| Feature | Status |
|---|---|
| Input Q shape [Batch Size, Head Num, Seq Len, Head Dim] | ✅ |
| Input K shape [Batch Size, Head Num, Seq Len, Head Dim] | ✅ |
| Input V shape [Batch Size, Head Num, Seq Len, Head Dim] | ✅ |
| 8-bit char Tensor Core | ✅ |
| Head Dim 64 | ✅ |
| Head Dim 128 | ✅ |
| Sequence Len multiple of 64 | ✅ |
| Sequence Len SRC != Sequence Length DST | Planning |
| Cuda Core Implementation | Planning |
| 8-bit hybrid uchar*char Tensor Core Implementation | Planning |
| Resolve uncoalsced Global Memory Read & Write of the fused kernel | Planning |
| Resolve bank conflict of col-major matrix (using cutlass) | Planning |
struct FMHAParamI8 {
float q_amax = 0.0f; // absoulte max value of q
float k_amax = 0.0f; // absoulte max value of k
float v_amax = 0.0f; // absoulte max value of v
float o_amax = 1.0f; // absoulte max value of o
float s_max = 1.0f; // absoulte max value of softmax result s (not used in this 8-bit fused kernel)
};
void FMHAInferI8(cudaStream_t stream,
FMHAParamI8 fmha_param,
AttnDataDescriptor attn_desc,
const void *q,
const void *k,
const void *v,
const void *padding_mask,
void *o,
const bool use_tcu)
- cudaStream_t stream: cuda stream
- FMHAParamI8 fmha_param: Attention Quantization parameters
- const void *q: shape = [batch_num, head_num, seq_len, head_dim], dtype = int8_t
- const void *k: shape = [batch_num, head_num, seq_len, head_dim], dtype = int8_t
- const void *v: shape = [batch_num, head_num, seq_len, head_dim], dtype = int8_t
- const void *padding_mask: shape = [batch_num, seq_len], dtype = int8_t
- void *o: shape = [batch_num, head_num, seq_len, head_dim], dtype = int8_t
- const bool use_tcu: currently only support
true
template <int HEAD_DIM, int BASE_SEQ_LEN, int SEQ_LEN, int NUM_WARPS, bool USE_TCU>
__global__ typename std::enable_if<(USE_TCU==true), void>::type
FMHAInferKernel(const int8_t * __restrict__ Q, const int8_t * __restrict__ K, const int8_t * __restrict__ V, const int8_t *padding_mask, int8_t * __restrict__ O, FMHAParamI8 fmha_param)
In this work, we quantize fused multi-head attention (FMHA) and Flash-Attention to lower precision 8-bit integers in the Transformer inference. The proposed method leverages the very nature of Softmax computation without requiring further prior knowledge of the input data. We improve the accuracy of the attention output of the fused kernel by about a factor of 2 in the simulation.
In this project, we aim to accelerate the FMHA mechanism during the 8-bit Transformer inference of language and vision models using GPGPU. Compared to FP32 inference, employing 8-bit integer (INT8 and UINT8) potentially consumes 4× less storage space but is up to 6× faster. To adapt FP32 algorithms to INT8 algorithms, we need two techniques - quantization and dequantization.
In the flash-attention, we use subscript
$$ \mathbf{m}{i} = \max(\mathbf{m}{i-1},\tilde{\mathbf{m}}_i) $$
$$ \mathbf{l}{i} = \exp{(\mathbf{m}{i-1}-\mathbf{m}{i})}\cdot \mathbf{l}{i-1} + \exp{(\tilde{\mathbf{m}}i-\mathbf{m}{i})}\cdot \tilde{\mathbf{l}}_i $$
$$ \mathbf{M}{i-1} = diag{(\mathbf{m}{i-1})} $$
$$ \mathbf{M}i = diag{(\mathbf{m}{i})} $$
$$ \mathbf{L}{i-1} = diag{(\mathbf{l}{i-1})} $$
$$ \mathbf{L}i = diag{(\mathbf{l}{i})} $$
$$ \mathbf{O}i = \mathbf{L}i^{-1} \cdot \left[ \mathbf{L}{i-1} \cdot \exp{(\mathbf{M}{i-1}-\mathbf{M}{i})} \cdot \mathbf{O}{i-1} + \exp{(\tilde{\mathbf{M}}i-\mathbf{M}{i})} \cdot \mathbf{P}_i \cdot\mathbf{V}_i \right] $$
where
| Tensor | Shape |
|---|---|
In the 8-bit versions, we use the respective subscript to indicate the datatypes of the variables.
