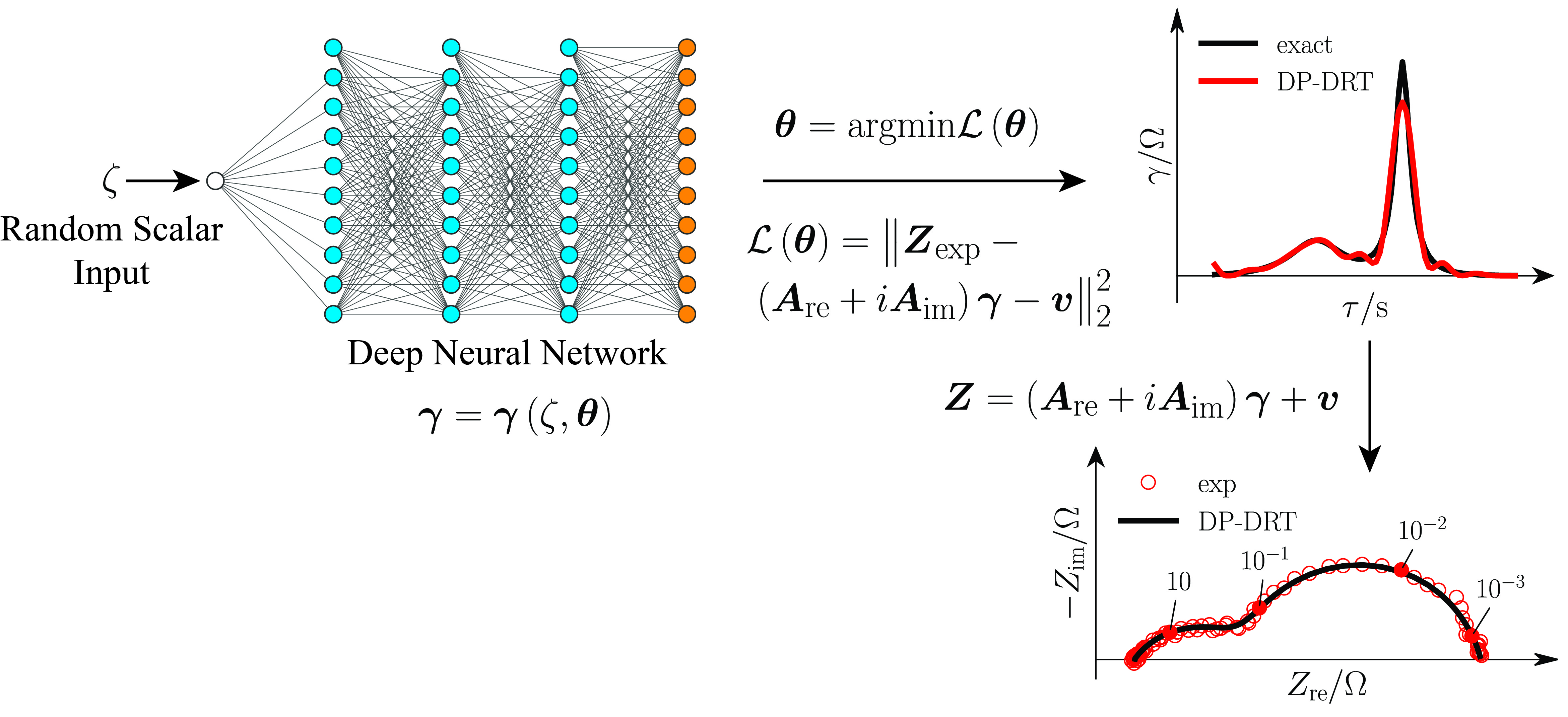
DP-DRT: Deep-Prior Distribution of Relaxation Times
This repository contains the code for one example as shown in the paper "The Deep-Prior Distribution of Relaxation Times" https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1149/1945-7111/ab631a/meta.
Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) is the established tool for the study of many electrochemical experiments[1]. While the analysis of EIS data is challenging, this can be assisted by the distribution of relaxation time (DRT) method[2-6]. However, obtaining the DRT is difficult as the underlying problem is ill-posed. Inspired by recent advances in image analysis, we develop a completely new approach, named the deep prior distribution of relaxation time (DP-DRT), for the deconvolution of the EIS to obtain the DRT[7]. The DP-DRT uses a deep neural network fed with a single random input to deconvolve the DRT and fit the EIS data. The DP-DRT has the peculiarity of having a number of parameters much larger than the number of observations. Further, unlike most supervised deep learning models, large datasets are not needed as the DP-DRT is trained against a single available EIS spectrum. The DP-DRT was successfully tested against both synthetic and real experiments displaying considerable promise and opportunities for extensions.
pytorch
numpy
matplotlib
- Figure_2.ipynb: shows how to recover DRT from impedance synthesized using one ZARC element consisting of a resistance placed in parallel to a constant phase element (CPE). The frequency range is from 1E-4 Hz to 1E4 Hz with 10 points per decade (ppd).
@article{Liu_2020,
doi = {10.1149/1945-7111/ab631a},
year = 2020,
month = {jan},
volume = {167},
number = {2},
pages = {026506},
author = {Jiapeng Liu and Francesco Ciucci},
title = {The Deep-Prior Distribution of Relaxation Times},
journal = {Journal of The Electrochemical Society},
}
- Ciucci, F. (2018). Modeling electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Current Opinion in Electrochemistry.132-139 doi.org/10.1016/j.coelec.2018.12.003
- Wan, T. H., Saccoccio, M., Chen, C., & Ciucci, F. (2015). Influence of the discretization methods on the distribution of relaxation times deconvolution: implementing radial basis functions with DRTtools. Electrochimica Acta, 184, 483-499. doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2015.09.097
- Saccoccio, M., Wan, T. H., Chen, C., & Ciucci, F. (2014). Optimal regularization in distribution of relaxation times applied to electrochemical impedance spectroscopy: ridge and lasso regression methods-a theoretical and experimental study. Electrochimica Acta, 147, 470-482. doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2014.09.058
- Effat, M. B., & Ciucci, F. (2017). Bayesian and hierarchical Bayesian based regularization for deconvolving the distribution of relaxation times from electrochemical impedance spectroscopy data. Electrochimica Acta, 247, 1117-1129. doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2017.07.050
- Ciucci, F., & Chen, C. (2015). Analysis of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy data using the distribution of relaxation times: A Bayesian and hierarchical Bayesian approach. Electrochimica Acta, 167, 439-454. doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2015.03.123
- Liu, J., & Ciucci, F. (2019). The Gaussian process distribution of relaxation times: A machine learning tool for the analysis and prediction of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy data. Electrochimica Acta, 135316. doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2019.135316
- Liu, J., & Ciucci, F. (2020). The Deep-Prior Distribution of Relaxation Times. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 167(2), 026506.10.1149/1945-7111/ab631a