By Chu Zhou, Hang Zhao, Jin Han, Chang Xu, Chao Xu, Tiejun Huang, Boxin Shi
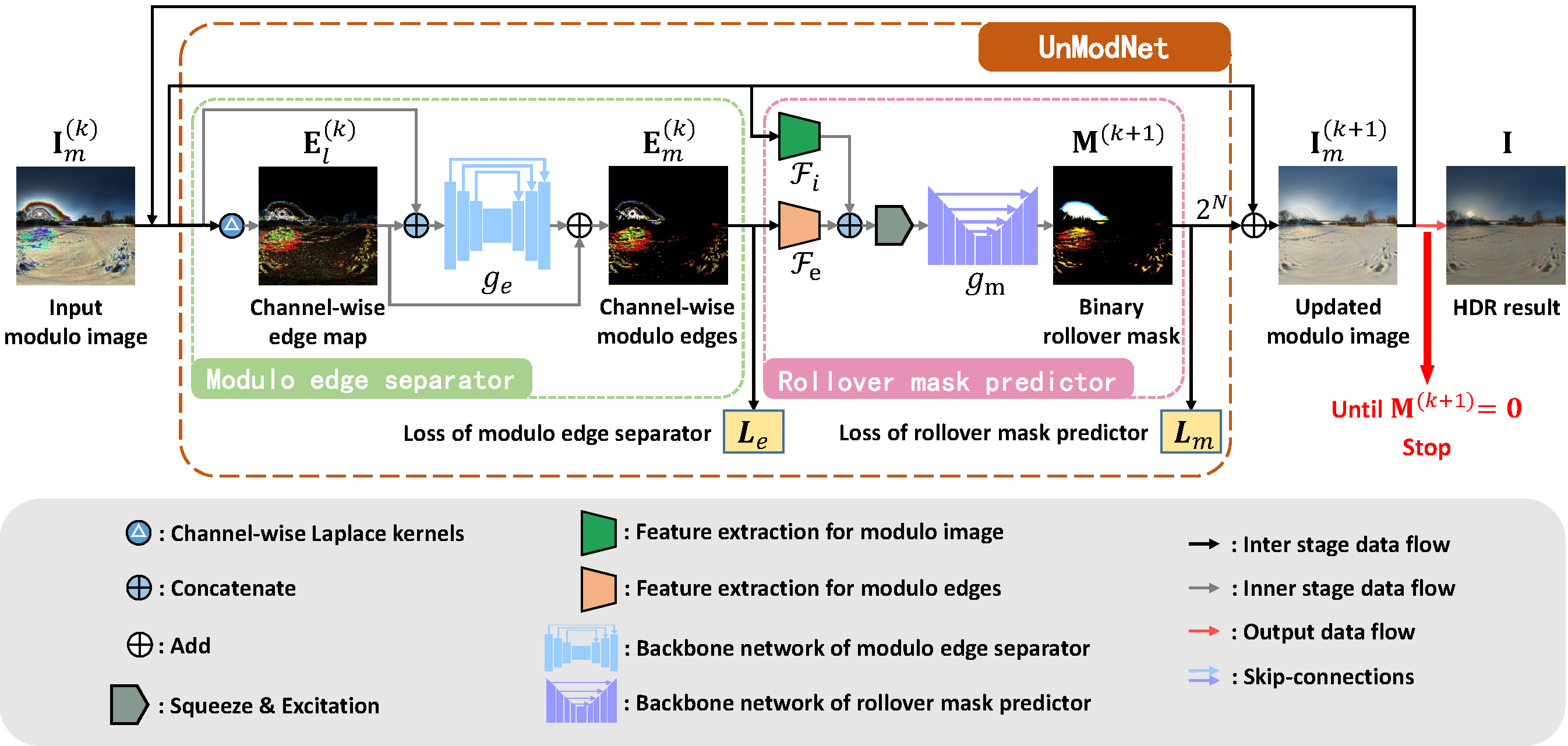
A conventional camera often suffers from over- or under-exposure when recording a real-world scene with a very high dynamic range (HDR). In contrast, a modulo camera with a Markov random field (MRF) based unwrapping algorithm can theoretically accomplish unbounded dynamic range but shows degenerate performances when there are modulus-intensity ambiguity, strong local contrast, and color misalignment. In this paper, we reformulate the modulo image unwrapping problem into a series of binary labeling problems and propose a modulo edge-aware model, named as UnModNet, to iteratively estimate the binary rollover masks of the modulo image for unwrapping. Experimental results show that our approach can generate 12-bit HDR images from 8-bit modulo images reliably, and runs much faster than the previous MRF-based algorithm thanks to the GPU acceleration.
- Linux Distributions (tested on Ubuntu 18.04).
- NVIDIA GPU and CUDA cuDNN
- Python >= 3.7
- Pytorch >= 1.1.0
- cv2
- numpy
- tqdm
- tensorboardX (for training visualization)
- To unwrap RGB modulo images (in
.npyformat and in(H, W, 3)shape):
python execute/infer_LearnMaskNet.py -r checkpoint/checkpoint-mask.pth --data_dir <path_to_modulo_images> --result_dir <path_to_result> --resume_edge_module checkpoint/checkpoint-edge.pth default
- To unwrap grayscale modulo images (in
.npyformat and in(H, W, 1)shape):
python execute/infer_LearnMaskNet.py -r checkpoint/checkpoint-mask-gray.pth --data_dir <path_to_modulo_images> --result_dir <path_to_result> --resume_edge_module checkpoint/checkpoint-edge-gray.pth default
- Use
TonemapReinhard_npy.pyto visualize the results. Note that the default tonemap method we use iscv2.createTonemapReinhard(intensity=-1.0, light_adapt=0.8, color_adapt=0.0).
https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/10Y8MOr2o2TZzTI5RZUQZQ-0RBezbzhIV?usp=sharing
-
Make dataset from original data (HDR images in
.npyformat):- make dataset:
python scripts/make_dataset.py --data_dir <path_to_original_data> --train_dir <path_to_training_dataset> --test_dir <path_to_test_dataset> --training_sample <number_of_training_samples>- make edge map:
python scripts/make_edge_map.py --data_dir <path_to_training_dataset> -
Configure the training parameters:
- write your own
config.jsonor use ours:config/edge_module.jsonandconfig/mask_module.jsonfor two stages respectively - edit the learning rate schedule function (LambdaLR) at
get_lr_lambdainutils/util.py
- write your own
-
Run:
python execute/train.py -c <path_to_config_file>
If you find this work helpful to your research, please cite:
@inproceedings{NEURIPS2020_1102a326,
author = {Zhou, Chu and Zhao, Hang and Han, Jin and Xu, Chang and Xu, Chao and Huang, Tiejun and Shi, Boxin},
booktitle = {Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems},
editor = {H. Larochelle and M. Ranzato and R. Hadsell and M. F. Balcan and H. Lin},
pages = {1559--1570},
publisher = {Curran Associates, Inc.},
title = {UnModNet: Learning to Unwrap a Modulo Image for High Dynamic Range Imaging},
url = {https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2020/file/1102a326d5f7c9e04fc3c89d0ede88c9-Paper.pdf},
volume = {33},
year = {2020}
}