Building the foxConda Installer
:author: The foxBMS Team (Tim Fühner tim.fuehner@iisb.fraunhofer.de) :version: 0.5
The foxBMS project comes with its own Python distribution, called foxConda. Python is a modern, interpreted programming language whose great popularity is still increasing, also owing to the multitude of libraries that are available for virtually any application. In combination with an easy-to-use distribution, like Anaconda, Python constitutes an ideal development platform. We have therefore decided to also employ it as a software development toolkit (SDK) for foxBMS. For an even improved user experience and maintainability, we are not only providing Python programs and packages to get you started with foxBMS, we have additionally devised a dedicated, comprehensive distribution, which includes all the packages you need. It is based on Anaconda and is hence fully compatible with it.
Creating a foxConda distribution and building the installer
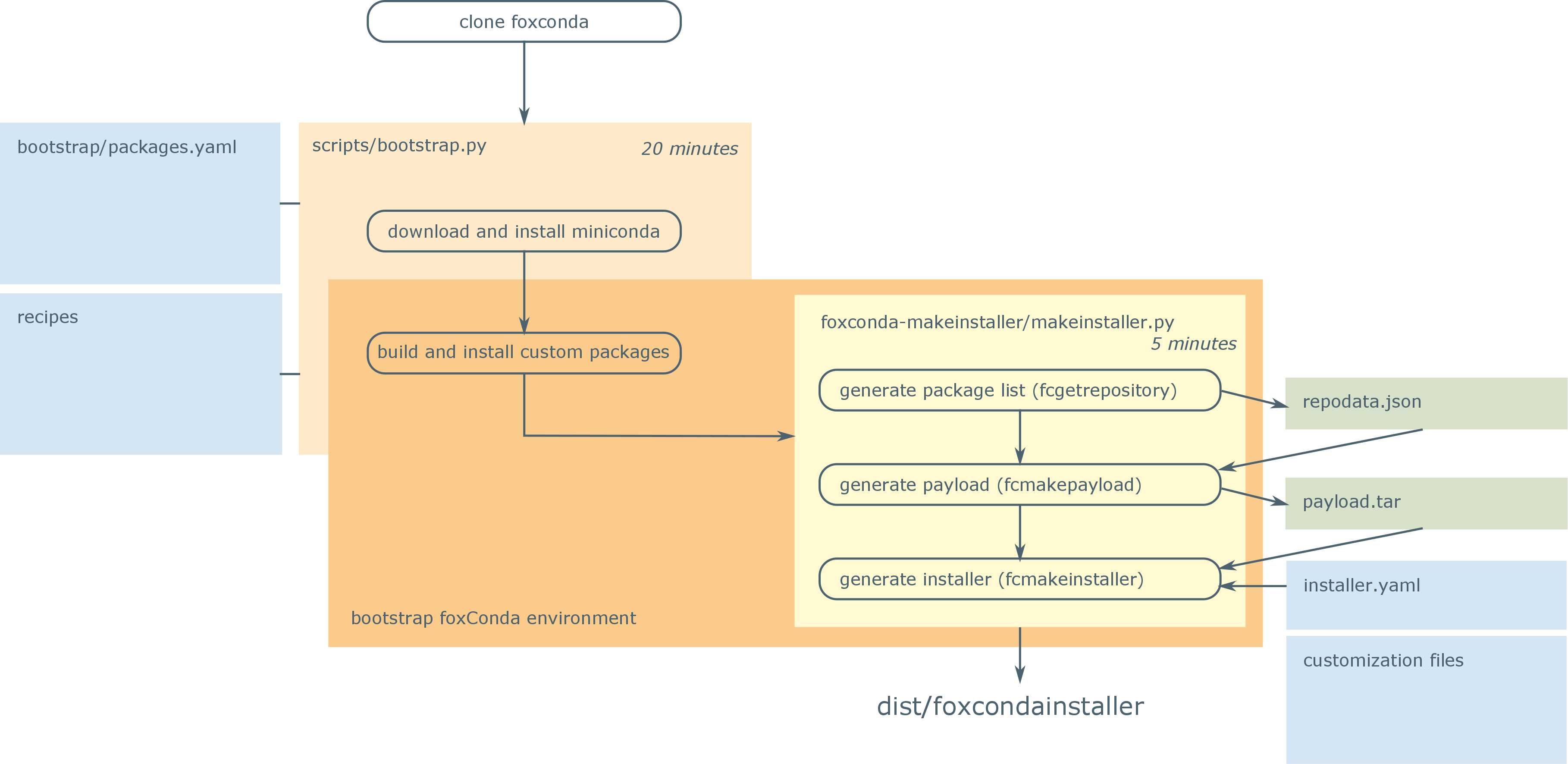
You can find the configuration files required to build a standard foxConda
distribution and its installer in the foxconda-makeinstaller
subdirectory of the foxconda repository. In addition, the list of
packages that are to be included in the "bootstrap" foxConda distribution,
is specified in the file bootstrap/packages.yaml in the same
repository. You will also need the scripts/bootstrap.py script, and a
running Python environment (version 2.6 or higher) and yaml support [#FIXME].
