Q: Write a 500-word explanation of Bitcoin stock-to-flow model and make an argument for why it is a bad model?
A: Bitcoin is a digital currency that utilizes a medium of exchange called cryptocurrency through a peer-to-peer (P2P) network as opposed to a central authority (such as a bank) to create and manage monetary transactions. Bitcoin models are used to predict the long-term trend of Bitcoin’s value, and consequently it’s price. There are a few prominent Bitcoin models such as the Stock-to-flow model, Elliot Wave, Hyperwave Theory and so on.
Stock-to-Flow Model in Detail
As the first and most widely acknowledged Bitcoin price model, it predicts the trend of Bitcoin’s price based on its scarcity. The term stock-to-flow refers to the flow of new supply relative to the amount of existing circulating supply. Also known as S2F, it attempts to value BTC in a way similar to commodity assets like gold and silver. The model takes the stock-to-flow of gold and silver as its benchmark – but unlike gold and silver the supply of Bitcoin is fixed at 21 million. Designed to shrink supply, every four years the reward issued to miners gets cut in half and as a result, the “flow” portion (denominator) in the S2F model gets smaller. Every halving decreases the rate of supply and in theory, Bitcoin is scarcer than gold and silver due to its higher S2F ratio. S2F then takes the total global supply of BTC and divides it by annual production, looks at historical values of BTC and projects where it might go over time.
Why S2F Is Bad (Criticisms)
Despite wide popularity, the S2F model’s flaws have been pointed out by analysts and Crypto enthusiasts. I will break down a few relevant points on why S2F model is bad.
- First, the assumption that Bitcoin’s value is derived solely from scarcity is inaccurate. The model is based on a strong assertion that the market capitalization of a monetary good (e.g. gold) is derived directly from their rate of new supply. No evidence or research is provided to support this idea. This becomes quite obvious when analysts extend the model into the near future. By 2045, the model estimates each Bitcoin will be worth $235,000,000,000.
- Second, the use of linear regression might lead to imprecise predictions due to a high probability of spurious results.
- The stock-to-flow model underestimates the challenge of maintaining the same exponential growth as the size (market cap) increases. It assumes non-stop exponential growth for decades, which is unrealistic – both theoretically and in real life
- The Achilles heel of bitcoin's stock-to-flow model is that it only looks at supply. Basic Economics teaches that the price of anything is driven by supply and demand. If you only know the supply, you cannot predict the price. "If there is no demand for something, the value is zero." In other words, Bitcoin's tightening supply is only half the story – not the whole.
Conclusively, the S2F model’s imperfections are magnified from the lens of a more long-term analysis, which makes the model both unsustainable and bad for accurate bitcoin predictions, even short-term.
Q: (Please show your workings). Yara Inc is listed on the NYSE with a stock price of $40 - the company is not known to pay dividends. We need to price a call option with a strike of $45 maturing in 4 months. The continuously-compounded risk-free rate is 3%/year, the mean return on the stock is 7%/year, and the standard deviation of the stock return is 40%/year. What is the Black-Scholes call price?
A:
The Black Scholes call price is: 1.88

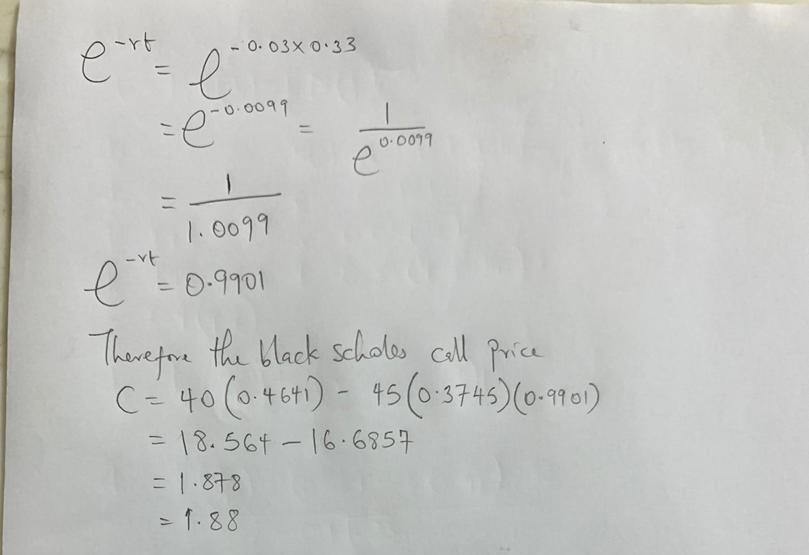
Q: Why is it a bad idea to use recursion method to find the fibonacci of a number?
A: Using recursion method to find the fibonacci of a number is a bad idea because it takes more time to run.
Q: Write a function that takes in a Proth Number and uses Proth's theorem to determine if said number is prime? You can write this in any programming language but C/C++/Golang are preferred
A: I am using the Python programming language to answer this question
def main(n):
'''This is a function to check if an entry is a prime nber or not based on Proth's principle
This function takes in one argument, n.
'n': must be an integer.
'''
def poweroftwo(n):
'''a function that determines if a number is a power of 2'''
return (n and (not(n & (n - 1))))
def prothchecker(n):
'''checks if a number is a proth number'''
n = n-1
k = 1
while(k < (n//k)):
if(n % k == 0):
if(poweroftwo(n//k)):
return True
k = k + 2
return False
def is_prime_number(x):
'''this is a function to check if a number is a prime number'''
if x >= 2:
for y in range(2,x):
if not ( x % y ):
return False
else:
return False
return True
if(prothchecker(n)):
if n > 1:
print(f'{n} is a proth number, checking if it is prime')
print('==================================================')
if is_prime_number(n):
print(f'\n{n} is a proth and a prime number.')
else:
print(f'{n} is a proth but not a prime number.')
else:
print("Not a proth number in the first place.")Q: (Please show your workings). Over all real numbers, find the minimum value of a positive real number, y such that y = sqrt((x+6)^2 + 25) + sqrt((x-6)^2 + 121)
A: The value of x to give the minimum real number value of y is -6