$$ Attention(\mathbf{Q}{\texttt{INT8}}, \mathbf{K}{\texttt{INT8}}, \mathbf{V}{\texttt{INT8}}) = \left \lbrace\left[ \left[ Softmax \left[ \frac{ \left[ \mathbf{Q}{\texttt{INT8}} \cdot \mathbf{K}^T_{\texttt{INT8}} \right]{\texttt{INT32}}}{\sqrt{d}{\texttt{FP32}}} \right]{\texttt{FP32}} \right]{\texttt{INT8}} \cdot \mathbf{V}{\texttt{INT8}}\right]{\texttt{INT32}}\right\rbrace_{\texttt{INT8}} $$
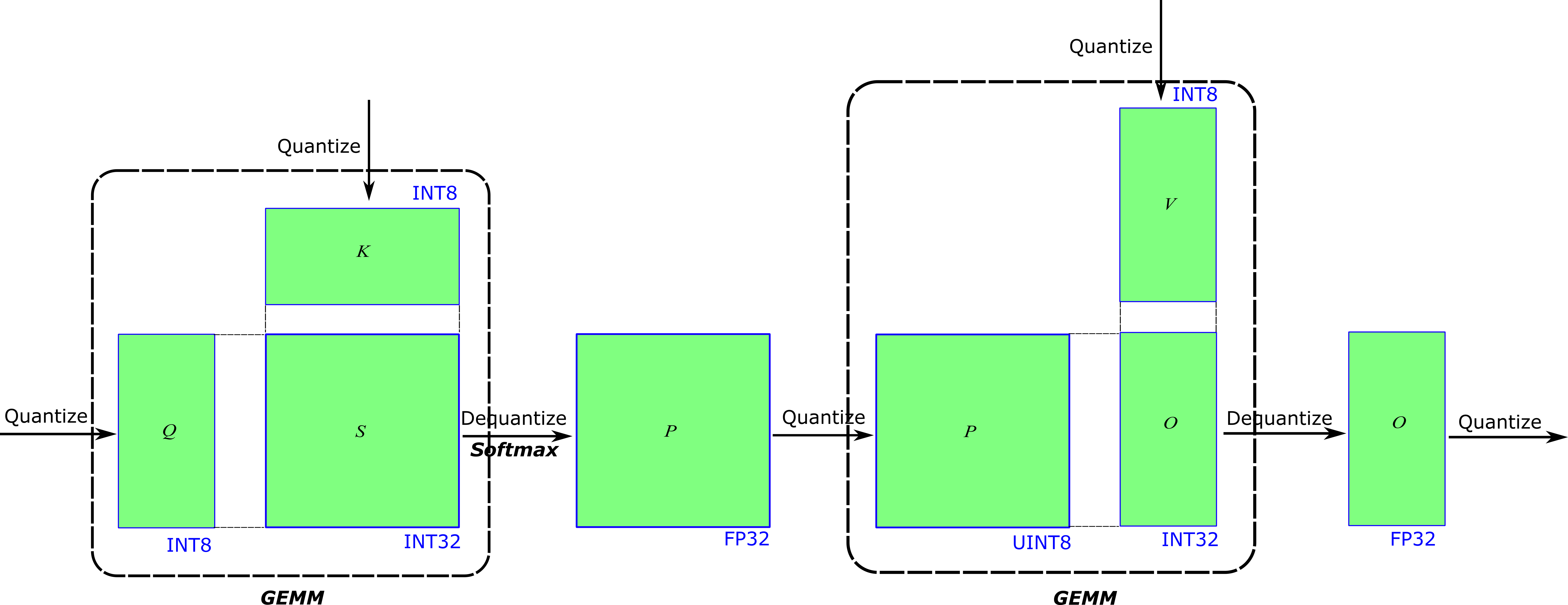
See the following figure
The 8-bit quantization schematic diagram of the forward FMHA.$$\mathbf{S}{\texttt{INT32}} = \mathbf{Q}{\texttt{INT8}} \cdot \mathbf{K}^T_{\texttt{INT8}}$$
$$\mathbf{S}{\texttt{FP32}} = \mathbf{S}{\texttt{INT32}}\cdot \frac{1}{\sqrt{d}} \cdot\frac{\alpha_q}{127}\cdot\frac{\alpha_k}{127}$$
$$ \mathbf{m}{\texttt{FP32}} = rowmax(\mathbf{S}{\texttt{FP32}}) $$
$$ \mathbf{M}{\texttt{FP32}} = diag(\mathbf{m}{\texttt{FP32}}) $$
$$ \mathbf{P}{\texttt{FP32}} = \exp{(\mathbf{S}{\texttt{FP32}}-\mathbf{M}_{\texttt{FP32}}\cdot \mathbf{J})} $$
$$ \mathbf{l}{\texttt{FP32}} = rowsum(\mathbf{P}{\texttt{FP32}}) $$
$$ \mathbf{L}{\texttt{FP32}} = diag(\mathbf{l}{\texttt{FP32}}) $$
$$ \mathbf{P}{\texttt{UINT8}} = \left[\left( \frac{\mathbf{L}{\texttt{FP32}}^{-1}}{255} \right)^{-1} \cdot \mathbf{L}{\texttt{FP32}}^{-1} \cdot \mathbf{P}{\texttt{FP32}}\right]{0}^{255} = \left[255 \cdot \mathbf{P}{\texttt{FP32}}\right]_{0}^{255} $$
$$ \mathbf{O}{\texttt{INT32}} = \mathbf{P}{\texttt{UINT8}} \cdot \mathbf{V}_{\texttt{INT8}} $$
