for compatibility with a specified version range. A warning is raised when
the Coder deployment build version is outside of compatibility range:
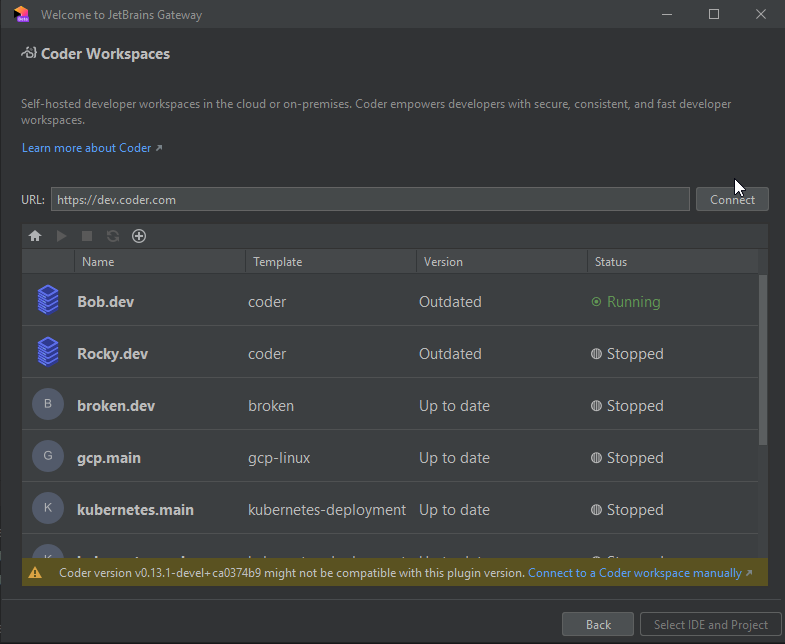
The range needs to be manually updated as often as possible. The lowest bound is specified by minCompatibleCoderVersion
property in the CoderSupportedVersions.properties
while maxCompatibleCoderVersion specifies the upper bound.