Furthermore, make sure you have a working Internet connection since the
bootstrap process will automatically download all required package and
source files.
Unless you would like to customize or modify it, no changes are required, and you can simply issue the build commands.
Simplified build
-
If not done so, clone
foxcondaand change into the working directory:git clone https://github.com/foxBMS/foxconda -
Issue:
Linux/OSX:
python scripts/bootstrap.py -p bootstrap/packages.yaml <INSTALLDIR>Windows:
python scripts\bootstrap.py -p bootstrap\packages_win.yaml <INSTALLDIR>Here, it is assumed that the
pythoncommand is in your system path.INSTALLDIRis the path to the bootstrap foxConda installation directory. It will be used to collect the third-party packages and build the foxBMS modules. After the foxConda installer has been built, it can be safely removed.The file containing the list of packages is specified using the
-poption. As shown above, you can simply use the provided list, located in thebootstrapdirectory.Further options of the
bootstrap.pyscript are shown when issuing:python scripts/bootstrap.py --help -
Afterward, your foxConda bootstrap directory is ready. For the next step, use Python from this bootstrap distribution by activating it:
Linux/OSX:
. <INSTALLDIR>/bin/activate rootWindows:
. <INSTALLDIR>\Scripts\activate root -
Change into the
foxconda-makeinstallerdirectory and execute:python makeinstaller.py all
The foxConda installer will be situated in the dist subdirectory.
Step-by-step build
-
Bootstrap the initial foxConda installation, as shown in the previous simplified build steps instructions (1.-3.).
-
Change into the
foxconda-makeinstallerdirectory. -
Fetch the repository file, which represents the package list of the bootstrap installation:
fcgetrepository file:///<INSTALLDIR>The package list will be stored in a file called
repodata.json. -
Generate the payload of the installer, i.e., an archive containing all packages the foxConda distribution is to contain:
fcmakepayload repodata.jsonThe payload will be stored in a file called
payload.tar. -
Generates the installer, issuing:
fcmakeinstaller installer.yamlThe file
installer.yamlcontains the configuration for the installer. The generated installer will be located in thedistsubdirectory.
Customizing foxConda
To create a custom foxConda distribution and the according installer from scratch, you have to provide a number of customization and configuration files.
-
bootstrap/packages.yamlThis file contains the list of packages that are to be installed in the bootstrap environment. It contains two sections: (1)installpackages: These packages will be fetched from Anaconda or other publicly available channels; and (2)buildpackages: These packages will be built, and their recepies are expected to be located in therecepiessubdirectory (or another location to which the--recipesdiroption ofscripts/bootstrap.pypoints).In addition, in the section
channels, you can specify custom channels for specific packages. -
recipesThis directory contains all the recipes for the foxBMS or their support packages. -
foxconda/makeinstallerThis directory contains the configuration files required for the installer generation: -
installer.yamlThis is the configuration file, which specifieѕ the behavior and appearance of the installer. It allows you to set logos, welcome screens, messages, version numbers and programs to be launched after the installation has finished. See the provided example configuration file for further details.Note: The names of the following files are specified in the
installer.yamlfile and may differ if you have chosen to give them different names. -
app.ico,app.icns,app.svgThese are the installer icons for Windows, MacOS and Linux, respectively. -
installer.pngThis is the welcome image of the installer. -
anaconda.LICENSE,LICENSEThese are the license files for the Anaconda Python distribution, which we supply since foxConda is derived work, and the foxConda license. You mileage may vary, but we strongly encourage you to leave the licenses as are and simply add your specific license file if required. -
install.pyThis script is required by the conda installation process. Unless you are certain about what you are doing, it is best to leave it as it is. -
postinstall.pyThis script will be executed after foxConda was successfully installed. It can be used to execute post-installation triggers. -
windowsexedetails.txtThis file is used to supply the Windows executable of the installer with version and credit information.