$$ \mathbf{O}{\texttt{FP32}} = \frac{\mathbf{L}{\texttt{FP32}}}{255} \cdot \frac{\alpha_v}{127} \cdot \mathbf{O}_{\texttt{INT32}} $$
$$ \mathbf{O}{\texttt{INT8}} = \left[\frac{127}{\alpha_o} \cdot \mathbf{O}{\texttt{FP32}}\right]_{-127}^{127} $$
$$ \mathbf{S}{\texttt{INT32},i} = \mathbf{Q}{\texttt{INT8}}\cdot\mathbf{K}^T_{\texttt{INT8},i} $$
$$ \mathbf{S}{\texttt{FP32},i} = \mathbf{S}{\texttt{INT32},i}\cdot \frac{1}{\sqrt{d}} \cdot\frac{\alpha_q}{127}\cdot\frac{\alpha_k}{127}$$
$$ \tilde{\mathbf{m}}{\texttt{FP32},i} = rowmax(\mathbf{S}{\texttt{FP32},i}) $$
$$ \tilde{\mathbf{M}}{\texttt{FP32},i} = diag{(\tilde{\mathbf{m}}{\texttt{FP32},i})} $$
$$ \mathbf{P}{\texttt{FP32},i} = \exp{(\mathbf{S}{\texttt{FP32},i}-\tilde{\mathbf{M}}_{\texttt{FP32},i}\cdot\mathbf{J})} $$
$$ \tilde{\mathbf{l}}{\texttt{FP32},i} = rowsum(\mathbf{P}{\texttt{FP32},i}) $$
$$ \tilde{\mathbf{L}}{\texttt{FP32},i} = diag{(\tilde{\mathbf{l}}{\texttt{FP32},i})} $$
$$ \mathbf{P}{\texttt{UINT8},i} = \left[\left( \frac{\tilde{\mathbf{L}}{\texttt{FP32,i}}^{-1}}{255} \right)^{-1} \cdot \tilde{\mathbf{L}}{\texttt{FP32,i}}^{-1} \cdot \mathbf{P}{\texttt{FP32},i}\right]{0}^{255}=\left[255 \cdot \mathbf{P}{\texttt{FP32},i}\right]_{0}^{255}$$
$$ \tilde{\mathbf{O}}{\texttt{INT32},i} = \mathbf{P}{\texttt{UINT8},i} \cdot\mathbf{V}_{\texttt{INT8},i} $$
$$ \tilde{\mathbf{O}}{\texttt{FP32},i} = \frac{\tilde{\mathbf{L}}{\texttt{FP32},i}^{-1}}{255} \cdot \frac{\alpha_v}{127} \cdot \tilde{\mathbf{O}}_{\texttt{INT32},i} $$
