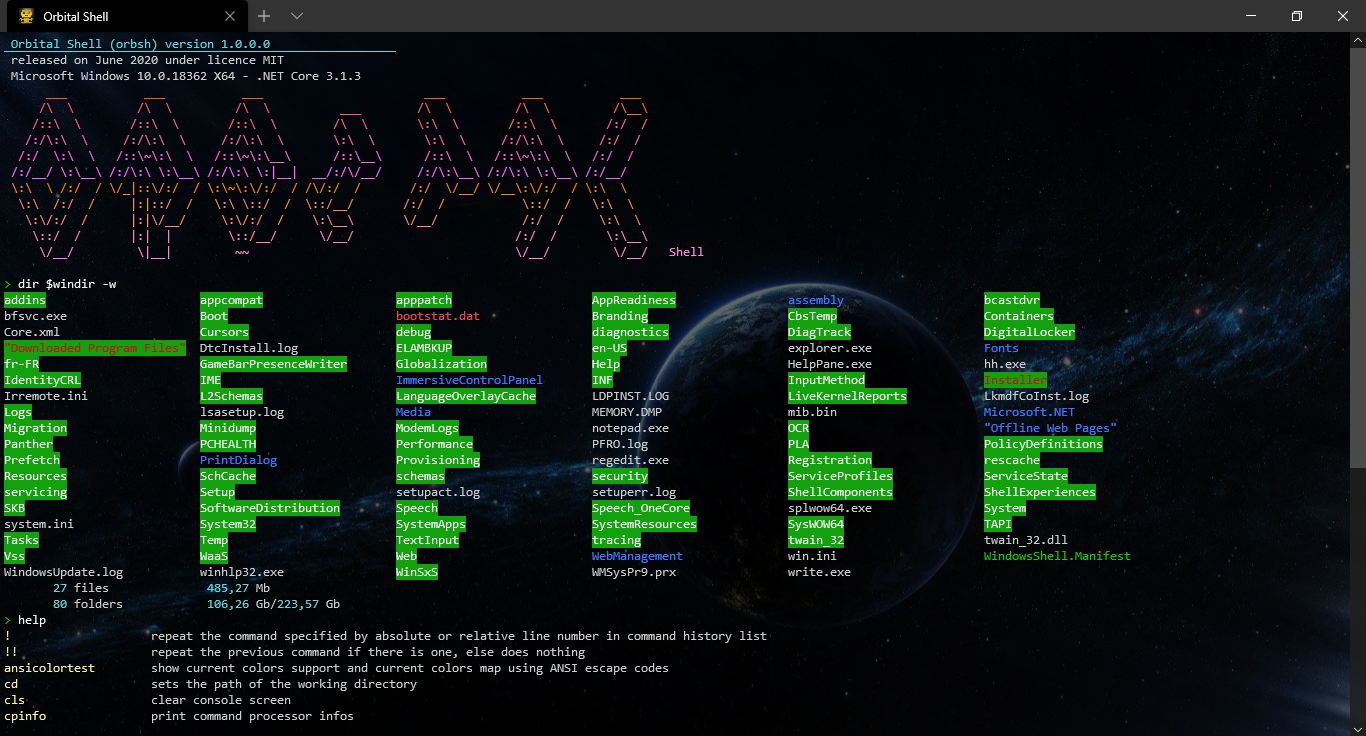
Dot Net Console App Toolkit helps build fastly nice multi-plateforms (windows, linux, macos) console applications using C# and .NET Core 3.1 and .NET Standard 2.1

The toolkit provides functionalities needed to build console applications running in a terminal (WSL/WSL2, cmd.exe, ConEmu, bash, ...) with text interface. That includes:
-
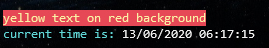
a text printer engine that supports print directives allowing to manage console functionalities from text itself, as html would do but with a simplest grammar (that can be configured). That makes possible colored outputs, cursor control, text scrolling and also dynamic C# execution (scripting), based on several APIs like System.Console and ANSI VT100 / VT52. The print directives are available as commands strings, as a command from the integrated shell or from an underlying shell
// -- example of a string containing print directives -- // 1) from the toolkit shell command line: echo "(br,f=yellow,b=red)yellow text on red background(br)(f=cyan)current time is: (exec=System.DateTime.Now,br)" // 2) invoking the toolkit: orbsh.exe "(br,f=yellow,b=red)yellow text on red background(br)(f=cyan)current time is: (exec=System.DateTime.Now,br)" // 3) from C# using DotNetConsole.cs Echo($"{Br}{Yellow}{BRed}yellow text on red background{Br}{Cyan}current time is: {System.DateTime.Now}{Br}");
-
UI controls for displaying texts and graphical characters in a various way and handling user inputs
-
libraries of methods for performing various print operations, data conversions, process management, ..
-
data types related to the system and the environment that provides usefull methods
This is a view of what is done with the C# project orbital-shell. The Dot Net Console App Toolkit Shell component integrates anything needed to run a complete shell, write shell commands using C# and use console UI components.
This shell example runs with just a few lines of code:
var commandLineProcessor = new CommandLineProcessor(args);
var commandLineReader = new CommandLineReader(commandLineProcessor);
var returnCode = commandLineReader.ReadCommandLine();
Environment.Exit(returnCode);Microsoft.CodeAnalysis.CSharp.Scripting 3.7.0-1.final