$$ \mathbf{m}{\texttt{FP32},i} = \max(\mathbf{m}{\texttt{FP32},i-1},\tilde{\mathbf{m}}_{\texttt{FP32},i}) $$
$$ \mathbf{l}{\texttt{FP32},i} = \exp{(\mathbf{m}{\texttt{FP32},i-1}-\mathbf{m}{\texttt{FP32},i})}\cdot \mathbf{l}{\texttt{FP32},i-1} + \exp{(\tilde{\mathbf{m}}{\texttt{FP32},i}-\mathbf{m}{\texttt{FP32},i})}\cdot \tilde{\mathbf{l}}_{\texttt{FP32},i} $$
$$ \mathbf{M}{\texttt{FP32},i} = diag{(\mathbf{m}{\texttt{FP32},i-1})} $$
$$ \mathbf{M}{\texttt{FP32},i} = diag{(\mathbf{m}{\texttt{FP32},i})} $$
$$ \mathbf{L}{\texttt{FP32},i-1} = diag{(\mathbf{l}{\texttt{FP32},i-1})} $$
$$ \mathbf{L}{\texttt{FP32},i} = diag{(\mathbf{l}{\texttt{FP32},i})} $$
$$ \mathbf{O}{\texttt{FP32},i} = \mathbf{L}{\texttt{FP32},i}^{-1} \cdot \left[ \mathbf{L}{\texttt{FP32},i-1} \cdot \exp{(\mathbf{M}{\texttt{FP32},i-1}-\mathbf{M}{\texttt{FP32},i})} \cdot \mathbf{O}{\texttt{FP32},i-1} + \tilde{\mathbf{L}}{\texttt{FP32,i}} \cdot \exp{(\tilde{\mathbf{M}}{\texttt{FP32},i}-\mathbf{M}{\texttt{FP32},i})} \cdot \tilde{\mathbf{O}}{\texttt{FP32},i} \right] $$
$$ \mathbf{O}{\texttt{INT8}, N} = \left[ \frac{127}{\alpha_o} \cdot \mathbf{O}{\texttt{FP32}} \right]_{-127}^{127} $$
One can use tensor core unit (TCU) with input matrix of different data type to explore the full range of the UINT8 to increase computation precision. Without which one shall lose half of the quatization range before the second GEMM resulting in a loss of precision.
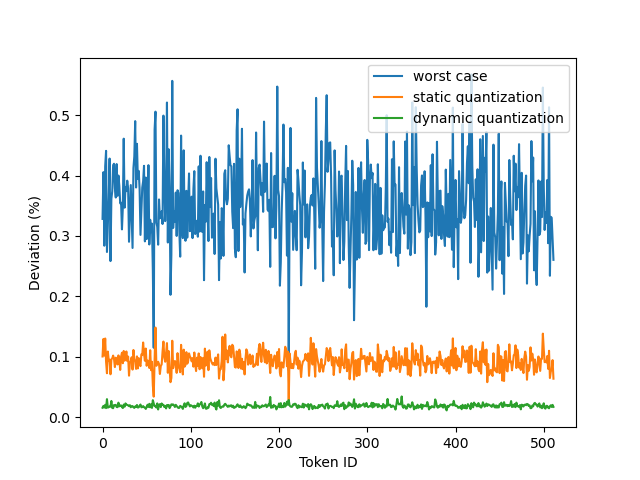
Run python simulation on 8-bit FMHA to show deviation between the 8-bit quantization output and the groudtruth (FP32 reference) as follows. The worst case occurs when the quantization parameter
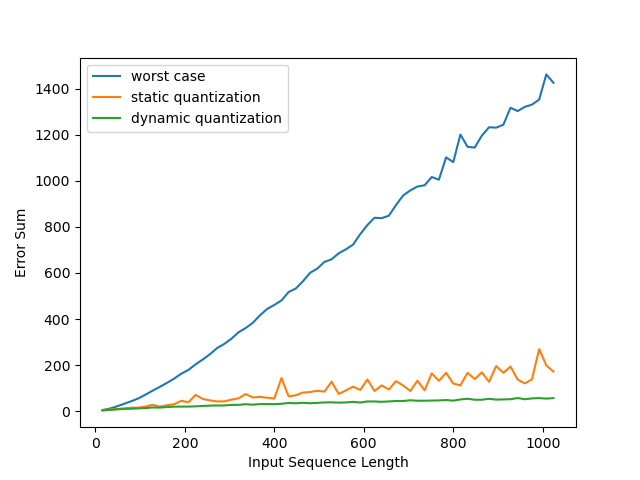
Run python simulation on 8-bit FMHA to show the error summation of the output when increasing the sequence length as follows. The error summation of the the 8-bit quantization output compared with the groudtruth (FP32 reference) increases when increasing the sequence length.
The following table lists the achieved F1 Scores of the BERT model during 8-bit inference.
| Model Precision | BERT BASE 384 | BERT LARGE 384 |
|---|---|---|
| Static 8-bit | 87.433 | 89.787 |
| Dynamic 8-bit | 87.526 | 89.861 |
The following table lists the achieved exact matches of the BERT model during 8-bit inference.
| Model Precision | BERT BASE 384 | BERT LARGE 384 |
|---|---|---|
| Static 8-bit | 80.123 | 82.800 |
| Dynamic 8-bit | 80.321 | 82.838 |
In practice, making the quantization factor greater while fixing the de-quantization factor can improve the two scores a little bit since it can amplify the elements
[CMPR21] Sneha Chaudhari, Varun Mithal, Gungor Polatkan, and Rohan Ramanath. An attentive survey of attention models. ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology (TIST), 12(5):1–32, 2021.
[DFE+22] Tri Dao, Daniel Y Fu, Stefano Ermon, Atri Rudra, and Christopher R ́e. Flashat- tention: Fast and memory-efficient exact attention with io-awareness. arXiv preprint arXiv:2205.14135, 2022.
[GSZ+18] Jiong Gong, Haihao Shen, Guoming Zhang, Xiaoli Liu, Shane Li, Ge Jin, Niharika Ma-heshwari, Evarist Fomenko, and Eden Segal. Highly efficient 8-bit low precision inference of convolutional neural networks with intelcaffe. In Proceedings of the 1st on Reproducible Quality-Efficient Systems Tournament on Co-designing Pareto-efficient Deep Learning, page 1. 2018.
[PTDU16] Ankur P Parikh, Oscar T ̈ackstr ̈om, Dipanjan Das, and Jakob Uszkoreit. A decomposable attention model for natural language inference. arXiv preprint arXiv:1606.01933, 2016.
[QB18] Jerry Quinn and Miguel Ballesteros. Pieces of eight: 8-bit neural machine translation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1804.05038, 2018.
[VSP+17] Ashish Vaswani, Noam Shazeer, Niki Parmar, Jakob Uszkoreit, Llion Jones, Aidan N Gomez, Lukasz Kaiser, and Illia Polosukhin. Attention is all you need. Advances in neural information processing systems, 30, 2017